
Can you calculate the most probable energy from the Maxwell-Boltzmann distribution?
If the Maxwell-Boltzmann distribution of energy is f (E)=2*pi*E 1/2 * (1/pi*k*T) 3/2 *e E/kT. Can you calculate the most probable energy from this? (The answer is kt/2). Some kind of integration (guassian integral) is needed from 0 to infinity I believe.
What is the most probable kinetic energy?
(Collision Theory Chemistry) Most probable kinetic energy is the energy possessed by the maximum number of reactant molecules at a temperature T, and it is shown as a peak on the Maxwell-Boltzmann energy distribution graph (fraction of molecules versus Kinetic energy).
How is the Maxwell-Boltzmann distribution function derived?
After all, the derivation of the Maxwell-Boltzmann distribution function is based on the assumption that the mean kinetic energy of a particle is linked to the temperature according to the equation ( 14 )! Since a certain kinetic energy can be assigned to each speed, the speed distribution can also be converted into an energy distribution.
How is kinetic energy displayed on a Maxwell Boltzmann graph?
The number of molecules in a gas with different kinetic energies is displayed on a Maxwell Boltzmann graph At the peak of the graph, is the most common amount of molecules which are at an average speed of movement Past the activation energy line is all of the molecules which are moving fast enough for them to react
What is the most probable kinetic energy?
Most probable kinetic energy is the energy possessed by the maximum number of reactant molecules at a temperature T, and it is shown as a peak on the Maxwell-Boltzmann energy distribution graph (fraction of molecules versus Kinetic energy).
What is Boltzmann distribution of energy?
The Maxwell–Boltzmann distribution concerns the distribution of an amount of energy between identical but distinguishable particles. It represents the probability for the distribution of the states in a system having different energies.
What is Boltzmann's probability distribution?
Boltzmann distribution is a probability function used in statistical physics to characterize state of a system of particles, with respect to temperature and energy. The system can exist in several states, however, the chance of being in certain subset of states is higher than other.
What does the peak in the Boltzmann distribution show?
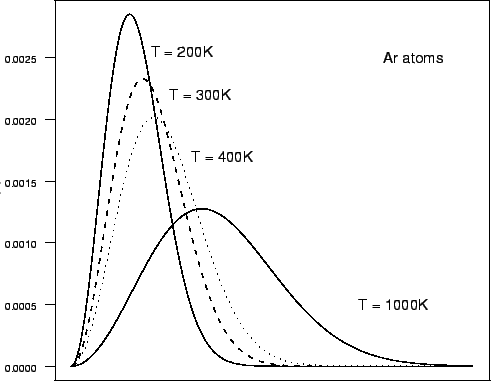
The total area under the entire curve is equal to the total number of molecules in the gas. If we heat the gas to a higher temperature, the peak of the graph will shift to the right (since the average molecular speed will increase).
What is meant by most probable distribution in statistical thermodynamics?
“Most probable” refers to having a large number of different ways of achieving the distribution. For example, in a solution, the solute molecules are typically equally distributed throughout the solution volume.
What is k in Boltzmann constant?
Having dimensions of energy per degree of temperature, the Boltzmann constant has a defined value of 1.380649 × 10−23 joule per kelvin (K), or 1.380649 × 10−16 erg per kelvin.
What is k in the Maxwell-Boltzmann distribution?
The distribution function for a gas obeying Maxwell-Boltzmann statistics ( fM–B) can be written in terms of the total energy (E) of the system of particles described by the distribution, the absolute temperature (T) of the gas, the Boltzmann constant (k = 1.38 × 10−16 erg per kelvin), and a normalizing constant (C) ...
What is the Boltzmann population ratio?
A) The Boltzmann equation gives ratios of level populations as a function of temperature: Nj. Ni. = gj.
What is Boltzmann distribution chemistry?
A Boltzmann Distribution shows the distribution of molecular energies in a gas at constant temperature. Most gas molecules have energies within a comparatively narrow range. • The curve will only meet the energy axis at infinity energy. No molecules have zero energy.
Which one of the following is the most probable speed?
As stated above, Cmp is the most probable speed, thus it will be at the top of the distribution curve. To the right of the most probable speed will be the average speed, followed by the root-mean-square speed.
What does Boltzmann distribution tell us?
The Boltzmann distribution gives the probability that a system will be in a certain state as a function of that state's energy, while the Maxwell-Boltzmann distributions give the probabilities of particle speeds or energies in ideal gases.
What is the most probable velocity?
Most probable velocity is the velocity possessed by maximum fraction of molecules at the same temperature.
Why do we use Boltzmann distribution?
The Boltzmann distribution describes the distribution of energy among classical (distinguishable) particles: It can be used to evaluate the average energy per particle in the circumstance where there is no energy-dependent density of states to skew the distribution.
