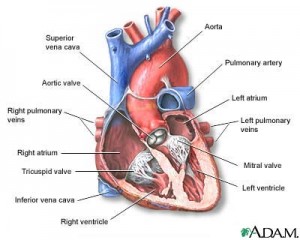
What part of the heart is pointed?
apexThe Heart Is Located in the Center of the Thoracic Cavity. The heart is located in the middle of the thoracic cavity, oriented obliquely, with the apex of the heart pointing down and to the left, as shown in Figures 5.4.
What is the pointed tip of the heart called?
the apexThe inferior tip of the heart, known as the apex, rests just superior to the diaphragm. The base of the heart is located along the body's midline with the apex pointing toward the left side.
What is the bottom pointed part of the heart called?
ventricles (VEN-trih-kuhls): The two chambers at the bottom of the heart are called the ventricles. The heart has a left ventricle and a right ventricle. Their job is to pump the blood to the body and lungs.
What is the pointed apex of the heart?
The apex (the most inferior, anterior, and lateral part as the heart lies in situ) is located on the midclavicular line, in the fifth intercostal space. It is formed by the left ventricle. The base of the heart, the posterior part, is formed by both atria, but mainly the left.
What are the 4 main parts of the heart?
Your heart is divided into four chambers. You have two chambers on the top (atrium, plural atria) and two on the bottom (ventricles), one on each side of the heart.
What are the 5 main arteries of the heart?
The major blood vessels connected to your heart are the aorta, the superior vena cava, the inferior vena cava, the pulmonary artery (which takes oxygen-poor blood from the heart to the lungs where it is oxygenated), the pulmonary veins (which bring oxygen-rich blood from the lungs to the heart), and the coronary ...
What are the 2 sides of the heart called?
Your heart is divided into two separate pumping systems, the right side and the left side.
How long can you have blocked arteries?
Sometimes there has been a complete blockage for many months or even years. However, only about 3% to 5% of these patients undergo a stent or bypass procedure, so there's a real need to help these untreated patients. Failure to diagnose and treat a CTO can lead to symptoms and impact your quality of life.
What are the 13 parts of the heart?
Anatomy of the heartLeft atrium and auricle. Left atrium. Left auricle.Right atrium and auricle. Right atrium. Right auricle.Interventricular septum and septal papillary muscles. Interventricular septum. ... Right ventricle and papillary muscles. Right ventricle. ... Left ventricle and papillary muscles. Left ventricle.
What is a pericardium?
The apex beat (lat. ictus cordis), also called the apical impulse, is the pulse felt at the point of maximum impulse (PMI), which is the point on the precordium farthest outwards (laterally) and downwards (inferiorly) from the sternum at which the cardiac impulse can be felt.Apex beat - Wikipediahttps://en.wikipedia.org › wiki › Apex_beathttps://en.wikipedia.org › wiki › Apex_beatSearch for: What does apex mean in heart?
What are the 12 parts of the heart?
The apex is the pointed tip of the heart. It is located on the lower portion of the heart (left ventricle).Apex - Medmovie.comhttps://medmovie.com › topichttps://medmovie.com › topicSearch for: What side is your apex?
What is the sternocostal surface of heart?
fifth intercostal space1. Apex Beat. The apex beat or apical impulse is the palpable cardiac impulse farthest away from the sternum and farthest down on the chest wall, usually caused by the LV and located near the midclavicular line (MCL) in the fifth intercostal space.Apex Beat - an overview | ScienceDirect Topicshttps://www.sciencedirect.com › medicine-and-dentistryhttps://www.sciencedirect.com › medicine-and-dentistrySearch for: Where is the apex beat of the heart located?
What is a fossa Ovalis?
The pericardium is a membrane, or sac, that surrounds your heart. It holds the heart in place and helps it work properly. Problems with the pericardium include: Pericarditis - an inflammation of the sac.
Where is the heart located in the human body?
In humans, the heart is situated between the two lungs and slightly to the left of center, behind the breastbone. It rests on the diaphragm, the mu...
What is the heart wall made up of?
The heart consists of several layers of a tough muscular wall, the myocardium. A thin layer of tissue, the pericardium, covers the outside, and ano...
What causes the heart to beat?
The pumping of the heart, or the heartbeat, is caused by alternating contractions and relaxations of the myocardium. These contractions are stimula...
What are heart sounds?
The rhythmic noises accompanying the heartbeat are called heart sounds. The two distinct sounds are heard, a low, slightly prolonged “lub” (first s...
What is the lining of the heart called?
The walls and lining of the pericardial cavity are a special membrane known as the pericardium. Pericardium is a type of serous membrane that produces serous fluid to lubricate the heart and prevent friction between the ever beating heart and its surrounding organs. Besides lubrication, the pericardium serves to hold the heart in position and maintain a hollow space for the heart to expand into when it is full. The pericardium has 2 layers—a visceral layer that covers the outside of the heart and a parietal layer that forms a sac around the outside of the pericardial cavity.
