What organism uses cilia for movement?
protists. …cilia, pseudopodia are responsible for amoeboid movement, a sliding or crawlinglike form of locomotion. The formation of cytoplasmic projections, or pseudopodia, on the forward edge of the cell, pulling the cell along, is characteristic of the microscopic unicellular protozoans known as amoebas.
Is the movement of cilia important why?
Cilia Function. The important functions performed by cilia involve locomotion and sensory functions. They play a major role in cell cycle and replication and also in the development of humans and animals. Multiple cilia move in a rhythmic motion that keeps the internal passageways free from mucus or any foreign agent.
What are cells of the body perform cilia movement?
The organisms that possess cilia are known as ciliates. They use their cilia for feeding and movement. These are found in large numbers on the surface of the cell. In humans, these are found in the respiratory epithelium of the respiratory tract. Here, they function by clearing the mucus and dust out of the lungs.
What is cilia and why is it important?
Impact of Defective Cilia
- Cognitive impairment
- Retinal degeneration, rod cone dystrophy and retinitis pigmentosa. Cilia are found inside photoreceptors in the eyes. ...
- Anosmia. Airway congestion, glue ear, hearing loss.
- Lung / airway abnormalities. Motile cilia line the respiratory airways, to help clear mucus and dust. ...
- Congenital heart defects. ...
- Renal anomalies, eg cystic kidneys. ...
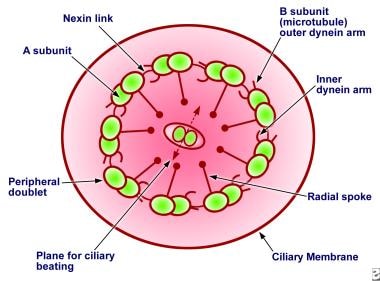
What causes movement in cilia?
Motility of cilia (also known as flagella in some eukaryotes) is based on axonemal doublet microtubule sliding that is driven by the dynein molecular motors. Dyneins are organized into intricately patterned inner and outer rows of arms, whose collective activity is to produce inter-microtubule movement.
What is the movement of cilia and flagella?
Flagella wriggle like eels. They generate waves that pass along their length, usually from base to tip at constant amplitude. Thus the movement of water by a flagellum is parallel to its axis while a cilium moves water perpendicular to its axis and, hence, perpendicular to the surface of the cell.
How do cilia move biology?
The primary purpose of cilia in mammalian cells is to move fluid, mucous, or cells over their surface. Cilia and flagella have the same internal structure. The major difference is in their length. Cilia and flagella move because of the interactions of a set of microtubules inside.
What is flagella movement?
Flagellar movement, or locomotion, occurs as either planar waves, oarlike beating, or three-dimensional waves. All three of these forms of flagellar locomotion consist of contraction waves that pass either from the base to the tip of the flagellum or in the reverse direction to produce forward or backward movement.
What moves faster cilia or flagella?
Cilia are present in organisms such as paramecium while flagella can be found in bacteria and sperm cells. Cilia are shorter and numerous than flagella. Cilia and flagella are the most common organelles for locomotion in unicellular organisms. Organisms with cilia can move faster and more efficiently.
How does motile cilia move?
Ciliary motility is driven by axonemal dyneins, which create sliding interactions between outer microtubules, while other motor proteins, intraflagellar transport proteins, carry cargo into and out of the cilium [1]. Ciliates can interact with their environment in complex ways [2].
What is cilia and its function?
Cilia are small, slender, hair-like structures present on the surface of all mammalian cells. They are primitive in nature and could be single or many. Cilia play a major role in locomotion. They are also involved in mechanoreception. The organisms that possess cilia are known as ciliates.
Does cilia help in movement?
Cilia are present in the epithelial lining such as the fallopian tube, respiratory tract, where they help in the movement of fluid as well as trap any external particles in the mucus. Cilia and flagella are Cytoskeleton made up of microtubules.
Does cilia help in movement?
Cilia are present in the epithelial lining such as the fallopian tube, respiratory tract, where they help in the movement of fluid as well as trap any external particles in the mucus. Cilia and flagella are Cytoskeleton made up of microtubules.
What do flagella and cilia have in common?
Eukaryotic flagella and cilia have long been recognized as organelles involved in motility, and their structure and function have both been studied in detail. Almost all motile (secondary) cilia and flagella have the same internal structure and have essentially the same function.
What is the main function of the cilia?
