
Common Causes
Types of Contractures
- Dupuytren's Contracture. Dupuytren's contracture is a type of contracture that specifically affects the hands and fingers. ...
- Capsular Contracture. Capsular contracture is a specific type of contracture that affects breast tissue following breast augmentation or reconstruction surgery.
- Marden-Walker Syndrome. ...
Related Conditions
Treatment
- Physical Therapy. Physical therapy can help decrease the severity of muscle contractures through stretching and soft tissue mobilization to decrease muscle tightness. ...
- Exercise. Regular exercise can help maintain proper joint mobility and range of motion to reduce joint stiffening and muscle tightening.
- Braces or Splints. ...
- Surgery. ...
What are the different types of contracture treatment?
- Being unable to place the hand flat, palm-down on the table
- Pits or dips in the skin of the palm
- Difficulty moving the hand
- Lumps and cords in the soles of the feet (called plantar fibromatosis), the back of the hands (called Garrod disease), or the genitals (called Peyronie's disease)
How do you treat contractures?
Capsular contracture is the most common complication following implant based breast surgery and is one of the most common reasons for reoperation. The formation of a “capsule” of scar tissue around any kind of implant (medical or cosmetic) is a normal part of the healing process. The body automatically reacts to any foreign object it ...
What are the causes and symptoms of contractures?
What is capsular contracture and how can it be treated?

Where are contractures common?
Contractures mostly occur in the skin, the tissues underneath, and the muscles, tendons, and ligaments surrounding a joint. They affect range of motion and function in a certain body part. Often, there is also pain.
What are types of contractures?
Types of Contractures Capsular Contracture: A response of the immune system to foreign materials in the human body. Dupuytren's Contracture: A condition in which one or more fingers become permanently bent in a flexed position. Muscle contracture: A muscle contracture is a tightening or shortening of muscles.
What is a severe contracture?
A contracture is a fixed tightening of muscle, tendons, ligaments, or skin. It prevents normal movement of the associated body part. An injury such as a severe burn can cause contracture of the skin. The skin becomes scarred and nonelastic which limits the range of movement of the affected area.
How do you identify contractures?
Contracture symptoms include pain and loss of movement in the joint. If this occurs, you should seek treatment right away....As tissue that stretches becomes less flexible, you might:Begin having contracture symptoms.Find it hard to move the affected area.Have limited range of motion.
What is an example of contracture?
For example, people with severe osteoarthritis (OA) or rheumatoid arthritis (RA) often develop contractures. Since they aren't moving their muscles and joints through their normal range of motion, these tissues are prime candidates for tightening.
What's another word for contracture?
In this page you can discover 14 synonyms, antonyms, idiomatic expressions, and related words for contracture, like: subluxation, tenosynovitis, subtalar, metatarsalgia, deformity, glenohumeral, hyperextension, synovitis, , dorsiflexion and sacroiliac.
How do you get rid of contractures?
How is a contracture treated?Physical therapy may be recommended. ... Heat therapy using ultrasound, liquid wax (paraffin), or water may be done. ... A support device , such as a brace, cast, or splint, may be used to keep a contracture in a stretched position. ... Medicines to decrease pain and spasms may be given.More items...
How fast can contractures develop?
Soft tissue changes that contribute to contractures begin very early after the onset of immobility. Protein synthesis within muscle fibers is reduced within 6 hours after a joint is immobilized. Shortening of muscle fibers occurs within 24 hours.
Can you reverse a contracture?
Contracture of nervous and vascular structures may limit the ability to lengthen soft tissues after long-standing contracture. Contractures are most easily reversed when they have recently developed but can usually be substantially corrected after months and sometimes even after years.
What do contractures feel like?
Symptoms of contractures include incredibly stiff and tight muscles that are resistant to stretching, which causes pain, decreased range of motion, and impaired joint mobility.
What joints are most affected by contractures?
Joint contracture is a painful deformity that prevents the movement of a joint through its normal range. The joints most frequently affected by contracture are the elbow, ankle, knee, hip and shoulder.
Does stretching Prevent contracture?
Stretch is widely used for the treatment and prevention of contractures. The aim of stretch is to maintain or increase joint mobility by influencing the extensibility of soft tissues spanning joints.
What is a Volkmann's contracture?
Volkmann contracture is a deformity of the hand, fingers, and wrist caused by injury to the muscles of the forearm. The condition is also called Volkmann ischemic contracture.
What joints are most affected by contractures?
Joint contracture is a painful deformity that prevents the movement of a joint through its normal range. The joints most frequently affected by contracture are the elbow, ankle, knee, hip and shoulder.
