
Acidosis is caused by an overproduction of acid that builds up in the blood or an excessive loss of bicarbonate from the blood (metabolic acidosis) or by a buildup of carbon dioxide in the blood that results from poor lung function or depressed breathing (respiratory acidosis).
How do the kidneys regulate acid base balance?
How the Kidneys Regulate Acid Base Balance
- Protons and Buffers. Whereas the buffers in your body and your lungs are involved in the rapid adjustment of your blood's pH, the kidneys adjust the pH more slowly.
- The Collecting Duct. ...
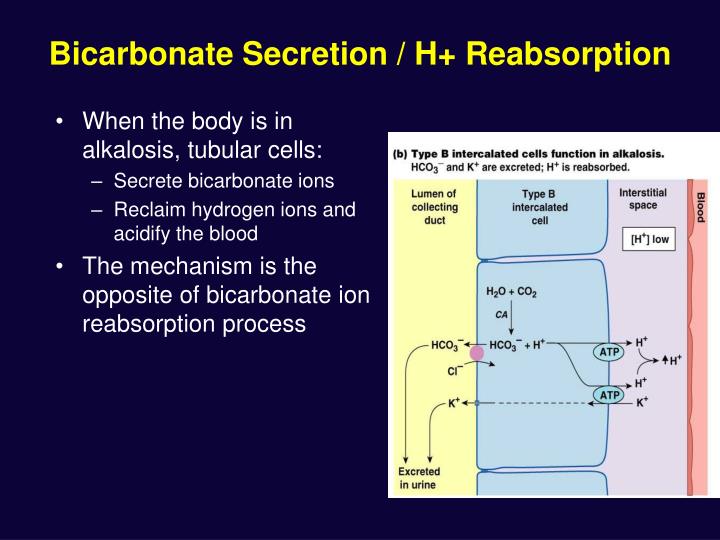
- Metabolic Alkalosis. ...
- Respiratory Alkalosis. ...
- Respiratory Acidosis. ...
- Metabolic Acidosis. ...
What are the causes of acid - base disorders?
What are the causes of Pediatric Acid-base and Electrolyte Disorders? Metabolic acidosis is caused by a range of conditions, including diabetes, cancer, liver disease, and kidney disease. When metabolic acidosis occurs in kidney patients, it may be associated with renal tubular acidosis, a disease that’s caused by the kidneys’ inability to ...
What is the normal range of acid base balance?
Acid–base imbalance occurs when a significant insult causes the blood pH to shift out of its normal range (7.35 to 7.45). An excess of acid in the blood is called acidemia and an excess of base is called alkalemia.
What is the regulation of acid base balance?
The renal regulation of the body’s acid-base balance addresses the metabolic component of the buffering system. Whereas the respiratory system (together with breathing centers in the brain) controls the blood levels of carbonic acid by controlling the exhalation of CO 2, the renal system controls the blood levels of bicarbonate.
See more
What is the most common acid-base imbalance?
Metabolic acidosis is the most common disorder encountered in clinical practice. The respiratory contribution to a change in pH can be determined by measuring PCO2 and the metabolic component by measuring the base excess.
What is the most common cause of acid-base imbalance quizlet?
What is respiratory acidosis? Most common cause of acid-base imbalance. Occurs when a person breathes shallowly, or gas exchange is hampered by diseases such as pneumonia, cystic fibrosis, or emphysema. - HYPOVENTILATION.
What are the causes of acid-base imbalances?
Causes of metabolic acidosisprolonged exercise.lack of oxygen.certain medications, including salicylates.low blood sugar, or hypoglycemia.alcohol.seizures.liver failure.cancer.More items...
What is the most common cause of acidosis?
Acidosis is caused by an overproduction of acid that builds up in the blood or an excessive loss of bicarbonate from the blood (metabolic acidosis) or by a buildup of carbon dioxide in the blood that results from poor lung function or depressed breathing (respiratory acidosis).