The bronchus in the lungs are lined with hair-like projections called cilia that move microbes and debris up and out of the airways. Scattered throughout the cilia are goblet cells that secrete mucus which helps protect the lining of the bronchus and trap microorganisms.
What is the structure of cilia and flagella?
Cilia and flagella are conserved, motile, and sensory cell organelles involved in signal transduction and human disease. Their scaffold consists of a 9-fold array of remarkably stable doublet microtubules (DMTs), along which motor proteins transmit force for ciliary motility and intraflagellar transport.
What are the functions of cilia?
Cilia acts as a sensory organelle and also helps in locomotion in a few organisms. Cilia also assists in feeding in a few ciliates.
What is the composition of cilia?
Cilia is composed of a motor protein dynein and microtubules. These comprise tubulin that are linear polymers of globular proteins.
Where are cilia located?
Motile cilia are located on the epithelial cells of several internal organs such as lungs, trachea, digestive system, etc. They are also found on t...
Do prokaryotes have cilia?
Cilia are found only in the eukaryotic cells. The prokaryotic cells contain whip-like structures called flagella that help them to move.
What are the causes of ciliopathies?
Ciliopathies are a recently defined class of human diseases caused by defects in assembly or function of motile and nonmotile cilia [1–7]. Ciliary dysfunction underlies a growing list of genetic conditions that affect multiple organ systems throughout the body. Pathologies associated with ciliary dysfunction range from blindness [8,9], chronic lung infections [10], male and female reproductive defects [11,12], cyst formation in the kidney and liver [13–15], congenital heart defects [16], laterality malformations [17], skeletal malformations [18], obesity [19,20], diabetes [21,22], and more. The list of genetic mutations resulting in ciliopathies is expanding and includes a number of genes encoding ciliary proteins, or proteins involved in building ciliary organelles [10]. The detailed structure of cilia/flagella, the dynein motors that generate their movement, and the regulatory pathways that control dynein motor function are detailed in other chapters (see Chapters 5, 6Chapter 5Chapter 6, 8, 9, and 11 (vol. 1 of this book) and Chapters 1 and 2Chapter 1Chapter 2 (this volume)). Here, we focus on the ODA motors of cilia and discuss the impact of alcohol on ODA function and ciliary beat frequency (CBF). This chapter highlights our current understanding of the acquired ciliopathy called alcohol-induced ciliary dysfunction (AICD).
What is the role of the N-DRC in the ciliary movement?
The N-DRC together with the RSs and the CP is responsible for modulation of ciliary movement and regulation of dynein arms. Inhibition of the sliding forces by the N-DRC converts the sliding forces into bending of the axoneme [161,162]. So far, mutations in three genes encoding for N-DRC components have been identified: CCDC164, CCDC65, and GAS8 [145,163–166]. Mutations in these genes result in isolated defects of the N-DRC and PCD.
How is cyclical bending produced?
In beating flagella, cyclical bending is produced by regulating the activity of all dynein arms in the bend plane as well as by switching the dynein activity in the plane of the central pair in the interbend regions ( Fig. 13.9 ). To understand flagellar oscillation, we need to elucidate the mechanism regulating the combination of these dynein functions. The disintegration of axonemes into smaller bundles or individual doublets induced by bending, which was observed frequently in axonemal fragments [104], was infrequent in quiescent flagella [106]. This suggests that the activation of all dynein arms by imposed bending requires that the force be applied to dynein arms in the direction not parallel to the beat plane. In addition to the change in the dynein attachment state resulting from the shear induced by the imposed bending, distortion of the axoneme could occur along the doublets in the bend plane, tilting the radial spokes and changing the geometric relationship between the doublets. These factors may activate the dynein arms on the doublets in the bend plane, and are probably linked to the switching of the activity of dynein on both sides of the central pair. Thus, the combination of the regulation of the activity of all dynein arms in the beat plane and the mechanism for switching the dynein activity on both sides of the central pair is essential for flagellar beating.
How is the motile activity of dynein switched on and off?
How the motile activity of dynein is switched on and off by the mechanical signal of bending – probably through nucleotide binding to the dynein heads, conformational and functional changes to the dynein tail and stalk, and the flexural rigidity of microtubules – is one of the important questions that the future must answer.
Which protein is involved in chromosome movement?
1 Kinesin and Dynein. Both the kinesin and dynein motor protein families are involved in microtubule-based intracellular transport, chromosome movement, ciliary and flagellar motion, and some forms of cell motility.
Is cleavage a monotreme?
