
What is found in a membrane?
What is found in the cell membrane? The principal components of the plasma membrane are lipids (phospholipids and cholesterol), proteins, and carbohydrate groups that are attached to some of the lipids and proteins. A phospholipid is a lipid made of glycerol, two fatty acid tails, and a phosphate-linked head group. Click to see full answer.
What is the membrane that surrounds all cells?
The plasma membrane, or cell membrane, is the phospholipid layer that surrounds the cell and protects it from the outside environment. Ribosomes are the non-membrane bound organelles where proteins are made, a process called protein synthesis.
What is the structural arrangement of the cell membrane?
Arrangement in Cell Membrane: Phospholipids (lipid) assume single and double layered (bilayer) configuration in the cell membrane. When two single layers of polar lipids come together to form a double layer, the outer hydrophilic face of each single layer orients itself towards the solution and the hydrophobic portion becomes immersed in the ...
What is the trilaminar unit membrane structure?
This conclusion led Robertson in 1953 to propose unit membrane hypothesis according to which all biological membranes show generalised unit membrane construction. The unit membrane model visualises cell membrane as a trilaminar and indicates structure consisting of two dark osmiophilic layers separated by a light osmiophilic layer.
What is a membrane structure?
The Water Cube in Beijing. Membrane structures are spatial structures made out of tensioned membranes. The structural use of membranes can be divided into pneumatic structures, tensile membrane structures, and cable domes.
What is the water cube?
The other major building on the site, built for the 2008 Summer Olympics, is the Beijing National Aquatics Center , also known as the Water Cube. It is entirely clad in 100,000 square metres of inflated ETFE foil cushions arranged as an apparently random cellular structure.
What are the components of the cell membrane?
Identify components of the cell membrane, including phospholipids, cholesterol, proteins, and carbohydrates. Explain why hydrophilic substances cannot pass through the interior of the cell membrane.
How thick is the plasma membrane?
Plasma membranes range from 5–10 nm thick. As a comparison, human red blood cells, visible via light microscopy, are approximately 8 µm thick, or approximately 1,000 times thicker than a plasma membrane.
How do phospholipids form a membrane?
This characteristic is vital to the structure of a plasma membrane because, in water, phospholipids tend to become arranged with their hydrophobic tails facing each other and their hydro philic heads facing out. In this way, they form a lipid bilayer—a barrier composed of a double layer of phospholipids that separates the water and other materials on one side of the barrier from the water and other materials on the other side. In fact, phospholipids heated in an aqueous solution tend to spontaneously form small spheres or droplets (called micelles or liposomes), with their hydrophilic heads forming the exterior and their hydrophobic tails on the inside (Figure 4).
Why is the plasma membrane flexible?
The plasma membrane must be sufficiently flexible to allow certain cells, such as red blood cells and white blood cells, to change shape as they pass through narrow capillaries.
What is the function of the plasma membrane?
Plasma membranes enclose the borders of cells, but rather than being a static bag, they are dynamic and constantly in flux. The plasma membrane must be sufficiently flexible to allow certain cells, such as red blood cells and white blood cells, to change shape as they pass through narrow capillaries. These are the more obvious functions of a plasma membrane. In addition, the surface of the plasma membrane carries markers that allow cells to recognize one another, which is vital as tissues and organs form during early development, and which later plays a role in the “self” versus “non-self” distinction of the immune response.
Which region of the cell is hydrophobic?
The hydrophilic regions of the phospholipids tend to form hydrogen bonds with water and other polar molecules on both the exterior and interior of the cell. Thus, the membrane surfaces that face the interior and exterior of the cell are hydrophilic. In contrast, the interior of the cell membrane is hydrophobic and will not interact with water.
Which membrane carries markers that allow cells to recognize one another?
In addition, the surface of the plasma membrane carries markers that allow cells to recognize one another, which is vital as tissues and organs form during early development, and which later plays a role in the “self” versus “non-self” distinction of the immune response.
What is the membrane in a cell?
Membrane, in biology, the thin layer that forms the outer boundary of a living cell or of an internal cell compartment.
What are the molecules that make up the cell membrane?
The fatty-acid chains allow many small, fat-soluble molecules, such as oxygen, to permeate the membrane, but they repel large, water-soluble molecules, such as sugar, and electrically charged ions, such as calcium.
