
There are multiple scales that are commonly used worldwide in the assessment of stroke victims, including the five listed below:
- National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale (NIHSS)
- Cincinnati Prehospital Stroke Scale (CPSS)
- Face Arm Speech Test (FAST)
- Los Angeles Prehospital Stroke Screen (LAPSS), and
- Recognition of Stroke in The Emergency Room (ROSIER)
What is the National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale?
The National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale (NHISS), considered the Gold Standard Acute Stroke Assessment, is a systematic assessment tool that provides a quantitative measure of stroke-related neurologic deficit.
What is the best Stroke Scale for You?
For example, if a rapid assessment needs to be performed, the Cincinnati Prehospital Stroke Scale may be the most advantageous. In other situations, a more thorough assessment may be warranted. It is also important to keep in mind that, although a stroke scale is a useful tool, it is only one piece of the puzzle.
What is the best way to measure stroke?
Measures of pathology (for example, size of infarct on imaging) or impairment (for example the Medical Research Council Motor Assessment Scale) are straightforward to perform and interpret, but give little useful information on how stroke affects the individual. For this reason, impairment scales are often used in early phase trials.
What are the different types of stroke tests?
• FAST -ED: Field Assessment Stroke Triage for Emergency Destination • CSTAT : Cincinnati Prehospital Stroke Severity Scale • VAN : Vision, Aphasia, Neglect Assessment • MEND : Miami Emergency Neurologic Deficit • ROSIER : Recognition of Stroke in the Emergency Room “Off hand, I’d say your suffering from an arrow through your head,
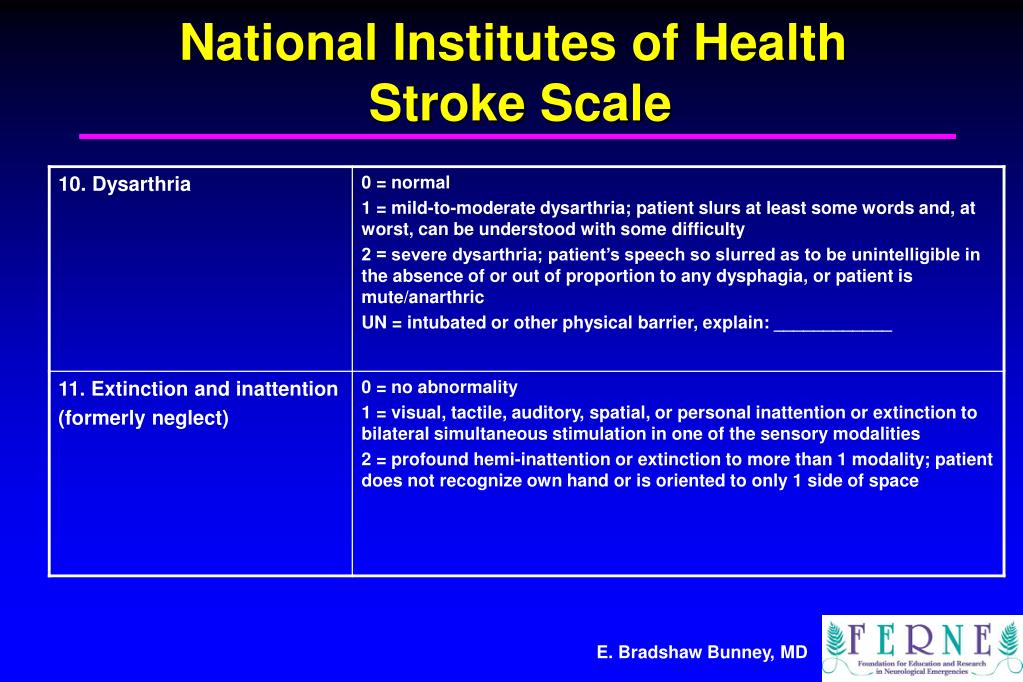
What is the simplest stroke scale?
What Does the NIHSS Measure?0 = no stroke.1–4 = minor stroke.5–15 = moderate stroke.15–20 = moderate/severe stroke.21–42 = severe stroke.
What is the best stroke assessment?
The National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale (NIHSS) was designed as a research tool to measure stroke severity. The NIHSS has evolved beyond academic research and has become the gold standard for clinical stroke assessment and measurement.
What is the scales that use assess stroke patients?
We will describe three common stroke assessments: the National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale (NIHSS), the modified Rankin Scale (mRS) and the Barthel Index (BI).
What is the stroke scale called?
The National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale, or NIH Stroke Scale (NIHSS), is a tool used by healthcare providers to objectively quantify the impairment caused by a stroke.
What is the NIH stroke scale used for?
The NIH Stroke Scale (NIHSS) measures neurological function in patients with signs and symptoms of stroke.