What is the heart base attached to?
On its superior end, the base of the heart is attached to the aorta,Continue Scrolling To Read More Below...
Why does the atria have a thin heart wall?
The atria of the heart have a very thin myocardium because they do not need to pump blood very far —only to the nearby ventricles. The ventricles, on the other hand, have a very thick myocardium to pump blood to the lungsor throughout the entire body. The right side of the heart has less myocardium in its walls than the left side because the left side has to pump blood through the entire body while the right side only has to pump to the lungs.
What are the two chambers of the heart?
At any given time the chambers of the heart may found in one of two states: 1 Systole. During systole, cardiac muscle tissue is contracting to push blood out of the chamber. 2 Diastole. During diastole, the cardiac muscle cells relax to allow the chamber to fill with blood. Blood pressure increases in the major arteries during ventricular systole and decreases during ventricular diastole. This leads to the 2 numbers associated with blood pressure—systolic blood pressure is the higher number and diastolic blood pressure is the lower number. For example, a blood pressure of 120/80 describes the systolic pressure (120) and the diastolic pressure (80).
What are the layers of the heart?
The heart wall is made of 3 layers: epicardium, myocardium and endocardium.
How does the heart work?
The heart functions by pumping blood both to the lungs and to the systems of the body. To prevent blood from flowing backwards or “regurgitating” back into the heart, a system of one-way valves are present in the heart. The heart valves can be broken down into two types: atrioventricular and semilunar valves.
Which layer of the heart contains the heart muscle tissue?
The myocardium is the muscular middle layer of the heart wall that contains the cardiac muscle tissue. Myocardium makes up the majority of the thickness and mass of the heart wall and is the part of the heart responsible for pumping blood. Below the myocardium is the thin endocardium layer. Endocardium.
What is the heart surrounded by?
The heart is situated within the chest cavity and surrounded by a fluid-filled sac called the pericardium. This amazing muscle produces electrical impulses that cause the heart to contract, pumping blood throughout the body. The heart and the circulatory system together form the cardiovascular system.
Which arteries carry oxygenated blood to the head and neck?
Carotid arteries: Supply oxygenated blood to the head and neck regions of the body. Common iliac arteries: Carry oxygenated blood from the abdominal aorta to the legs and feet. Coronary arteries: Carry oxygenated and nutrient-filled blood to the heart muscle. Pulmonary artery: Carries deoxygenated blood from the right ventricle to the lungs.
Which veins join to form the superior vena cava?
Brachiocephalic veins: Two large veins that join to form the superior vena cava. Common iliac veins: Veins that join to form the inferior vena cava. Pulmonary veins: Transport oxygenated blood from the lungs to the heart. Venae cavae: Transport de-oxygenated blood from various regions of the body to the heart.
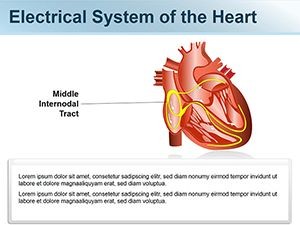
What is the section of nodal tissue that delays and relays cardiac impulses?
Atrioventricular Node: A section of nodal tissue that delays and relays cardiac impulses. Purkinje Fibers: Fiber branches that extend from the atrioventricular bundle. Sinoatrial Nod e: A section of nodal tissue that sets the rate of contraction for the heart.
What is the role of the heart in conduction?
Cardiac conduction is the rate at which the heart conducts electrical impulses. Heart nodes and nerve fibers play an important role in causing the heart to contract. Atrioventricular Bundle: A bundle of fibers that carry cardiac impulses. Atrioventricular Node: A section of nodal tissue that delays and relays cardiac impulses.
What is the blood vessel?
Blood vessels are intricate networks of hollow tubes that transport blood throughout the entire body. The following are some of the blood vessels associated with the heart:
How many layers are there in the heart wall?
The heart wall consists of three layers:
What are the parts of the heart called?
The parts of the human heart can be broken down into four chambers, muscular walls, vessels, and a conductive system. The two upper chambers are called the atria, with lower parts called ventricles. These all work together to make up the vital function of your heart.
Where is the heart located in the body?
It is between the lungs, approximately in the middle of the chest, right behind the sternum (breastbone) but slightly to the left.
What Are the Parts of the Human Heart?
Here is the full list of all the parts of the human heart and their essential functions:
What is the largest vein in the human body?
The Vena Cava: this is the largest vein in the human body ( vena is Latin for vein). Its essential function is to carry blood from all around the body all the way to the heart. There is a superior vena cava and an inferior vena cava.
Which artery is the largest in the human body?
