How are sugars transported through the leaves of a plant?
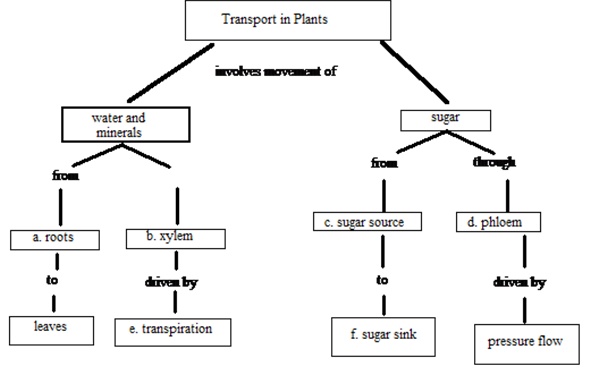
This is called transpiration; the movement of water out out the leaves pulling water from the roots all the way up through the plant. Sugars are conducted through plant tissue by the? Phloem transports sugars and nutrients. Xylem transports water. How are the sugars made in leaves transported in plants?
What is the movement of water through a plant called?
The movement of water in/out of a plant is called osmosis. What is growth movement of a plant toward light called? phototropism. Structure in which a plant makes sugar? The structures that makes sugar in leaves is called chloroplast. What is the movement of sugars through a plant called? Photosynthesis What is a movement to plant trees in Africa?
What is the role of sugar in photosynthesis?
Sugars, which are formed by the plant during photosynthesis, are an essential component of plant nutrition. Like water, sugar (usually in the form of sucrose, though glucose is the original photosynthetic product) is carried throughout the parts of the plant by the vascular system.
What plant did the Victorians use to make sugar from?
the Victorians used to make sugar from a plant called the sugar beet. What is a responsive movement of a plant that is not dependent on the direction of the stimulus is called? Nastic Movement
Which type of roots can be produced by the pericycle?
What is root pressure?
What happens if a plant doesn't regain turgor?
What increases the potential energy of the water inside by exerting pressure on the water?
What is water absorbed by?
About this website

Which type of roots can be produced by the pericycle?
The pericycle can become meristematic and produce lateral roots.
What is root pressure?
Root pressure, a pressure potential that develops in roots, could drive water up against the force of gravity.
What happens if a plant doesn't regain turgor?
wilt. If the cells do not regain turgor soon, they, and so the plant, will be at risk of dying.
What increases the potential energy of the water inside by exerting pressure on the water?
positive inside cells. It increases the potential energy of the water inside by exerting pressure on the water, making it more likely to move out of the cell.
What is water absorbed by?
absorbed by roots. Water moves from roots to leaves passively (no use of ATP).
What is the movement of a plant due to growth?
Autonomic movements of curvature due to growth- There occurs bending in plants due to unequal growth of the organs of the plants. It can be of the following types-. 1. Nutation – This type of movement is seen in growing tips of vine or tendril. In this, there are differences in the growth of different parts of the plant.
What is the movement of the whole plant body from one place to another?
1. Movements of Locomotion. It refers to the movement of the whole plant body from one place to another. Like that of male gametes of Bryophytes and Pteridophytes. Male gametes here are flagellated and move from one place to another, i.e. from the male reproductive part to the female gamete.
What is the movement of the upper surface of the organ of a plant called?
Like if movement occurs due to the fast growth of the upper surface of the organ of a plant, then this type of movement is called epinastic movement.
What is the movement of plants in response to touch?
Like bending the stem of a growing plant towards the light source. 3. Thigmotropic – It refers to the movement of plants in response to touch. This movement is directional, and the movement is called thigmotropic movement and, the phenomenon is called thigmotropism.
What is the term for the tropic movement of a plant?
2. Phototropic – It refers to the tropic movement which occurs in response to light. Here light acts as an external stimulus. These types of movements are called phototropic movements, and the phenomenon is called phototropism. Like bending the stem of a growing plant towards the light source.
What is the term for the movement of a chlamydomonas towards the warmer side?
Example- This can be seen in Chlamydomonas that will move towards the warmer side called positive thermotaxis while if the temperature is too high, then it will move away from the high temperature and is called negative thermotaxis. 2. Movements of Curvature.
What type of movement is due to the formation of pseudopodia?
Amoeboid Movements – This type of movement is due to the formation of pseudopodia. Like in Amoeba, amoeboid movement is seen to capture food. c. Cyclosis- It refers to the protoplasmic movement of a cell. It can be rotational movement or circular movement.
Which tissue is responsible for transporting sugars around the plant body?
Phloem, the vascular tissue responsible for transporting organic nutrients around the plant body, carries dissolved sugars from the leaves (their site of production) or storage sites to other parts of the plant that require nutrients.
How does water move sugars into the sieve?
Water follows the sugar molecules into the sieve elements through osmosis (since water passively diffuses into regions of higher solute concentration). This water creates turgor pressure in the sieve elements, which forces the sugars and fluids down the phloem tubes toward the sinks.
What are the nutrient rich regions that supply sugars for the rest of the plant called?
The nutrient-rich regions that supply sugars for the rest of the plant are called the sources . Sources include the leaves, where sugar is generated through photosynthesis. When they are high in supplies, the nutrient storage areas, such as the roots and stems, can also function as sources .
How are sugars transported through the phloem?
The mechanism by which sugars are transported through the phloem, from sources to sinks, is called pressure flow. At the sources (usually the leaves), sugar molecules are moved into the sieve elements (phloem cells) through active transport. Water follows the sugar molecules into the sieve elements through osmosis ...
Where do sugars travel in a phloem?
Within the phloem, sugars travel from areas of high osmotic concentration and high water pressure, called sources, to regions of low osmotic concentration and low water pressure, called sinks. (Osmotic concentration refers the concentration of solutes, or sugars in this case; where the concentration of solutes is highest, ...
What are the essential processes of plants?
Plants: Essential Processes. Sugars, which are formed by the plant during photosynthesis, are an essential component of plant nutrition. Like water, sugar (usually in the form of sucrose, though glucose is the original photosynthetic product) is carried throughout the parts of the plant by the vascular system.
Which type of roots can be produced by the pericycle?
The pericycle can become meristematic and produce lateral roots.
What is root pressure?
Root pressure, a pressure potential that develops in roots, could drive water up against the force of gravity.
What happens if a plant doesn't regain turgor?
wilt. If the cells do not regain turgor soon, they, and so the plant, will be at risk of dying.
What increases the potential energy of the water inside by exerting pressure on the water?
positive inside cells. It increases the potential energy of the water inside by exerting pressure on the water, making it more likely to move out of the cell.
What is water absorbed by?
absorbed by roots. Water moves from roots to leaves passively (no use of ATP).