What is an example of an acid-base imbalance?
Examples include vomiting (metabolic alkalosis), diarrhea (metabolic acidosis), chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (respiratory acidosis), pneumonia (respiratory alkalosis), and so on.
What are the two types of acid-base imbalances?
Fluid, Electrolyte, and Acid-Base Balance Metabolic acidosis and alkalosis can coexist and either or sometimes both of these metabolic abnormalities may occur with either respiratory acidosis or alkalosis (Nairns and Emmett, 1980; Wilson and Green, 1985).
What is the most common acid-base imbalance in general in the hospital setting?
Metabolic alkalosis is the most common acid–base disorder in ICU patients - PMC. The . gov means it's official.
What are 4 causes for metabolic acidosis?
It can be caused by:Cancer.Carbon monoxide poisoning.Drinking too much alcohol.Exercising vigorously for a very long time.Liver failure.Low blood sugar (hypoglycemia)Medicines, such as salicylates, metformin, anti-retrovirals.MELAS (a very rare genetic mitochondrial disorder that affects energy production)More items...
What are the 3 major mechanisms the human body uses to regulate acid-base balances?
Acid–base balance. The pH of the extracellular fluid, including the blood plasma, is normally tightly regulated between 7.32 and 7.42 by the chemical buffers, the respiratory system, and the renal system.
What pH causes acidosis?
Acidosis is characterized by a pH of 7.35 or lower. Alkalosis is characterized by a pH level of 7.45 or higher.
What drug causes acidosis?
The most common drugs and chemicals that induce the anion gap type of acidosis are biguanides, alcohols, polyhydric sugars, salicylates, cyanide and carbon monoxide.
What are the types and causes of acidosis?
Acidosis is caused by an overproduction of acid that builds up in the blood or an excessive loss of bicarbonate from the blood (metabolic acidosis) or by a buildup of carbon dioxide in the blood that results from poor lung function or depressed breathing (respiratory acidosis).
What is the most probable acid-base imbalance in the patient described below quizlet?
What is the most probable acid/base imbalance in the patient described below? Hysterical hyperventilation. Respiratory alkalosis can be seen in patients with: TCO2.
What is the most common acid-base imbalance in general in the hospital setting?
Metabolic alkalosis is the most common acid–base disorder in ICU patients - PMC. The . gov means it's official.
What is the main cause for the acid-base imbalance called respiratory acidosis?
Respiratory acidosis typically occurs due to failure of ventilation and accumulation of carbon dioxide. The primary disturbance is an elevated arterial partial pressure of carbon dioxide (pCO2) and a decreased ratio of arterial bicarbonate to arterial pCO2, which results in a decrease in the pH of the blood.
What is acid-base balance quizlet?
Acid base balance is defined as the process of regulating the pH, bicarbonate concentration and. partial pressure of carbon dioxide of body fluids.
Respiratory alkalosis
A respiratory imbalance occurs when there is too much, or too little, carbon dioxide in arterial blood. The higher the level, the more acidic, the lower the level, the more basic.
Respiratory acidosis
Respiratory acidosis is a condition when the lungs cannot remove all of the carbon dioxide the body produces.
Metabolic alkalosis
For metabolic disorders, the two key lab values to pay attention to are pH and bicarbonate (HCO3). HCO3 is excreted by the kidneys and acts as a buffer for the acid-base system. Too little can result in metabolic alkalosis, too much can lead to metabolic acidosis.
Metabolic acidosis
A patient experiencing metabolic acidosis will have a pH of less than 7.35 and an HCO3 of less than 21.
Full Transcript
Hi, I'm Meris. And in this video, we're going to be talking about acid-base imbalances. I'm going to be following along using our Fundamentals of Nursing flash cards. These are available on our website, leveluprn.com. And if you already have a set for yourself, I'm going to be starting on card number 99. Let's get started.
What is the normal range for acid-base imbalance?