What is the lipid bilayer of a membrane?
Membranes consist largely of a lipid bilayer, which is a double layer of phospholipid, cholesterol, and glycolipid molecules that contains chains of fatty acids and determines whether a membrane is formed into long flat sheets or round vesicles.
What are the proteins that transport water molecules across the membrane?
Embedded in the lipid bilayer are large proteins, many of which transport ions and water-soluble molecules across the membrane. Some proteins in the plasma membrane form open pores, called membrane channels, which allow the free diffusion of ions into and out of the cell.
What is the outer boundary of a cell called?
Membrane, in biology, the thin layer that forms the outer boundary of a living cell or of an internal cell compartment. The outer boundary is the plasma membrane, and the compartments enclosed by internal membranes are called organelles.
What are the functions of the membrane organelles?
Many cellular functions, including the uptake and conversion of nutrients, synthesis of new molecules, production of energy, and regulation of metabolic sequences, take place in the membranous organelles. The nucleus, containing the genetic material of the cell, is surrounded by a double membrane with large pores that permit the exchange of materials between the nucleus and cytoplasm. The outer nuclear membrane is an extension of the membrane of the endoplasmic reticulum, which synthesizes the lipids for all cell membranes. Proteins are synthesized by ribosomes that are either attached to the endoplasmic reticulum or suspended freely in the cell contents. The mitochondria, the oxidizing and energy-storing units of the cell, have an outer membrane readily permeable to many substances, and a less-permeable inner membrane studded with transport proteins and energy-producing enzymes.
What is the encapsulating membrane of the blastocyst?
The way in which the encapsulating membrane of the blastocyst becomes the chorion, and the most deeply embedded part of it becomes the fetal placenta, has already been described. There are still other important membrane s that develop from those portions of the inner cell…
What is the cell membrane?
The cell membrane, also called the plasma membrane, is found in all cells and separates the interior of the cell from the outside environment. The cell membrane consists of a lipid bilayer that is semipermeable. The cell membrane regulates the transport of materials entering and exiting the cell.
What is the function of the plasma membrane?
One is to transport nutrients into the cell and also to transport toxic substances out of the cell.
What are the proteins that interact with other cells?
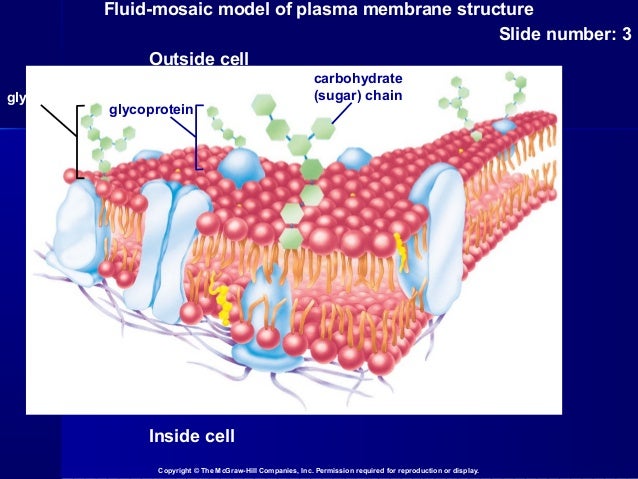
Another is that the membrane of the cell, which would be the plasma membrane, will have proteins on it which interact with other cells. Those proteins can be glycoproteins, meaning there's a sugar and a protein moiety, or they could be lipid proteins, meaning that there's a fat and a protein.
Is the cell wall tougher than the plasma membrane?
In fact, they have a cell wall outside of them, and that cell wall is much tougher and is structurally more sound than a plasma membrane is. William Gahl, M.D., Ph.D.
Is cholesterol in the plasma membrane?
And there are different types of plasma membranes in different types of cells, and the plasma membrane has in it in general a lot of cholesterol as its lipid component. That's different from certain other membranes from within the cell.
What is the cell membrane made of?
Cell Membrane Structure. The cell membrane is primarily composed of a mix of proteins and lipids. Depending on the membrane’s location and role in the body, lipids can make up anywhere from 20 to 80 percent of the membrane, with the remainder being proteins.
What is the function of the cell membrane?
Its function is to protect the integrity of the interior of the cell by allowing certain substances into the cell while keeping other substances out. It also serves as a base of attachment for the cytoskeleton in some organisms and ...
