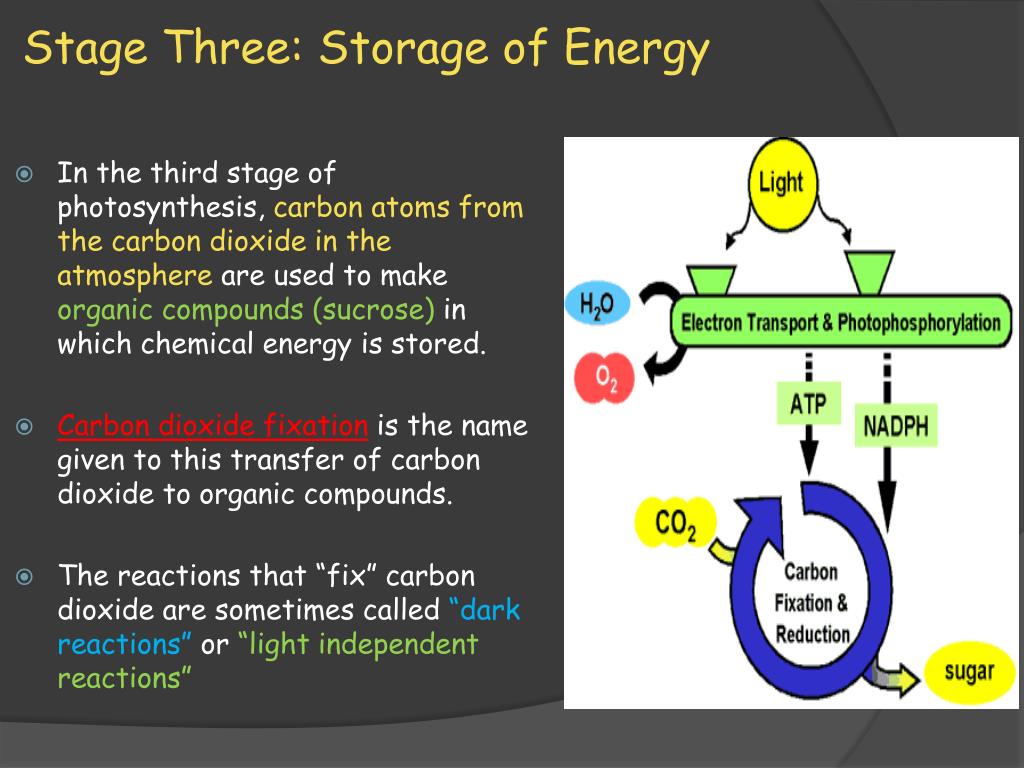
What is the most common method of carbon fixation in photosynthesis?
1) in the process of photosynthesis, CO2 is fixed by plants. 2) through carbon cycle. 3) dissolved CO2 is used by marine organisms to make their carbonate shells. 4) after the death of plant or animal, decomposition takes place and CO2 is released into atmosphere.
What is the process of carbon fixation?
Feb 12, 2020 · Most common method of carbon dioxide fixation in photosynthesis, A series of enzyme-assisted chemical reactions that produces a 3-carbon sugar. How does photosynthesis reduce carbon dioxide? Plants convert carbon dioxide and water into sugar and oxygen through the process of photosynthesis.
What is the first product of carbon dioxide fixation?
Dec 05, 2010 · The Calvin cycle is the most widespread carbon dioxide fixation pathway in bacteria What is the most common method of carbon dioxide fixation? Calvin Cycle! The Calvin cycle is a common method of...
How do autotrophs fix atmospheric carbon dioxide?
Sep 07, 2020 · All the autotrophs, bacteria, algae and plants fix atmospheric carbon dioxide by the process of photosynthesis or chemosynthesis. Carbon Fixation Process. Photosynthesis is the main process of carbon fixation. Carbon fixation occurs in the dark reaction or light-independent reaction of the photosynthesis process.

What is the method of fixing carbon dioxide?