Metabolic imbalances such as this are indicated by bicarbonate levels below or above the normal range, which is 22–26 mEq/L. Metabolic acidosis may be caused by accumulation of nonrespiratory acids or loss of bases, such as in the following conditions:
How to treat metabolic alkalosis?
Symptoms include decreased breathing rate and depth and increased blood carbon dioxide. The com-pensatory factors for metabolic alkalosis include reduced breathing rate, with a loss of bicarbonate ions in the urine. For mild cases, treatment usually is focused on controlling vomiting or treating other causative factors. Solutions that may be administered include sodium chloride or potassium chloride. Acute metabolic alkalosis is treated with ammonium chloride. As the ammonium ions are metabolized in the liver, hydrogen ions are liberated, which basically means hydrochloric acid is generated in greater quantities. As it diffuses into the bloodstream, the pH falls to normal levels. The effects of respiratory and metabolic acidosis and alkalosis are described in TABLE 23-4.
What happens to the respiratory system when the kidneys are insuffi-cient?
If the lung or kidney buffer systems become insuffi-cient, the acid-base balance is disrupted. As a result, the undisturbed system tries to compensate. The respiratory system is responsible for compensation of metabolic acid-base imbalances and works rela-tively quickly. The urinary system, although slower, is responsible for compensation of respiratory-related acid-base imbalances. The ways these systems com-pensate are reflected in changes in the Pco2 and concentrations of bicarbonate ions. A patient can have a serious medical condition and still show a normal pH because of how these systems compensate.
How does metabolic alkalosis occur?
Metabolic alkalosis results from excessive loss of hydrogen ions or gain of bases or bicarbonate ions. It is much less common than metabolic acidosis. In metabolic alkalosis, there is in an increase in blood pH, called alkalemia, after gastric drainage or lavage, use of certain diuretics, overuse of antacids, or pro-longed vomiting. Loss of acidic gastric juice leaves body fluids more basic. A condition called alkaline tide may occur, caused by many bicarbonate ions moving into the extracellular fluid. This movement is related to secretion of hydrochloric acid from the gastric mucosa. Temporary elevation of bicar-bonate ions in the extracellular fluid occurs during eating, but serious metabolic alkalosis may occur because of repeated vomiting as the stomach gen-erates more stomach acids to replace those regur-gitated. This means bicarbonate ion concentrations in the extracellular fluid rise continually. Metabolic alkalosis may also develop from taking excessive quantities of antacids.
How does lactic acidosis affect the respiratory system?
Lactic acid dominates the muscles because of the attempts of the drowning person to stay above water. Dissociation of lactic acids releases lactate and hydrogen ions. Emergency treatment is vital, including artificial or mechanical respiratory assistance and intravenous administration of an isotonic solution. This solution contains sodium bicarbonate, sodium gluconate, or sodium lactate.
What is respiratory alkalosis?
Respiratory alkalosis is a less common condition that results from excessive carbon dioxide and car-bonic acid loss. Called hypocapnia, this condition is signified by a Pco2 < 35 mm Hg, with raised blood pH. A temporary hypocapnia can be produced by hyperventilation, often in response to anxiety, pain, fever, or poisoning due to salicylates. Hyper-ventilation depletes carbon dioxide and increases body fluid pH to as high as 8.0. Fortunately, respi-ratory alkalosis is usually self-corrected, because chemoreceptor stimulation stops and the urge to breathe reduces. Carbon dioxide levels then return to normal.
Why is respiratory rate elevated in metabolic acidosis?
They are usually elevated in metabolic acido-sis. This is because high hydrogen ion levels stimulate the respiratory centers . Blood pH is below 7.35, and bicarbonate ion levels are below 22 mEq/L. The Pco2 falls below 35 mm Hg as carbon dioxide is removed and excess acid leaves the blood. In respiratory aci-dosis, respiratory rate is often depressed, which is the immediate cause of the acidosis. This is not true for conditions of gas exchange impairment, such as pneumonia or emphysema.