The Aorta: this is the largest artery in the human body. Arteries are tubular branching elastic-walled muscle vessels that carry blood all the way from the heart through the body. The main function of the aorta is to take oxygenated blood all the way from the left ventricle to the rest of the body.
Which vessel is responsible for carrying blood away from the heart?
There is a right coronary vessel that goes into the right marginal artery, supplying blood to the right atrium and the right ventricle. The Arteries: the arteries are tasked with carrying blood away from the heart. These blood vessels are muscular tubes. The aorta is the largest artery.
Which vessel supplies the heart muscle with the necessary supply of blood?
The Right Ventricle: The right ventricle is tasked with pumping deoxygenated blood into the pulmonary artery. The Coronary Vessels: these vessels supply the myocardium (the heart muscle) with the necessary supply of blood. There is a main left coronary that goes into the circumflex artery, supplying blood to the left atrium.
Where is the heart located in the human body?
In humans it is situated between the two lungs and slightly to the left of centre, behind the breastbone; it rests on the diaphragm, the muscular partition between the chest and the abdominal cavity.
What is the heart in a fish?
In fishes the heart is a folded tube, with three or four enlarged areas ...
What are the two sounds that occur at the beginning of ventricular contraction?
The two distinct sounds are heard, a low, slightly prolonged “lub” (first sound) occurring at the beginning of ventricular contraction or systole and a sharper, higher-pitched “dup” (second sound), caused by the closure of aortic and pulmonary valves at the end of systole. In humans and other mammals and in birds, ...
What are the two sounds that accompany the heartbeat?
The rhythmic noises accompanying the heartbeat are called heart sounds . The two distinct sounds are heard, a low, slightly prolonged “lub” (first sound) occurring at the beginning of ventricular contraction or systole and a sharper, higher-pitched “dup” (second sound), caused by the closure of aortic and pulmonary valves at the end of systole.
What is the heart? What function does it serve?
heart, organ that serves as a pump to circulate the blood. It may be a straight tube, as in spiders and annelid worms, or a somewhat more elaborate structure with one or more receiving chambers (atria) and a main pumping chamber (ventricle), as in mollusks. In fishes the heart is a folded tube, with three or four enlarged areas that correspond to the chambers in the mammalian heart. In animals with lungs —amphibians, reptiles, birds, and mammals—the heart shows various stages of evolution from a single to a double pump that circulates blood (1) to the lungs and (2) to the body as a whole.
What does it mean when your heart murmurs?
Murmurs may indicate that blood is leaking through an imperfectly closed valve and may signal the presence of a serious heart problem.
Where is the greatest pressure in the body?
Blood pressure is greatest in the left ventricle and in the aorta and its arterial branches. Pressure is reduced in the capillaries (vessels of minute diameter) and is reduced further in the veins returning blood to the right atrium.
Where is the heart located?
The heart is located in the chest cavity just posterior to the breastbone, between the lungs, and superior to the diaphragm. It is surrounded by a fluid-filled sac called the pericardium, which serves to protect this vital organ.
What is the heart?
The heart is an extraordinary organ. It is about the size of a clenched fist, weighs about 10.5 ounces and is shaped like a cone. Along with the circulatory system, the heart works to supply blood and oxygen to all parts of the body. The heart is located in the chest cavity just posterior to the breastbone, between the lungs, ...
What is the epicardium made of?
The epicardium is composed primarily of loose connective tissue, including elastic fibers and adipose tissue. The epicardium functions to protect the inner heart layers and also assists in the production of pericardial fluid. This fluid fills the pericardial cavity and helps to reduce friction between pericardial membranes.
Which layer of the heart is covered by the heart valves?
This layer lines the inner heart chambers, covers heart valves, and is continuous with the endothelium of large blood vessels. The endocardium of heart atria consists of smooth muscle, as well as elastic fibers. An infection of the endocardium can lead to a condition known as endocarditis.
Which layer of the heart is the thickest?
The myocardium is the thickest layer of the heart wall, with its thickness varying in different parts of the heart. The myocardium of the left ventricle is the thickest, as this ventricle is responsible for generating the power needed to pump oxygenated blood from the heart to the rest of the body.
What is the outer protective layer of the heart?
Epicardium: the outer protective layer of the heart.
What are the layers of the heart wall?
It is the cardiac muscle that enables the heart to contract and allows for the synchronization of the heartbeat. The heart wall is divided into three layers: epicardium, myocardium, and endocardium.
What is the Latin name for the heart?
It is confined within the pericardium. It pumps blood to disparate parts of the body to meet their nutritive requirements. The Greek name for the heart is cardia from which we have the attributive cardia. The Latin name for the heart is cor from which we have the adjective coronary.
What is the base of the heart called?
The base of the heart is also called the posterior surface. it is formed mainly by the left atrium and by a small part of the right atrium.
What are the two types of valves in the heart?
There are two pairs of valves in the heart, a pair of atrioventricular valves and a pair of semilunar valves.