What is the difference between spasticity and contracture?
Spasticity and contractures are conditions in which muscle imbalance across a joint leads to abnormal positioning and tightness. Spasticity refers to involuntary tightening or stiffening of muscles. The term contracture refers to abnormal positioning of a joint.
What causes joint contractures?
Joint contracture is caused by shortening of muscles, tendons, ligaments, and joint capsules or by heterotopic ossification. Contractures are a common consequence of weakness, hypertonia, or hypotonia, and disuse.
Can you reverse a contracture?
Some contractures can be reverse or fixed. Physical and occupational therapy can include exercises and stretches that loosen the contractures. Addi...
What causes a contracture?
Contractures form due to inactivity of the affected body part. Situations that often reduce activity of a body part and result in contractures incl...
What is a muscle contracture?
A muscle contracture occurs when the normally soft muscle tissue becomes stiff, constricted, and/or shortened. Muscle contractures often occur due...
What are the types of contractures?
There are several different types of contractures, which include Dupuytren's contracture, Marden-Walker syndrome, and capsular contractures. Dupuyt...
How do you treat contractures?
Treatment of contractures often includes physical and/or occupational therapy which involves various exercises and stretches to increase strength a...
What are body contractures?
Contractures occur when soft connective tissues of the body become stiff and shortened resulting in reduced range of motion of the affected body pa...
How common is contracture in older adults?
Overall, the prevalence has been reported to be between 15% and 70% in older adults. 5 Patients with acquired brain injury developed contractures between 16% and 81%. 6 . 60% of stroke, 36% of cerebral palsy, and about 11 to 48% of spinal cord injury patients develop some form of joint contracture. 7
What causes contracture in the body?
The most frequent cause of contracture is immobilization, but they can be also be caused by congenital conditions (e.g., Duchenne’s Muscular Dystrophy, Cerebral Palsy), muscle imbalances, arthritic conditions, heterotopic ossification, prolonged hypertonic spasticity, ulcers, burns, total knee arthroplasty (TKA), local trauma, diabetes, or in rare cases, hypothalamus-pituitary-adrenal axis (HPA) hormone deficiency. 1 Manual work and vibration exposure have also been associated with the development of Dupuytren’s contracture. 2,3
What is the primary risk factor for contracture development?
Overall, the primary risk factor for contracture development is immobility. Spasticity is a risk factor for later development, but paralysis is foremost. 14
Why is it important to control lower limb contractures?
Controlling lower limb contractures is important to minimize their adverse effects on independent ambulation. Static positioning of both upper and lower limbs is an important cause of contracture formation. Mild upper limb contractures may not negatively impact function 21.
How to prevent contracture?
The best treatment is to slow or prevent contracture formation. Clinically, this largely involves PROM and stretching exercises daily . However, some evidence-based research has made these longstanding interventions controversial. Cochrane review articles have suggested that passive movements are not effective for the prevention and treatment of contractures, 19 and stretch does not prevent or reverse joint contractures in people with neurologic conditions. 20 Many argue, however, that these clinical trials did not provide a sufficient dose or have not combined modalities together. As such, PROM, proper positioning, and stretching are still the clinical mainstays of treatment and prevention.
Why do burns cause contractures?
Contractures specific to burn injuries occur due to thermal damage from vascular insufficiency or from compressive edema or eschar causing eventual joint and myofascial deformities. 22 One additional consideration is that Denmark researchers in 2016 published a comprehensive theory about how contracture develops under central motor lesions. They have proposed that the adaptation of the neuromuscular-tendon-connective tissue complex to the central motor lesion with several other factors (neural activation, bone/muscle growth mismatch, mechanotransduction, tensional homeostasis, microvascularization, genetics, epigenetics) are key to preventing and treating muscle contractures.
Why are contractures so controversial?
There is a lack of knowledge about the pathophysiology and disease course that lead to contractures. Due to the lack of standardization in assessment, quantification of disability, and evidence-based treatment, there remains a tremendous amount of individual interpretation without many unifying theories or clinical research studies. Clinical studies vary widely in what constitutes a contracture. Even still, evidence-based treatment options remain controversial, putting into question longstanding traditional interventions. There are no concise outcome measures that have been validated that can predict the prognosis or the effect of treatments, and criteria need to be developed to allow for better assessment, prognosis, and measure of outcomes.
What is muscle contracture?
A muscle contracture involves the shortening and tightening of the muscles. Joints. If there’s contracture in the joint capsule where two or more bones connect, you’ll experience limited range of motion in that area of your body. Skin. Skin may contract where it’s been scarred from an injury, burn, or past surgery.
