What is the mechanism of action of antifungal drugs?
These mechanisms include alteration in drug target, alteration in sterol biosynthesis, reduction in the intercellular concentration of target enzyme, and overexpression of the antifungal drug target.
Which medications Express antifungal activity in vitro?
a) Zoric N, Horvat I, Kopjar N, Vucemilovic A, Kremer D, Tomic S, Kosalec I. Hydroxytyrosol expresses antifungal activity in vitro. Curr. Drug Targets. 2013;14:992–998.
Why are antifungal drugs not used to treat fungal infections?
The reason is quite clear that most of the eukaryotic fungal cells have a lot in common with human cells, so antifungal drugs can also damage the host body cells. Also, some fungi have detoxification properties that can modify antifungal drugs and as a result, the effectiveness of these drugs will be reduced.
What are the different types of antifungal agents?
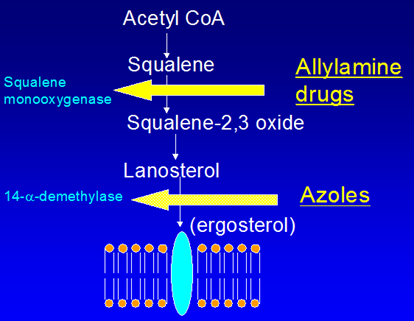
The three major groups of antifungal agents in clinical use, azoles, polyenes, and allylamine/thiocarbamates, all owe their antifungal activities to inhibition of synthesis of or direct interaction with ergosterol.

How do most antifungal drugs work?
Antifungal medications usually work either by killing the fungal cells or stopping them from growing and multiplying. Parts of the cell that the antifungal drugs target include the fungal cell membrane and the fungal cell wall.
What are the mechanisms of antifungal drug resistance?
Many different types of mechanisms contribute to the development of resistance to antifungals. These mechanisms include alteration in drug target, alteration in sterol biosynthesis, reduction in the intercellular concentration of target enzyme, and overexpression of the antifungal drug target.
What is the mechanism of action of the antifungal azoles?
Mechanism of Action of Azoles Azoles exert their action by inhibiting the C14α demethylation of lanosterol in fungi, which interferes with the synthesis of ergosterol in the fungal cell membrane.
What is the mechanism of action of echinocandins?
The echinocandins have a unique mechanism of action, inhibiting beta-(1,3)-D-glucan synthase, an enzyme that is necessary for the synthesis of an essential component of the cell wall of several fungi. The echinocandins display fungistatic activity against Aspergillus spp.
What are the different antifungal drugs?
Common names for antifungal medicines include:clotrimazole (Canesten)econazole.miconazole.terbinafine (Lamisil)fluconazole (Diflucan)ketoconazole (Daktarin)nystatin (Nystan)amphotericin.
What is the mode of action for fluconazole?
Mechanism of Action Fluconazole interacts with 14-demethylase, a cytochrome P-450 enzyme responsible for catalyzing the conversion of lanosterol to ergosterol. [3] As ergosterol forms a critical part of the fungal cell membrane, fluconazole inhibits the synthesis of ergosterol to increase cellular permeability.
What is the mode of action of griseofulvin?
Griseofulvin is fungistatic, however the exact mechanism by which it inhibits the growth of dermatophytes is not clear. It is thought to inhibit fungal cell mitosis and nuclear acid synthesis. It also binds to and interferes with the function of spindle and cytoplasmic microtubules by binding to alpha and beta tubulin.
What is the mode of action of terbinafine?
Mechanism: Terbinafine has a fungicidal effect by inhibiting the enzyme squalene monooxygenase which is involved in the synthesis of sterol in fungi. This inhibits fungal sterol biosynthesis by decreasing ergosterol levels.
What is anidulafungin?
Anidulafungin is a type of semi-synthetic lipopeptide antifungal drug which is synthesized from a fermentation product of Aspergillus nidulans. Anidulafungin act by inhibiting an enzyme, glucan synthase which is present in the fungal cell and responsible for the formation of 1,3-β-D-glucan.
What is the action of amphotericin B?
Mode of Action of Amphotericin B: The mode of action of Amphotericin B depends on the concentration obtained in body fluids and the susceptibility of the fungus. This drug binds with the ergosterol in the cell membrane of susceptible fungi. After binding to ergosterol it creates a transmembrane channel.
What is Azoles used for?
Azoles is a type of Antifungal drug Which is predominantly used for the treatment of different antifungal infection. This drug act by preventing the synthesis of ergosterol on fungal cell membranes.
What is the best antibiotic for eye infections?
A. Natamycin . Natamycin is an antifungal antibiotic that is derived from Streptomyces natalensis or S. chattanoogensis. Natamycin mainly used to treat fungal infections of the eye. Natamycin has a high affinity for steroids. This antibiotic prevents fungal growth by binding to sterols on cell membrane.
What is the action of ciclopirox?
Ciclopirox also acts by modifying the plasma membrane of fungi, which is resulting in the disorganization of internal structures. Ciclopirox also shows anti-inflammatory action by inhibition of 5-lipoxygenase and cyclooxygenase. 7. Flucytosine Antifungal Drug.
How does flucytosine act?
Flucytosine act by competitive inhibition of purine base and pyrimidine bae uptake and also indirectly by intracellular metabolism to 5-fluorouracil.#N#Flucytosine also enters into the fungal cell with the helps of cytosine permease; After entering flucytosine started to metabolized 5-fluorouracil within fungal organisms. The 5-fluorouracil is started to incorporated into fungal RNA and inhibits the synthesis of both DNA and RNA. This results in an unbalanced growth and death of the fungal organism.#N#Flucytosine also acts by inhibitions of fungal thymidylate synthase.
What is the action of Azoles?
Mode of action of Azoles: At first, the drug will destabilize the fungal cytochrome p450 51 enzyme, which leads to cell lysis. The disruption in production of ergosterol creates holes on membrane as a result essential constituents of the fungal cells started to leak out. This kills the fungi.
What is the mechanism of action of imidazole derivatives?
A mechanism of action via inhibition of DNA synthesis is an alternative explanation. The imidazole derivatives inhibit the biosynthesis of ergosterol, the main sterol in membranes of fungi. These agents also affect the synthesis of triglycerides and phospholipids.
What is the effect of imidazole on the invasive mycelial form?
The imidazole derivatives inhibit the transformation of blastospores of Candida albicans into the invasive mycelial form. This inhibition probably facilitates the task of host defense cells and may be the principal factor leading to clearance of infection.
What is the role of griseofulvin in hyphal tips?
Griseofulvin deteriorates spindle and cytoplasmic microtubules, influencing cell division and outgrowth of hyphal tips. Flucytosine is deaminated to 5-fluorouracil, which is then phosphorylated and incorporated into RNA; protein synthesis is consequently impaired.