What is the role of cholesterol in animal cell membranes?
Cholesterol molecules are selectively dispersed between membrane phospholipids. This helps to keep cell membranes from becoming stiff by preventing phospholipids from being too closely packed together. Cholesterol is not found in the membranes of plant cells.
What are the functions of cell membrane receptor proteins?
Cell membrane receptor proteins help cells communicate with their external environment through the use of hormones, neurotransmitters, and other signaling molecules.
Why is the cell membrane important?
Thus the cell membrane also serves to help support the cell and help maintain its shape.
What is the function of the nucleus?
The nucleus and mitochondria are two examples. Another function of the membrane is to regulate cell growth through the balance of endocytosis and exocytosis. In endocytosis, lipids and proteins are removed from the cell membrane as substances are internalized. In exocytosis, vesicles containing lipids and proteins fuse with ...
Which bilayer of lipids is hydrophobic?
Phospholipids form a lipid bilayer in which their hydrophilic (attracted to water) head areas spontaneously arrange to face the aqueous cytosol and the extracellular fluid, while their hydrophobic (repelled by water) tail areas face away from the cytosol and extracellular fluid.
What is membrane structure?
Applications. Membrane structures are lightweight spatial structures made of tensioned membranes. Membrane can be used to construct roofs and façades, free-standing buildings, building envelopes, skylights, indoor ceilings and/or accent enclosures. Lightweight structures are ideal for use in building types in the areas of infrastructure, culture, ...
How are membrane structures determined?
In contrast to conventional structures, the final shape of membrane structures is only determined by the statics. This means that the design planning must be carried out in close coordination with the static analysis in order to achieve an economically and creatively optimal conception. Due to the long service life of the materials, membrane structures are classified as permanent structures like conventional structures. They are therefore subject to approval in accordance with the standards of the individual countries and must correspond to the load assumptions contained in the respective building regulations. Regional regulations such as wind and snow loads, for example, must be taken into account, as well as climatic characteristics.
What is the term for the creation of the desired surface/shape out of a flexible membrane material?
That means, the primary structure made of rigid materials, like steel or wood, doesn’t collapse, when the membrane structure (as secondary structure) is taken away. Formfinding. Formfinding is by definition the creation of the desired surface/shape out of a flexible membrane material.
What is statics in membrane design?
The statics of the membrane determine the requirements for the overall detailed design of the Membrane Structure. Edge geometry and detail design used for load transfer are defined here. The same applies to load transfer points in the load-bearing structure. It should be noted that membrane structures are subject to deformation when exposed to external loads (e. g. wind and snow). These must be absorbed by the connection points to the load-bearing structure, to existing conventional structures or in foundations.
What is a lightweight structure?
Membrane Structures also know as Lightweight Strutures have a unique visual character and give designers, architects and engineers the ability to experiment with forms full of beauty and elegance meeting highest esthetical requirements.
What are the two main types of membrane structures?
In principle, the membrane structures can be divided into two main different types: The mechanically pre-tensioned and pneumatically pre-tensioned Structures.
Why are membrane structures so environmentally sensitive?
The enormous range of spanning capability require less primary structure and are thus very cost-effective. Due to these savings and other unique properties , Membrane Structures are environmentally sensitive and ideal for sustainable construction solutions.
What is the membrane of a cell?
In the case of plant cells, a cell wall is observed before the plasma membrane in the exterior part of the plant cells. The same is the case for some bacterial cells as well. The plasma membrane is mainly composed of a layer of lipid molecules. This layer is semipermeable and is responsible for the regulation and transportation of materials. Also, the movement of molecules, both large and small, in and out of the cell is controlled by the plasma membrane.
What is the structure of the plasma membrane?
Plasma Membrane Structure and Function. The plasma membrane is fluid in nature and as mentioned is made up of proteins, lipids, and carbohydrates. It does not allow the ions and other water-soluble molecules to pass through.
What is the composition of the plasma membrane?
When asked what is the composition of the plasma membrane the composition can be divided into lipids and proteins. The main constituents that form the composition of plasma membrane are:
How thick is the plasma membrane?
It is approximately 5nm - 10 nm thick. The components of the plasma membrane, i.e., carbohydrates, lipids, and proteins differ from cell to cell.
Why is the membrane important to the cell?