What causes a person to contracture?
Common causes of contracture deformity. The most common causes of contracture are inactivity and scarring from an injury or burn. People who have other conditions that keep them from moving around are also at higher risk for contracture deformity.
What is a contracture deformity?
A muscle contracture, or contracture deformity, is the result of stiffness or constriction in the connective tissues of your body. This can occur in: your muscles. tendons. ligaments. skin. You can also experience a contracture deformity in your joint capsules. This is the dense, fibrous connective tissue that stabilizes ...
What causes joint contractures in children?
Other causes include diseases that are inherited or that develop in early childhood, such as: Muscular dystrophy.
How to prevent contracture?
Follow their treatment recommendations to help prevent contracture. Physical therapy, occupational therapy, and devices that passively move your joints can also help prevent problem areas from stiffening. Last medically reviewed on October 2, 2019.
Can OA cause contractures?
For example, people with severe osteoarthritis (OA) or rheumatoid arthritis (RA) often develop contractures. Since they aren’t moving their muscles and joints through their normal range of motion, these tissues are prime candidates for tightening.
Can contracture deformity affect movement?
Skin. Skin may contract where it’s been scarred from an injury, burn, or past surgery. This will limit your ability to move that part of your body. The main symptom of contracture deformity is reduced ability to move an area of your body. You might also have pain, depending on the location and cause of the problem.
Types of muscle contractures
Depending on the moment in which they appear and the reason, muscle contractures can be divided into two different types:
Causes of muscle contracture
In most cases, contractures appear when performing an activity or effort inappropriately. Executing a bad gesture and maintaining it over time or taking excessive weight can overload an area and cause contracture. Despite being a fairly common muscle damage, there are factors that contribute to making it more frequent.
Treatment of muscle contracture
Before telling how to treat it, it is important to talk about preventing it. To avoid a muscle injury, we recommend that you ensure correct posture when performing daily activities, warm up well before exercising , avoid gestures or repetitive movements, and do physical activity progressively, without forcing yourself excessively.
Which muscle is most affected by contractures?
Muscles that are flexors, those that bend the joints to bring body parts closer to the body, are the ones most affected by contractures. The stiffening and tightening of these muscles prevent the body parts from being moved out and away from the body.
What is contracture deformity?
A muscle contracture, also known as a contracture deformity, is a permanent shortening and tightening of muscle fibers that reduces flexibility and makes movement difficult. It is caused when a muscle loses elasticity. If a muscle cannot move and be stretched, the nearby joints also lose mobility and become painful. 1.
How to prevent contractures in joints?
Regular exercise can help maintain proper joint mobility and range of motion to reduce joint stiffening and muscle tightening. Exercise also improves blood flow and activates muscles, which helps prevent contractures from forming. 1
What muscles are involved in knee contracture?
In babies and children, typical areas affected by muscle contracture include the elbows, wrists, fingers, knees, and ankles.
What prevents muscle from contracting normally?
This increase in sarcomere length prevents the muscle from contracting normally, resulting in muscle weakness. 1. Muscle fibers are encased in an extracellular matrix, a mesh-like web composed of collagen and other proteins that help transmit force and provide muscle contraction.
What is the most common motor disability in children?
Cerebral palsy is present at birth and is the most common motor disability in children. It causes cognitive impairment, decreased muscle strength, and problems with movement, coordination, and functional motions like walking.
Can a burn cause a contracture?
Injury to muscles or tendons can cause contractures as scar tissue develops, joining muscle fibers and joints together. This development significantly restricts movement. Large burns also can cause contractures of the skin, muscles, and joints. Without aggressive treatment, range of motion can become significantly limited, and these changes can become irreversible.
What are the three categories of muscle contraction?
Here we explain isotonic, isometric, isokinetic, concentric and eccentric muscle contractions .
How are isokinetic contractions similar to isotonic contractions?
Isokinetic contractions are similar to Isotonic in that the muscle changes length during the contraction, where they differ is that Isokinetic contractions produce movements of a constant speed. To measure this a special piece of equipment known as an Isokinetic dynamometer is required. Examples of using Isokinetic contractions in the day-to-day and sporting activities are rare. The best is breaststroke in swimming, where the water provides a constant, even resistance to the movement of adduction.
What is the opposite of concentric contractions?
Eccentric contractions are the opposite of concentric and occur when the muscle lengthens as it contracts. This occurs when lowering the dumbbell down in a bicep curl exercise. The muscle is still contracting to hold the weight all the way down but the bicep muscle is lengthening.
What is the purpose of the muscles contracting in the hand?