In contrast to monotremes and marsupials, cleavage in eutherians is equal and holoblastic. Coordinated oviduct musculature contractions, tubal fluids, and ciliary movement of the epithelium transport the cleaving oocyte through the uterine tube towards the uterus (Fig. 1 (b) ). A glycoprotein layer (Zona pellucida) prevents the fertilized oocyte (zygote) from implantation into the tubal epithelium. In eutherian taxa studied, the period of oviduct zygote transport varies between 2 days ( Sus scrofa f. domestica) and 6 days ( Neovison vison, Equus przewalskii f. caballus) but can be greatly prolonged in bat species possessing delayed fertilization.
What is Cilia?
Cilia are small appendages that whip back and forth in eukaryotic cells. The primary purpose of cilia is to help a cell move in cellular fluid and help particles move past the cell in one direction, accomplishing this by their back and forth movements. However, cilia are only about 0.1 millimeters in size. In the human body, cilia are found in almost all of the cells.
What is the term for when the cilia work together to help move particles past the cell?
Intraflagellar transport is when the cilia work together to help move particles past the cell. When the cilia are not functioning correctly, it can affect the rest of the cell. Ciliopathy is when the cilia are not working correctly.
What is the structure of the cilia?
Cilia also have a unique molecular structure. Inside the cilia, a microtubular cytoskeleton backbone is surrounded by a plasma membrane called the ciliary axoneme. Each ciliary axoneme has nine microtubular pairs; however, the arrangement of the microtubular pairs is different in motile cilium and non-motile cilium. In motile cilium, there is a microtubular pair found in the center (9 + 2), but in the non-motile cilium, there are no centrally located microtubular pairs (9 + 0).
What is the plural of cilia?
In Latin, the term cilia means eyelashes and is the plural form of a cilium. Thus, a group of tiny hair-like structures on a cell is called cilia, whereas one or two hair-like structures are called flagellum. There are also synonyms for cilia and cilium, undulipodium being the synonym for cilium and undulipodia being the synonym for cilia. Therefore, undulipodia is a group of tiny appendages that can be found on eukaryotic cells.
What is the function of cilia in the human body?
Almost every cell in the human body contains cilia. These cells are responsible for moving molecules and lipids past the cell. This process helps keep the cells and human body functioning properly. Cilia are also found on eukaryotic cells and help eukaryotic cells move. Many unicellular Protozoa have cilia on the cell.
What are the two main structures of the cilia?
Tubulin and basal bodies make up the two main structures of cilia. Tubulin are the hair-like structure of the cilia and are composed of small protein pieces connected to the cell by basal bodies. These protein pieces are made in the cell and delivered to the tubulin.
Where are the cilia found?
The motile cilia are commonly found in unicellular organisms and the respiratory tract, while non-motile cilia are found in mammalian cells and are used for sensory purposes. The nodal cilia are located in the early stages of embryo development.
How does a cilia help?
Cilia also help to clear your ear of wax buildup, moving the wax through the inner parts of the ear to keep your ear canal open. Finally, these little hairs can act as motion sensors, monitoring the fluid in the ear to help the brain maintain its sense of balance.
Why is the cilia important?
Important to kidney function , cilia monitor the flow of urine in this pair of organs. For nearly a decade, scientists have looked for a link between kidney disease and cilia. Although the exact mechanism isn’t clear, researchers believe that kidney cilia become damaged and unable to monitor urine flow, causing the kidneys to become scarred and diseased, leading to kidney failure.
How does the cilia help the female reproductive system?
In the female reproductive system, cilia help move the egg along the fallopian tube where it can be fertilized. Likewise, in the male reproductive system, cilia help power sperm. Each sperm cell has a type of cilium called a flagellum that propels it along the fallopian tube. That whipping tail action, coupled with the cilia on the cells lining the tube, help ensure that egg and sperm meet at precisely the right place at the right time.
What do the cilia do in the tongue?
Cilia on the cells in the tongue help the brain detect different tastes. These tongue cilia partner with ones in the nose, gathering information from food and relaying it to the brain to interpret specific tastes, such as sweet, salty, bitter, or bland.
What is the ability of the cilia to sweep and clean?
Cilia’s ability to sweep and clean is particularly evident in the heart. Researchers looking at mice hearts have found that cilia are especially dense in areas where blood vessels come together or curve. Scientists believe the cilia in these spaces help to keep those vessels open and free from the buildup of plaque, a disease called atherosclerosis.
How does cilia help with hearing?