What does 3 on a stroke Scale mean?
Methods— The new stroke scale assessed 3 parameters: (1) level of consciousness, (2) gaze, and (3) motor function. Each item was graded 0 to 2, where 0 indicated normal findings and 2 severe abnormalities (ie, profound drowsiness or worse, forced gaze deviation, and severe hemiparesis, respectively).
Is NIHSS used for hemorrhagic strokes?
The National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale (NIHSS) is commonly used to measure neurologic function and guide treatment after spontaneous intracerebral hemorrhage (ICH) in routine stroke clinics.
How do you do a stroke scale?
Ask patient to read or repeat a list of words. Simultaneously touch patient on both hands, show fingers in both visual fields, ask patient to describe deficit, left hand. Most people receive a score 0 after taking the NIH stroke scale. Scores as low as one to four could indicate a mild stroke.
What is a normal NIH stroke scale score?
Stroke severity may be stratified on the basis of NIHSS scores as follows (Brott et al, 1989): Very Severe: >25. Severe: 15 – 24. Mild to Moderately Severe: 5 – 14.
Is Glasgow Coma Scale used for stroke patients?
The Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS) was developed to describe the depth and duration of impaired consciousness or coma. In this measure, three aspects of behaviour are independently measured: motor responsiveness. , verbal performance, and eye opening. The GCS can be used with individuals with traumatic brain injury, stroke.
What is NIH stroke scale test?
The scale assesses level of consciousness, extraocular movements, visual fields, facial muscle function, extremity strength, sensory function, coordination (ataxia), language (aphasia. It is most often the result of stroke or head injury.
What is the rosier scale?
ROSIER is a 7-item recognition instrument (ranging from − 2 to + 5) that based on the clinical history and neurological signs. A score of + 1 or above was considered positive of stroke or transient ischemic attack [7].
What is the National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale?
The National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale (NHISS), considered the Gold Standard Acute Stroke Assessment, is a systematic assessment tool that provides a quantitative measure of stroke-related neurologic deficit. The NIHSS was originally designed as a research tool to measure baseline data on patients in acute stroke clinical trials. Now, the scale is also widely used as a clinical assessment tool to evaluate acuity of stroke patients, determine appropriate treatment, and predict patient outcome.
What is the European stroke scale?
The European Stroke Scale (ESS), which consists of 14 items selected for their specificity and their prognostic value, was designed specificallyfor clinical stroke trials in patients with middle cerebral artery stroke . This scale can be used as an instrument for matching of treatment groups as well as for evaluation of the patient's level of impairment. The scale consists of 14 items selected on the basis of their specificity and their prognostic value. The 14 items are level of consciousness, comprehension, speech, visual field, gaze, facial movement, maintainence of arm position, arm raising, wrist extension, finger strength, maintainence of leg position, leg flexing, foot dorsiflexion, and gait. Because gait is part of the standard clinical neurological evaluation and can be considered as a mixture of different prognostic levels of impairments (ie, proximal and distal motor function of the leg, postural control), this item was included in the scale . This scale is heavily weighted toward motor function.
What is the CNS score?
One of the first scales developed to assess stroke patients, the Canadian Neurological Scale (CNS) developed in 1986 as a simple tool to be used in the evaluation and monitoring of neurological status of patients with stroke in the acute phase and is a validated score to assess stroke severity . Lower scores indicate greater stroke severity. The CNS evaluates 10 clinical domains, including mentation (level of conciousness, orientation and speech) and motor function (face, arm and leg). Previous studies showed good to excellent interrater agreement . The CNS has been found to be brief, valid and reliable, and can be administered in approximately five minutes but should not be used for the unconscious/stuporous patient .The CNS can also be reliably converted to the NIHSS using a simple conversion formula: NIHSS = 23 - 2 x CNS. This finding may have a practical impact by permitting reliable comparisons with NIHSS-based evaluations and simplifying the routine assessment of acute-stroke patients in more diverse settings . The CNS can be accessed here.
What is the rapid artery occlusion scale?
The Rapid Arterial oCclusion Evaluation (RACE) Scale is the most recent scale developed and was designed based on the National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale (NIHSS) to accurately assess stroke severity and identify patients with acute stroke with large artery occlusion at prehospital setting by medical emergency technicians who may be candidates to be treated with endovascular techniques in a comprehensive stroke center. The RACE Scale takes slightly more time to perform than the CPSS and the LAPSS with the goal of the scale to more accurately identify Stroke Severity and localise the area affected .
What is the Los Angeles Motor Scale?