What is the pH of blood?
Acidosis and alkalosis describe conditions in which a person’s blood is, respectively, too acidic (pH below 7.35) and too alkaline (pH above 7.45). Each of these conditions can be caused either by metabolic problems related to bicarbonate levels or by respiratory problems related to carbonic acid and CO 2 levels. Several compensatory mechanisms allow the body to maintain a normal pH.
How does renal compensation affect respiratory disease?
Metabolic and renal compensation for respiratory diseases that can create acidosis revolves around the conservation of bicarbonate ions. In cases of respiratory acidosis, the kidney increases the conservation of bicarbonate and secretion of H + through the exchange mechanism discussed earlier. These processes increase the concentration of bicarbonate in the blood, reestablishing the proper relative concentrations of bicarbonate and carbonic acid. In cases of respiratory alkalosis, the kidneys decrease the production of bicarbonate and reabsorb H + from the tubular fluid. These processes can be limited by the exchange of potassium by the renal cells, which use a K + -H + exchange mechanism (antiporter).
How does respiratory compensation affect acidosis?
Respiratory compensation for metabolic acidosis increases the respiratory rate to drive off CO 2 and readjust the bicarbonate to carbonic acid ratio to the 20:1 level. This adjustment can occur within minutes. Respiratory compensation for metabolic alkalosis is not as adept as its compensation for acidosis. The normal response of the respiratory system to elevated pH is to increase the amount of CO 2 in the blood by decreasing the respiratory rate to conserve CO 2. There is a limit to the decrease in respiration, however, that the body can tolerate. Hence, the respiratory route is less efficient at compensating for metabolic alkalosis than for acidosis.
What is the pH of a normal pH for bicarbonate deficiency?
At the normal pH of 7.40 , the ratio of bicarbonate to carbonic acid buffer is 20:1.
Why is my respiratory system alkaline?
Respiratory alkalosis occurs when the blood is overly alkaline due to a deficiency in carbonic acid and CO 2 levels in the blood. This condition usually occurs when too much CO 2 is exhaled from the lungs, as occurs in hyperventilation, which is breathing that is deeper or more frequent than normal.
What is respiratory acidosis?
Respiratory acidosis occurs when the blood is overly acidic due to an excess of carbonic acid, resulting from too much CO 2 in the blood. Respiratory acidosis can result from anything that interferes with respiration, such as pneumonia, emphysema, or congestive heart failure.
What is the pH of 7.40?
At the normal pH of 7.40, the ratio of bicarbonate to carbonic acid buffer is 20:1. If a person’s blood pH drops below 7.35, then he or she is in metabolic acidosis. The most common cause of metabolic acidosis is the presence of organic acids or excessive ketones in the blood. Table 1 lists some other causes of metabolic acidosis.
What causes hyponatremia in the kidney?
A decrease in renin and aldosterone and an increase in antidiuretic hormone (ADH) and atrial natriuretic peptide (ANP) lead to decreased sodium reabsorption and increased water retention by the kidney, both of which lead to hyponatremia. Loss of subcutaneous tissue and thinning dermis of aging lead to increased moisture lost through the skin. Plasma oncotic pressure is frequently decreased because of lack of protein intake.
What is the force that moves fluid into the interstitial space?
hydrostatic pressure exceeds plasma oncotic pressure and fluid moves into the interstitial space. At the capillary level, hydrostatic pressure is the major force causing fluid to shift from vascular to the interstitial space. The other options would not cause edema.
What is the primary hypothalamic mechanism of water intake?
a. The primary hypothalamic mechanism of water intake is thirst.
What does a nurse do when a patient is 84?
While caring for an 84-yr-old patient, the nurse monitors the patient's fluid and electrolyte balance, recognizing what as a normal change of aging?
Which cells are most sensitive to shrinking or swelling?
As water shifts into and out of cells in response to the osmolality of the blood, the cells that are most sensitive to shrinking or swelling are those of the brain, resulting in neurologic symptoms.