The membrane also helps the proteins to monitor and maintain the chemical climate inside the cell, and also provides aids in shifting the molecules in the membrane.
Which two components are made up of the plasma membrane?
When asked the plasma membrane is made up of which two components the answer is the lipids and the proteins. The plasma membrane is composed of a phospholipid bilayer, i.e. two layers set up back-to-back. When asked what is the chemical composition of the plasma membrane the general answer is the phospholipid bilayer because ...
How many segments are in a complex protein?
Some complex proteins contain 12 segments of one protein, in a highly convoluted form while being implanted into the membrane. Such types of proteins contain a hydrophilic region along with one or more hydrophobic areas. Owing to this nature, they typically align along with the phospholipids.
What is the landscape of the membrane?
The landscape of the membrane is studded with proteins, some of which span the membrane. Some of these proteins serve to transport materials into or out of the cell. Carbohydrates are attached to some of the proteins and lipids on the outward-facing surface of the membrane.
What was the plasma membrane's core made of?
They made the analogy of proteins to bread, and lipids to the filling. In the 1950s, advances in microscopy, notably transmission electron microscopy (TEM), allowed researchers to see that the plasma membrane’s core consisted of a double, rather than a single, layer.
What percentage of the plasma membrane is protein?
The protein, lipid, and carbohydrate proportions in the plasma membrane vary with cell type, but for a typical human cell, protein accounts for about 50 percent of the composition by mass, lipids (of all types) account for about 40 percent, and carbohydrates comprise the remaining 10 percent. However, protein and lipid concentration varies ...
What is the protein in the mitochondria?
The mitochondrial inner membrane contains 76 percent protein and only 24 percent lipid. The plasma membrane of human red blood cells is 30 percent lipid. Carbohydrates are present only on the plasma membrane’s exterior surface and are attached to proteins, forming glycoproteins, or attached to lipids, forming glycolipids.
What are phospholipids made of?
A phospholipid is a molecule consisting of glycerol, two fatty acids, and a phosphate-linked head group. Cholesterol, another lipid comprised of four fused carbon rings, is situated alongside the phospholipids in the membrane’s core. The protein, lipid, and carbohydrate proportions in the plasma membrane vary with cell type, ...
What are the functions of the plasma membrane?
Among the most sophisticated plasma membrane functions is the ability for complex, integral proteins, receptors to transmit signals. These proteins act both as extracellular input receivers and as intracellular processing activators.
When was the plasma membrane discovered?
Scientists identified the plasma membrane in the 1890s, and its chemical components in 1915. The principal components they identified were lipids and proteins. In 1935, Hugh Davson and James Danielli proposed the plasma membrane’s structure. This was the first model that others in the scientific community widely accepted.
What is the structure of a nuclear membrane?
Nuclear Membrane Structure. A nuclear membrane is composed up of two membranes – an inner and an outer membrane. Both membranes consist of phospholipids that are organized in a bilayer. The complete nuclear membrane includes four series of phospholipids. The perinuclear space separates the outer and inner membrane.
What is the Nuclear Membrane?
Every nucleus is girdled and covered by a double-layered membrane, known as the nuclear envelope or nuclear membrane. It separates the nucleoplasm (the fluid present in the nucleus), from the cytoplasm.
What is the nuclear envelope?
The nuclear envelope is also called nuclear membrane. It is made up of two lipid bilayer membranes. The nuclear membrane is present in both the plant and animal cells. Cells carry out a multitude of functions such as protein building, conversion of molecules into energy and elimination of unnecessary products.
What is the function of the membrane in the nucleus?
This membrane guards the genetic material of the cells against the exterior of the nucleus where chemical reactions are taking place. Also, it carries several proteins which are crucial in the organization of DNA and to control genes.
How many proteins are in the nuclear pores?
Each of the nuclear pores consists of 30 distinct proteins which operate together to transfer materials.
What is the role of the nuclear lamina in DNA?
The nuclear lamina also attaches to and secures chromatin which is organized loosely in protein structure and DNA. A protein layer gives support and strength to the nuclear membrane. Also Read: The Nucleus.
What are the constituents of the nucleoplasm?
The constituents of the nucleoplasm are water, dissolved ions, and a blend of other substances. This element is completely confined in the nuclear envelope containing nucleotides and crucial enzymes that promote replication. Also Read: Nucleoplasm.