The Los Angeles Motor Scale (LAMS) is a brief 3-item stroke severity assessment measure designed for prehospital and Emergency Department use, derived from the Los Angeles Prehospital Stroke Screen which quantitatively characterizes stroke severity in the field, and predicts functional outcomes with accuracy nearly comparable to that of the full NIHSS. The Los Angeles Motor Scale (LAMS) was constructed by assigning point values to LAPSS items of Facial Weakness (0,1), Arm Strength (0,1,2) and Grip (0,1,2) to yield a total 0–5 Scale . A motor score derived from the LAMS rapidly quantifies stroke severity in the field and predicts functional outcomes with accuracy comparable to that of the full NIHSS and the sNIHSS . A score ≥ 4 is highly predicted of large artery occlusion . Compared with other instruments proposed for prehospital stroke severity assessment the LAMS has advantages of greater simplicity, more rapid administration, and of being immediately derivable from a validated stroke recognition instrument, rather than requiring separate examinations for stroke diagnosis and stroke severity assessment .
What is the Fast Scale?
FAST was created to expedite administration of intravenous tissue plasminogen activator to patients within 3 hours of acute stroke symptom onset. During the development of FAST Scale, emphasis was placed on producing a simple test that would complement existing assessments used by UK paramedics, such as the Glasgow Coma Scale. FAST contains 3 key elements from the CPSS ( (Facial Weakness, Arm Weakness, and Speech Disturbance) but avoids the need to repeat a sentence as a measure of speech, instead using assessment of language ability by the paramedic during normal conversation with the patient. The 3 assessments contained within the FAST were incorporated into the standard ambulance report form used for recording all ambulance contacts within the UK .
What is the Gold Standard for stroke assessment?
The National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale (NHISS), considered the Gold Standard Acute Stroke Assessment, is a systematic assessment tool that provides a quantitative measure of stroke-related neurologic deficit.
What is the purpose of stroke scales?
Stroke scales are standardized assessment tools used to identify stroke and clear a path to reperfusion.
How long does it take to complete the NIH stroke scale?
It has 15 items to test, including level of consciousness, speech, vision, movement, and sensation. The exam takes approximately 10 minutes to complete, and is considered to be too time-consuming and cumbersome for prehospital use by EMS. The NIH scale is, however, the standard that stroke scales developed for EMS are compared to for sensitivity and specificity.
What is rapid arterial occlusion?
Rapid Arterial oCclusion Evaluation (RACE) is the most recent scale developed and is gaining popularity. RACE takes slightly more time to perform than the CPSS and LAMS, with the goal of more accurately identifying stroke severity and localizing the area affected by the stroke. RACE includes:
What is the Cincinnati scale?
The Cincinnati Prehospital Stroke Scale (CPSS) takes the least amount of time to perform and is one of the most widely used in EMS. The CPSS or, as it is sometimes referred to, Cincinnati scale assesses for:
How does FaceTime help with stroke?
Smartphone apps, such as FaceTime, also allow physicians at the stroke center to see the patient and discuss a treatment plan with EMS before transport is initiated, reduce the time to treatment at the appropriate destination, and share data for quality improvement. Interdisciplinary teams can also quickly assess patients' needs ahead of arriving at the hospital in mobile stroke units. A recent study revealed stroke patients transported via a mobile stroke unit receive a clot-busting procedure 10 minutes faster than when they are transported via an ambulance.
What is the score of an ELVO?
A stroke is likely with a score above 1, and ELVO is likely if the cumulative score is above 5. 7. Stroke scales are a work in progress. Patients with ELVOs are best served at comprehensive stroke centers. However, most strokes do not involve major arteries and can be managed at primary stroke centers.
What is the Los Angeles Motor Score?
The Los Angeles Motor Score (LAMS) is another popular scale that can be performed quickly. The facial droop and arm drifts are tested the same way as in the CPSS, though grip strength is assessed instead of speech. Points are assigned to the findings to determine stroke severity. LAMS includes screening for:
What are the different stroke scales?
There are multiple scales that are commonly used worldwide in the assessment of stroke victims, including the five listed below: 1 National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale (NIHSS) 2 Cincinnati Prehospital Stroke Scale (CPSS) 3 Face Arm Speech Test (FAST) 4 Los Angeles Prehospital Stroke Screen (LAPSS), and 5 Recognition of Stroke in The Emergency Room (ROSIER)
What is the National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale?
The National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale (NIHSS) was designed as a research tool to measure stroke severity. 2 The NIHSS has evolved beyond academic research and has become the gold standard for clinical stroke assessment and measurement. 6 The NIHSS is a valuable tool for both initial assessments of stroke severity and ongoing assessment to monitor for actionable changes in patient condition. 3
What are the disadvantages of using the stroke scale?
One possible disadvantage to using this stroke scale is that it only based on a few parameters, and therefore may not be an efficient way to assess for a posterior circulation stroke, which may cause symptoms such as dizziness and vomiting and is responsible for 5 to 10% of all ischemic strokes.