Is hydrostatic pressure less than plasma oncotic pressure?
a. Plasma hydrostatic pressure is less than plasma oncotic pressure.
Which gland secretes aldosterone?
Aldosterone is secreted by the adrenal cortex in response to a decrease in plasma volume (loss of water) and resulting decreased renal perfusion; decreased serum sodium, increased serum potassium, or adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH).
What causes alkalosis in the body?
Other causes of metabolic alkalosis include medical conditions such as: Cystic fibrosis. Dehydration. Electrolyte imbalances, which affect levels of sodium, chloride, potassium and other electrolytes. High levels of the adrenal hormone aldosterone ( hyperaldosteronism ).
Why is metabolic alkalosis important?
Metabolic alkalosis is usually not life-threatening. It does not have lingering effects on your health once it is treated. But it’s important to seek medical care because it can lead to severe complications. Treatment with IV fluids helps many people make a full recovery. Addressing the cause can lower your risk of future episodes.
Why does alkalosis occur?
It can occur in a variety of conditions. It may be due to digestive issues, like repeated vomiting, that disrupt the blood ’s acid-base balance. It can also be due to complications of conditions affecting the heart, liver and kidneys.
What to do after alkalosis treatment?
You may wish to make small changes to lower your risk of future episodes. These changes may include: Decreasing the dose of or discontinuing steroids, laxatives, water pills or antacids.
What is the term for the body's acid-base balance?
What is alkalosis ? Alkalosis occurs when your blood and body fluids contain an excess of bases or alkali. Your blood’s acid-base (alkali) balance is critical to your well-being. When the balance is off, even by a small amount, it can make you sick.
What are the symptoms of metabolic alkalosis?
Many metabolic alkalosis symptoms are concerning and need prompt medical evaluation. If you are experiencing an arrhythmia, seizures or confusion, seek care right away.
What tests are used to check for metabolic alkalosis?
Blood tests to measure blood gases, acid-base balance and electrolyte levels. Electrocardiogram (EKG) to check for an arrhythmia. Urinalysis that may help find the cause of the metabolic alkalosis.
How do the kidneys and lungs maintain pH?
How the lungs and kidneys maintain the pH balance. The lungs control your body’s pH balance by releasing carbon dioxide. Carbon dioxide is a slightly acidic compound. It’s also a waste product produced by cells in the body as they use oxygen. The cells release it into your blood, and it’s taken to your lungs.
What causes a person to have a high fever and a high fever?
Respiratory alkalosis. Respiratory alkalosis is when there’s too little carbon dioxide in your blood. Causes of respiratory alkalosis include hyperventilation due to anxiety, aspirin overdose, high fever, and possibly even pain. Symptoms of respiratory alkalosis are muscle cramping and twitching.
How do you know if you have respiratory alkalosis?
Symptoms of respiratory alkalosis are muscle cramping and twitching. You may also notice tingling in your fingers, toes, and lips, as well as irritability.
How do kidneys help the body maintain pH balance?
Your brain constantly monitors this in order to maintain the proper pH balance in your body. The kidneys help the lungs maintain acid-base balance by excreting acids or bases into the blood. The kidneys’ effect on acidity works much more slowly than that of the lungs.
What is the pH balance of the body?
What is pH balance? Your body’s pH balance, also referred to as its acid-base balance, is the level of acids and bases in your blood at which your body functions best. The human body is built to naturally maintain a healthy balance of acidity and alkalinity. The lungs and kidneys play a key role in this process.
What happens if your blood pH is too low?
If the lungs or kidneys are malfunctioning, your blood’s pH level can become imbalanced. Disruption in your acid-base balance can lead to medical conditions known as acidosis and alkalosis. Both conditions require treatment from a medical professional, not simply dietary changes.
What are the two conditions that can lead to a blood pH imbalance?
A blood pH imbalance can lead to two conditions: acidosis and alkalosis.