What are the two ways of carbon dioxide fixation in atmosphere?
What are the 3 types of carbon fixation?
What is the best example of carbon fixation?
Where does carbon fixation occur?
How is carbon dioxide fixed during photosynthesis?
What is carbon sequestration methods?
What does carbon dioxide fixation mean?
What are the steps of carbon fixation?
Why is carbon dioxide needed in carbon fixation?
Which of the plant groups utilize the most energy efficient method of carbon fixation?
Is carbon fixation the same as Calvin cycle?
What is carbon fixation and why is it important?
Carbon fixation is the process by which inorganic carbon from the atmosphere is assimilated into living organisms and converted into organic compou...
What happens in carbon fixation?
Carbon fixation is a biosynthetic pathway by which atmospheric carbon is converted into metabolically active organic compounds. Carbon fixation in...
What is carbon fixation in the Calvin cycle?
Calvin cycle is the dark reaction of photosynthesis. It is the biosynthetic phase where CO2 is converted into sugar. It utilises ATP and NADPH prod...
What are the alternative pathways for carbon fixation?
Calvin cycle is the main pathway of carbon fixation in plants, algae and cyanobacteria. The alternative pathways of carbon fixation are: Reductive...
What are the 3 stages of Calvin cycle?
The three stages of Calvin cycle are: Carboxylation – It is the first step where RuBisCO catalyses the carboxylation of RUBP to form two molecules...
Does carbon fixation require light?
Carbon fixation is a dark reaction or light-independent reaction of photosynthesis. It does not require light directly but depends on the products...
What enzyme is responsible for carbon fixation?
Enzyme RuBisCO (Ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase-oxygenase) is responsible for carbon fixation by the Calvin cycle. It catalyses the carboxyla...
What is the first product of carbon dioxide fixation?
The first product of carbon dioxide fixation is 4 carbon compound OAA. OAA is then converted to other 4C acids like malic acid and aspartic acid. They are transported to bundle sheath cells. By decarboxylation in bundle sheath cells, CO 2 is released, which enters Calvin cycle.
What does carbon fixation mean in C3?
Meaning Process Carbon Fixation in C3 Plants Carbon Fixation in C4 Plants Carbon Fixation in CAM Plants#N#Carbon fixation means assimilation of inorganic carbon and conversion to organic compounds, which can be used as an energy store and for the synthesis of biomolecules.
Where does the Calvin cycle occur?
It is also known as the Calvin Cycle. Calvin cycle occurs in all the plants, be it C 3, C 4, CAM or any other plants. It occurs in the stroma of chloroplasts. The first product of carbon dioxide fixation is 3 carbon compound known as 3-phosphoglyceric acid or PGA. CO 2 acceptor is a 5 carbon compound ribulose biphosphate or RUBP.
What is the CAM pathway?
CAM pathway of carbon fixation or Crassulacean acid metabolism is present in plants present in arid conditions, e.g. cactus. In the CAM pathway, plants take CO 2 during the night through the stomatal opening. It is converted to malic acid (4 carbon compound) and stored in vacuoles.
What is the first step in the Calvin cycle?
It is the biosynthetic phase where CO2 is converted into sugar. It utilises ATP and NADPH produced during the light reaction of photosynthesis. Carbon fixation is the first step in the Calvin cycle where carboxylation of RUBP results in the fixation of CO2 to stable organic intermediate.
What is the Calvin cycle?
Calvin cycle is the main pathway of carbon fixation in plants, algae and cyanobacteria. The alternative pathways of carbon fixation are: Reductive citric acid cycle – in bacteria. 3-hydroxypropionate cycle – in bacteria and archaea. Reductive acetyl CoA pathway – in bacteria and archaea.
What is the Kranz anatomy of C4 plants?
C 4 plants have Kranz anatomy in leaves to tolerate high temperature. Large bundle sheath cells are present around vascular bundles of leaves. Bundle sheath cells have thick walls, no intercellular spaces and have large chloroplasts. Carbon fixation occurs in mesophyll cells.