There is no movement in the joints of the hand, but the muscles are contracting to provide a force sufficient enough to keep a steady hold on the racket. The amount of force a muscle is able to produce during an isometric contraction depends on the length of the muscle at the point of contraction.
What type of exercise puts a lot of strain through the muscle and is commonly involved in muscle injuries?
This type puts a lot of strain through the muscle and is commonly involved in muscle injuries. Plyometric training exercises (hopping and bounding) involve a lot of eccentric contractions and can lead to severe muscle soreness ( DOMS) if you overdo it too soon.
What is isotonic contraction?
Isotonic contractions are those where the muscle changes length as it contracts whilst the load or resistance remains the same. As a result, this causes movement of a body part. There are two types of Isotonic contraction:
When does isometric contraction occur?
Isometric contractions occur when there is no change in the length of the contracting muscle. This occurs when carrying an object in front of you as the weight of the object is pulling your arms down but your muscles are contracting to hold the object at the same level.
What causes contractures in the body?
A number of other local conditions, such as joint infections, hemarthroses, and burns, will cause contractures. In addition, conditions affecting multiple systems, such as muscular dystrophy, diabetes, Parkinson, and Alzheimer diseases can limit mobility or initiation and put the patient at risk for contractures.
What is joint contracture?
A joint contracture is a limitation in the passive range of motion of a joint. Changes in intra-articular structures (bone, cartilage, capsule) or extra-articular structures (muscles, tendons, skin) can prevent a joint from moving passively through its full range. A classification according to the tissue limiting the range ...
Why do muscle contractions occur?
Neurologic conditions that increase muscle tone or cause weakness contribute to contractures because of unequal forces generated by opposing muscle groups. In upper motor neuron conditions, such as after a stroke or traumatic brain injury, excessive muscle tone prevents a joint from accessing portions of its normal range opposite the spastic muscle. Similarly, in lower motor neuron injuries, such as a plexopathy or peripheral nerve injury, the unopposed pull of spared muscles will limit joint motion toward the paralyzed muscle. The range of motion not accessed will eventually be lost, resulting in a joint contracture.
How to diagnose a joint contracture?
The clinical diagnosis of a joint contracture occurs at the bedside, more precisely with a goniometer. Radiography may reveal contributing structural abnormalities. Prevention of joint contractures in at-risk individuals is paramount considering their refractory nature; once a joint contracture is established, full recovery of ROM is difficult to achieve. Awareness and monitoring of predisposing conditions is therefore critical. Treatment options include addressing the causative underlying disease, manual stretching, static and dynamic bracing, use of modalities, and motor point blocks. Functionally limiting joint contractures may benefit from surgical interventions such as tenotomy, tendon lengthening, joint capsule release, or removal of bony obstructions.
What is the most common form of arthritis?
Osteoarthritis ( OA) is the most common form of arthritis and the fastest growing chronic disease worldwide. As many as one third of patients with knee OA presenting for total knee replacement have a contracture in the affected knee. Of these, one third will also have a contracture of the opposite knee.
Is bed rest a risk factor for contractures in multiple joints?
Prolonged bed rest is a risk factor for contractures in multiple joints. (A) Common bed rest position placing patient at risk of developing contractures in multiple joints. (B) Plantar-flexion contracture due to prolonged bed rest in a patient with severe brain injury. (C) Elbow, wrist, and finger flexor contractures in same patient shown in (B).
Can joint contractures be painful?
Joint contractures develop insidiously and may progress asymptomatically. They are often painful only with attempts to move the joint through its full range beyond the restriction. Many daily activities do not require a joint to move through its entire range.
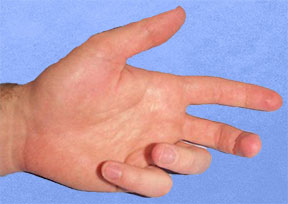
What is Dupuytren's contracture?
Dupuytren's contracture (also called Dupuytren's disease) is an abnormal thickening of the skin in the palm of your hand at the base of your fingers. This thickened area may develop into a hard lump or thick band. Over time, it can cause one or more fingers to curl (contract), or pull sideways or in toward your palm.
How is Dupuytren’s contracture diagnosed?
Your provider will examine your hand. He or she will test the flexibility and feeling in your thumb and fingers. Your grip and pinch strength may also be tested.
Why does Dupuytren's contracture run in families?
The exact cause is not known. It may be linked to cigarette smoking, alcoholism, diabetes, nutritional deficiencies, or medicines used to treat seizures.
Is Dupuytren's contracture more common in men than women?