Cilia in the ear can have a variety of functions. One type of cilia helps with hearing and detecting sound. They capture sound signals and then send them to your brain for processing, which is why cilia damage in the ear can lead to significant hearing loss. Cilia also help to clear your ear of wax buildup, moving the wax through the inner parts of the ear to keep your ear canal open. Finally, these little hairs can act as motion sensors, monitoring the fluid in the ear to help the brain maintain its sense of balance.
What does a cilia do to the brain?
Cilia in the eye’s retina help convert light into electrical signals that are then sent to the brain. The brain sorts through these light signals, packages them, and transforms them into the images we can see. Cilia damage in the eye can lead to vision loss.
Which direction do cilia move?
These cilia can move in a clockwise direction resulting in the movement of extraembryonic fluid through the nodal surface.
What is the process of cilia formation?
Cilia formation mechanism/ Ciliogenesis. The process of formation of cilia in the cell, often termed ciliogenesis, occurs in several stages. Biogenesis of a cilium is a highly complex, elaborate, and regulated process occurring with the help of many organelles, cellular mechanisms, and signaling pathways.
What is the space within the ciliary membrane formed of a watery matrix?
The space within the ciliary membrane formed of a watery matrix is the ciliary matrix. The matrix consists of embedded microtubules forming the axoneme of the cilium.
What are the two types of cilia?
Cilia are distinguished into two types; motile cilia and nonmotile cilia, based on the patterns of microtubules present in the axonemes of the cilia. The overall basic structure of both the cilia is the same, except the axoneme. Figure: Structure of Cilium. Image Source: LadyofHats.
What is the outer covering of the cilia?
The ciliary membrane is the outer covering of the cilia that surrounds the internal axoneme and core of the cilia. The membrane is continuous with the cell membrane but is different from the cell membrane in its overall composition. The membrane is about 9.5 nm thick with far fewer proteins than the cell membrane.
How are cilia and flagella different?
Cilia are different from flagella which are mostly longer and fewer in number on the cell. Cilia also differ from flagella in other aspects like composition, movement, and functions. Read Also: 19 Differences between cilia and flagella (cilia vs flagella) Image Source: LadyofHats. Created with BioRender.com.
How big is the cilia?
The axoneme of the cilia is about 0.2-10 µm in diameter, and the length ranges from a few microns to 1-2 mm.
What are cilia used for?
In higher organisms, cilia is often used to propel substances in a desired direction. Some cilia, however, do not function in movement but in sensing.
What Are Cilia and Flagella?
Both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells contain structures known as cilia and flagella. These extensions from the cell surface aid in cell movement. They also help to move substances around cells and direct the flow of substances along tracts. Cilia and flagella are formed from specialized groupings of microtubules called basal bodies. If the protrusions are short and numerous they are termed cilia. If they are longer and less numerous (usually only one or two) they are termed flagella.
Where Can Cilia and Flagella Be Found?
Both cilia and flagella are found in numerous types of cells. For instance, the sperm of many animals, algae, and even ferns have flagella. Prokaryotic organisms may also possess a single flagellum or more. A bacterium, for example, may have: one flagellum located at one end of the cell (montrichous), one or more flagella located at both ends of the cell (amphitrichous), several flagella at one end of the cell (lophotrichous), or flagella distributed all around the cell (peritrichous). Cilia can be found in areas such as the respiratory tract and female reproductive tract. In the respiratory tract, cilia helps to sweep mucus containing dust, germs, pollen, and other debris away from the lungs. In the female reproductive tract, cilia helps to sweep sperm in the direction of the uterus.
What are the protrusions of cilia and flagella called?
Cilia and flagella are formed from specialized groupings of microtubules called basal bodies. If the protrusions are short and numerous they are termed cilia. If they are longer and less numerous (usually only one or two) they are termed flagella.
What are the sacs of enzymes that digest cellular macromolecules?
Lysosomes: Lysosomes are sacs of enzymes that digest cellular macromolecules.
Where are flagella located?
A bacterium, for example, may have: one flagellum located at one end of the cell (montrichous), one or more flagella located at both ends of the cell (amphitrichous), several flagella at one end of the cell (lophotrichous), or flagella distributed all around the cell (peritrichous). Cilia can be found in areas such as the respiratory tract ...
Which protein is responsible for generating the force required for movement?
Movement is produced when the nine paired microtubule sets of the axoneme slide against one another causing cilia and flagella to bend. The motor protein dynein is responsible for generating the force required for movement. This type of organization is found in most eukaryotic cilia and flagella.