How is the first heart sound produced?
The first heart sound is originated by the cessation of the atrioventricular valves. The second heart sound is produced by closure of the semilunar valves (Figs 18.19a and b).
Where are the atria located?
The atria (Latin chamber) lie above and behind the ventricles. On the surface of the heart, they are separated from the ventricles by an atrioventricular groove. The ventricles are separated from each other by an interventricular groove, which is subdivided into anterior and posterior parts. The heart has.
What is the left surface of the heart?
The left surface is formed mostly by the left ventricle, and the upper end by the left ventricle, and at the upper end by the left auricle. In its upper part, the surface is crossed by the coronary sulcus. It is related to the left phrenic nerve, the left pericardiacophrenic vessels, and the pericardium.
How many chambers does the heart have?
In the title ‘ Anatomy of the heart ’ let’s learn about the external features of the heart. The human heart has four chambers. These are the right and left atria and the right and left ventricles.
Where is the aortic valve located?
The aortic valve and pulmonic valve are located between the ventricles and the major blood vessels leaving the heart.
How does blood flow from the right atrium to the left ventricle?
1. Open tricuspid and mitral valves. Blood flows from the right atrium into the right ventricle through the open tricuspid valve, and from the left atrium into the left ventricle through the open mitral valve. 2. Closed tricuspid and mitral valves.
What valves close when the right ventricle is full?
Closed tricuspid and mitral valves. When the right ventricle is full, the tricuspid valve closes and keeps blood from flowing backward into the right atrium when the ventricle contracts (squeezes). When the left ventricle is full, the mitral valve closes and keeps blood from flowing backward into the left atrium when the ventricle contracts.
How many valves are there in the heart?
The heart has four valves - one for each chamber of the heart. The valves keep blood moving through the heart in the right direction. The mitral valve and tricuspid valve are located between the atria (upper heart chambers) and the ventricles (lower heart chambers). The aortic valve and pulmonic valve are located between the ventricles and ...
What is the tissue that supports the leaflets of the mitral valve?
The leaflets are attached to and supported by a ring of tough, fibrous tissue called the annulus. The annulus helps to maintain the proper shape of the valve. The leaflets of the mitral and tricuspid valves are also supported by: Chordae tendineae: tough, fibrous strings. These are similar to the strings supporting a parachute.
Where is blood pumped out of the lungs?
Blood is pumped out of the right ventricle through the pulmonic valve into the pulmonary artery to the lungs. As the left ventricle begins to contract, the aortic valve is forced open. Blood is pumped out of the left ventricle through the aortic valve into the aorta.
What happens when the right ventricle relaxes?
When the right ventricle finishes contracting and starts to relax, the pulmonic valve snaps shut. This keeps blood from flowing back into the right ventricle. When the left ventricle finishes contracting and begins to relax, the aortic valve snaps shut. This keeps blood from flowing back into the left ventricle.
Which side of the heart is used for auscultation?
The bell is the smaller, concave side that allows for auscultation of lower-pitched sounds like some heart murmurs. When performing a cardiac exam, auscultation should be performed with the diaphragm and then repeated with the bell.
What is the apex of the heart?
The apex is where the tricuspid and mitral S1 sound is loudest upon auscultation. The apex region will also be where S3 and S4 sounds (extra heart sounds not usually noted in normal assessments) and mitral stenosis murmurs may be auscultated, if present.
Where is the aortic point located?
The aortic point is located right of the sternal border in the second intercostal space. The pulmonic point is to the left of the sternal border in the second intercostal space. The sound that emits from the aortic and pulmonic points is the S2 “dub” of the typical “lub-dub” heartbeat.
Where are the aortic, pulmonic, tricuspid, and mitral valves located?
The locations of auscultation center around the heart valves. The aortic, pulmonic, tricuspid, and mitral valves are four of the five points of auscultation. The fifth is Erb’s point, located left of the sternal border in the third intercostal space. The aortic point is located right of the sternal border in the second intercostal space. The pulmonic point is to the left of the sternal border in the second intercostal space. The sound that emits from the aortic and pulmonic points is the S2 “dub” of the typical “lub-dub” heartbeat. The S1 and S2 sounds are present in normal heartbeat patterns.
How many points should be used during a heart assessment?
It is important to perform a comprehensive assessment of the heart, listening to all five points and keeping in mind which side of the chestpiece should be utilized during listening, as well as the patient’s position during auscultation.
What side should a patient be positioned on during an auscultation assessment?
Then, patients should be positioned laterally onto their left side so the provider can listen with the bell of the stethoscope for any S3, S4 (extra heart sounds) and/or mitral stenosis murmurs in the apex region. Aortic and pulmonic murmurs are more easily identified with the diaphragm of the stethoscope when patients are in a sitting position, leaned forward, and asked to exhale.