You may be at greater risk for Dupuytren’s contracture if you: Are older. The condition usually starts in middle age. Are male. It is more common in men than women. Have a Scandinavian or Northern European background. It is most common in people whose families come from these regions.
Disease/Disorder
A permanent tightening of the muscles, tendons, skin, and surrounding tissues that causes the joints to shorten and stiffen.
Essentials of Assessment
Rehabilitation Management and Treatments
Cutting Edge/Emerging and Unique Concepts and Practice
- Definition
Contractures are the chronic loss of joint mobility caused by structural changes in non-bony tissue, including muscles, ligaments, and tendons. They develop when these normally elastic tissues are replaced by inelastic tissues. This results in the shortening and hardening of these ti… - Etiology
Contractures are a final common pathway for many conditions. The most frequent cause of contracture is immobilization, but they can be also be caused by congenital conditions (e.g., Duchenne’s Muscular Dystrophy, Cerebral Palsy), muscle imbalances, arthritic conditions, heter…
Gaps in The Evidence-Based Knowledge
- History
History should include the etiology of the contracture, its natural course, and its impact on the patient’s functionality. This includes pain, difficulties in mobility and transfers, activities of daily living (ADLs), and hygiene. Details regarding caregiver burden should also be explored. - Physical examination
Ideally, the patient should be free from pain that may interfere with the examination. Inspect the patient for joint size, symmetry, and resting position compared with the contralateral side. A goniometer can measure residual range of motion and document changes over time. Joint defor…
References
- General approach to Contractures: Key principles
The best treatment is to slow or prevent contracture formation. Clinically, this largely involves PROM and stretching exercises daily. However, some evidence-based research has made these longstanding interventions controversial. Cochrane review articles have suggested that passive … - Approach to contractures at different stages
Once a contracture has developed, prolonged and continuous stretching of the joint is accomplished through dynamic bracing or serial casting. After maximal stretching, an orthotic or cast is applied to fix the joint at that position. The device is removed every few days, and the pro…
Muscles Affected
- Cutting edge concepts and practice
In one animal model, radiofrequency treatments successfully treated underlying collagen contractures and helped in new collagen formation.25 In another study comparing speed and torque in range of motion exercises using rats, high torque and long-duration static stretching we…
Causes
- Gaps in the evidence-based knowledge
There is a lack of knowledge about the pathophysiology and disease course that lead to contractures. Due to the lack of standardization in assessment, quantification of disability, and evidence-based treatment, there remains a tremendous amount of individual interpretation witho…
Symptoms
- Syriou V, Moisidis A, Tamouridis N, Alexandraki KI, Anapliotou M. Isolated adrenocorticotropin deficiency and flexion contractures syndrome. Hormones (Athens). 2008;7(4):320-4.
- Descatha A, Jauffret P, Chastang JF, Roquelaure Y, Leclerc A. Should we consider Dupuytren’s contracture as work-related? A review and meta-analysis of an old debate. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2011...
- Syriou V, Moisidis A, Tamouridis N, Alexandraki KI, Anapliotou M. Isolated adrenocorticotropin deficiency and flexion contractures syndrome. Hormones (Athens). 2008;7(4):320-4.
- Descatha A, Jauffret P, Chastang JF, Roquelaure Y, Leclerc A. Should we consider Dupuytren’s contracture as work-related? A review and meta-analysis of an old debate. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2011...
- Fadel M, Leclerc A, Evanoff B, Dale AM, Ngabirano L, Roquelaure Y, Descatha A . Association between occupational exposure and Dupuytren’s contracture using a job-exposure matrix and self-reported e...
- Fergusson D, Hutton B, Drodge A. The epidemiology of major joint contractures: a systematic review of the literature.ClinOrthop Relat Res. 2007;456:22-29.
Treatment
- Muscles that are flexors, those that bend the joints to bring body parts closer to the body, are the ones most affected by contractures. The stiffening and tightening of these muscles prevent the body parts from being moved out and away from the body. The most common muscles affected by muscle contractures are: 1. Wrist and finger flexors:Groups of...
Summary
- Muscle contractures, or muscle tissue that is stiffer than normal and difficult to stretch, are caused by permanent shortening of muscle fibers and the change in normal muscle structure. Sarcomeres are fundamental units of muscles that cause muscle fibers to contract. With muscle contractures, sarcomeres overly lengthen when muscle fibers tighten. This increase in sarcomer…
A Word from Verywell
- Symptoms of contractures include incredibly stiff and tight muscles that are resistant to stretching, which causes pain, decreased range of motion, and impaired joint mobility. When contractures are severe, they can interfere with the functional range of motionneeded to move joints to complete daily tasks and movements like standing up from a chair and walking.