What is Boltzmann distribution chemistry?
A Boltzmann Distribution shows the distribution of molecular energies in a gas at constant temperature. Most gas molecules have energies within a comparatively narrow range. • The curve will only meet the energy axis at infinity energy. No molecules have zero energy.
What is Boltzmann constant in physics?
The value of Boltzmann's constant is approximately 1.3807 x 10 -23 joule s per kelvin (J · K -1 ). In general, the energy in a gas molecule is directly proportional to the absolute temperature. As the temperature increases, the kinetic energy per molecule increases. As a gas is heated, its molecules move more rapidly.
What does the Boltzmann equation describe?
The Boltzmann equation is a integro-differential equation which describes the dynamics of a rarefied gas. It is one of the fundamental equations of statistical physics, and despite a long history it remains far from fully under- stood.
Homework Statement
If the Maxwell-Boltzmann distribution of energy is f (E)=2*pi*E 1/2 * (1/pi*k*T) 3/2 *e E/kT. Can you calculate the most probable energy from this? (The answer is kt/2).
Homework Equations
Some kind of integration (guassian integral) is needed from 0 to infinity I believe.
The Attempt at a Solution
I tried integration by parts and some other methods with no luck. My teacher made it clear that this is not a gamma function (my initial thought since the E 1/2 is paired with an exponential function) and that the answer is relatively easy. Any help would be much appreciated!
Answers and Replies
Wikipedia says that it is a gamma distribution... Also, shouldn't it be e -E/kT?
What is the Maxwell-Boltzmann distribution?
The Maxwell–Boltzmann distribution concerns the distribution of an amount of energy between identical but distinguishable particles. It represents the probability for the distribution of the states in a system having different energies. A special case is the so-called Maxwell distribution law of molecular velocities. Maxwell introduced this law for the velocities of particles of a fluid ( Maxwell, 1868 ), e.g. a gas or a liquid solution in thermal equilibrium, and gives the probability f ( v) d v that the velocity v will be found in the infinitesimal range v to v + d v and gives the frequency of occurrence of the specific value v for the chosen velocity component vx, vy, vz per each direction x, y, z.
How are rates of elementary reactions given?
The rates of elementary reactions are given by the frequency or chance of reactant ions or components having , when they interact , the energy of the transition state ( Fig. 2 ). The Arrhenius relationship, empirically expresses these chances using the Boltzmann distribution of molecular energies:
Is temperature an average property?
In thermodynamics, temperature is an average property describing a system; however, in this case, it will be useful to extend to each molecule the concept of individual temperature (e.g. cold, mild and hot) according to Eqn (4.4) relating temperature with kinetic energy.
What is the most probable kinetic energy?
What is known as the Most Probable kinetic energy? (Collision Theory Chemistry) Most probable kinetic energy is the energy possessed by the maximum number of reactant molecules at a temperature T, and it is shown as a peak on the Maxwell-Boltzmann energy distribution graph (fraction of molecules versus Kinetic energy).
What does it mean when kinetic energy is less?
What it means is that earlier the kinetic energy was less, but due to the increase in temperature, there is an increase in the kinetic energy and a decrease in the activation energy so now more molecules can attain the threshold value for the reaction to occur. In short, as the Kinetic energy increases more molecules now undergo effective ...
What is Maxwell Boltzmann distribution?
The Maxwell-Boltzmann distribution describes the frequency with which certain molecular speeds occur in an ideal gas. In principle, however, it is not possible to assign a specific number of molecules to a specific speed. One will never find a single molecule with a specified velocity down to the “last” decimal place.
What is the most probable speed?
Most probable speed. If a particle is randomly picked out of an ideal gas, it is most likely to be in the speed range with the highest proportion. This corresponds to the maximum of the speed distribution and is referred to as the most probable speed ˆv. Figure: Definition of the different speeds.
What is the particle speed of argon at 473 K?
Even at temperatures of 473 K (200 °C ) the particle speeds of argon are more than half lower compared to the particle speeds of helium at 273 K (0 °C), because argon has an atomic mass about 40 times larger than helium. Rather, the statement about the temperature aims at the average kinetic energy of the molecules.
Is the temperature a measure of the speed of particles?
The different speeds (the most probable speed, the average speed and the root-mean-square speed) depend not only on the temperature but also on the particle mass. The frequently heard statement that the temperature is a measure for the speed of the particles is strictly speaking not correct.
Is temperature a measure of kinetic energy?
The average kinetic energy of a particle is directly connected to the temperature and independent of the particle mass! Thus the temperature is directly a measure for the average kinetic energy of the gas particles of an ideal gas.