What is the benefit of using a stroke scale?
One benefit of using a stroke scale is that it provides a standardized tool for initial neurological evaluation. The type of scale selected may vary depending on employer or facility policy. For example, certain emergency service agencies may utilize a specific stroke scale.
How long does it take to complete a stroke assessment?
The items must be administered in order and without patient coaching. Although it may be completed in six to ten minutes, the assessment is far longer than some other stroke scales.
What is a laps scale?
The LAPSS is a longer instrument consisting of four history items, a blood glucose measurement, and three examination items designed to detect unilateral motor weakness (facial droop, handgrip, and arm strength). 5 The scale takes into consideration the patient’s age, whether or not the patient has ever had a seizure, the length of time symptoms have been present, and whether at baseline the patient is bedridden or wheelchair-bound.
Is the Cincinnati prehospital stroke scale fast?
An obvious advantage of using the Cincinnati Prehospital Stroke Scale is that it is fast. The evaluation can usually be completed in less than a minute. In some situations, using the fastest stroke scale may be most beneficial.
What is the most widely used deficit rating scale in neurology?
The National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale (NIHSS) is the most widely used deficit rating scale in modern neurology: over 500 000 healthcare professionals have been certified to administer it using a web-based platform. Every clinical trial in vascular neurology—prevention, acute treatment, recovery—requires a severity assessment, and the NIHSS became the gold standard for stroke severity rating after the first successful trial in acute stroke therapy, the NINDS r-tPA (National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke recombinant tissue-type plasminogen activator) for Acute Stroke Trial (the Trial). 1 As part of the Trial, detailed and rigorous training/certification procedures were created for the NIHSS that facilitate wider use of the scale outside of research. 2
What scales were used in the 1980s?
During the late 1980s, several stroke-deficit rating scales were in use. 7 – 10 For use in a National Institutes of Health–sponsored trial of naloxone for acute stroke, investigators combined scales that had been developed at the University of Cincinnati, Canadian neurological scale, the Edinburgh-2 coma scale, and the Oxbury initial severity scale. 11 Greater scores correlated with larger infarctions. 12 This Cincinnati/Naloxone version of the NIHSS served the intended purpose in the Naloxone trial. 13 An intermediate version was used in the Pilot r-tPA for Acute Stroke Trial, 14 but when designing the NINDS r-tPA for Acute Stroke Trial, significant modifications were made to facilitate using the NIHSS in a larger clinical trial. 15 The version used today is this final iteration of the NIHSS, and it differs in important ways from the Cincinnati/Naloxone NIHSS ( Table 1 ). A modified version contains fewer, more reliable items. 16
What is the NIHSS scale?
The NIHSS in current use evolved from an earlier version that is no longer used. The scale now used ( Table 1) was designed to be reproducible when used by physicians and nurses seeking to participate in clinical trials, and may be useful in clinical practice with appropriate training and certification. Scores for left hemisphere stroke exceed right hemisphere by four points, so severity scoring must include the side of the infarct. Online video training and certification systems are available and widely used. Use of the NIHSS by casual (nonresearch) bedside users has not been extensively validated, however, and the NIHSS should be used with caution outside of a research trial for rating stroke patients’ severity. Regulators seeking to add a severity adjustment to administrative data should approach the NIHSS with a full understanding of its limitations.
Is the scale valid without the scoring sheet?
The current version uses a form for recording the data that contains detailed instructions for the use of the scale; the scale is not valid without the instructions physically attached to the scoring sheet, and simple summary sheets are likely not valid.
Is the NIHSS accurate?
In addition to certifying examiners involved in clinical trials, the NIHSS has been used in demographic and epidemiological studies. A reasonably accurate NIHSS can be reconstructed from well-documented neurological examinations recorded in medical records. 24 Extracted NIHSS scores may not be comparable to scores recorded by certified users working in the context of clinical trials, however.
Why is assessment important in rehabilitation?
Assessment is arguably the most important step in the rehabilitation process, as our clinical reasoning is based on the information it provides and provides the basis for our decision making throughout the rehabilitation process.
What is subjective assessment?
The subjective assessment is used to provide a detailed picture of how the present condition affects the patient. Always consider your verbal and non-verbal communication as this will influence your interaction, as will the environment and your position in relation to the patient.
What is the measurement of movement around a specific joint or body part?
Range of Motion is the measurement of movement around a specific joint or body part or is the distance or amount of freedom your joint can be moved in a certain direction. Range of motion is measured in angle degrees normally with a Goniometer. There are three primary elements related to range of motion .
Is chorea a movement disorder?
Thus, chorea is said to be a hyperkinetic movement disorder. Associated Reactions. An involuntary movement of a body part associated with the resisted movement of another body part. Movements of body parts other than the ones that are intended to move, often increased with increased effort.
