What exercises strengthen the bladder?
To get started:
- Find the right muscles. To identify your pelvic floor muscles, stop urination in midstream. ...
- Perfect your technique. To do Kegels, imagine you are sitting on a marble and tighten your pelvic muscles as if you're lifting the marble. ...
- Maintain your focus. For best results, focus on tightening only your pelvic floor muscles. ...
- Repeat three times a day. ...
How to strengthen your bladder muscles?
- Use the bathroom often and when needed. ...
- Be in a relaxed position while urinating. ...
- Take enough time to fully empty the bladder when urinating. ...
- Wipe from front to back after using the toilet. ...
- Urinate after sex. ...
- Do pelvic floor muscle exercises. ...
- Wear cotton underwear and loose-fitting clothes. ...
- Exercise regularly. ...
- Keep a healthy weight. ...
- Watch what you eat. ...
How to strengthen your bladder and urinate less often?
Step-by-step bladder-training technique
- Keep track. For a day or two, keep track of the times you urinate or leak urine during the day.
- Calculate. On average, how many hours do you wait between urinations during the day?
- Choose an interval. Based on your typical interval between urinations, select a starting interval for training that is 15 minutes longer. ...
- Hold back. ...
- Increase your interval. ...
What causes weak bladder muscles?
- age-related loss of bladder muscle strength
- overdistention—a bladder that has been stretched such that the muscles are damaged
- pregnancy and childbirth
- trauma
How many muscles does the bladder have?
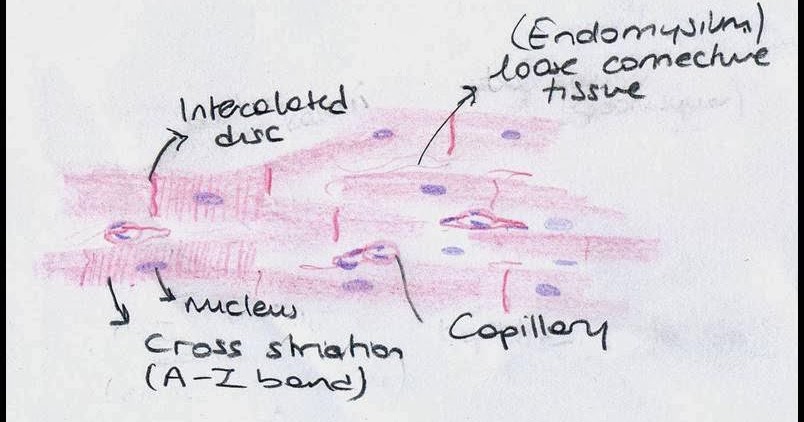
The bladder wall contains two smooth muscle layers: (1) an outer layer of longitudinal to obliquely arranged muscle fibers and (2) an inner layer of transversely or circularly arranged muscle fibers.
What muscles control the bladder?
The bladder sphincter is made up of two muscles, the internal and external sphincter muscles. The internal sphincter muscle is located at the opening of the bladder to the urethra. It is a smooth, involuntary muscle. Because of its location, it is also primary muscle prohibiting the release of urine.
What muscle prevents urine from leaking?
The sphincter is a muscle around the opening of the bladder. It squeezes to prevent urine from leaking into the urethra. This is the tube that urine passes through from your bladder to the outside. The bladder wall muscle relaxes so the bladder can expand and hold urine.
Where is the muscle that controls urine flow?
Controlling the outflow of urine are two valves, or sphincters, located in the bladder neck and earliest portion of the urethra. The bladder neck sphincter is under involuntary (autonomic) control while the urethral sphincter has both voluntary and involuntary components.
Can Tight muscles cause bladder problems?
Tight muscles can cause too much tension in the pelvic floor, which increases the pressure on the bladder. This increase in pressure can then lead to urge incontinence.
What nerve controls bladder?
Pelvic parasympathetic nerves: arise at the sacral level of the spinal cord, excite the bladder, and relax the urethra. Lumbar sympathetic nerves: inhibit the bladder body and excite the bladder base and urethra.
What part of the brain controls bladder and bowel?
Brainstem. The brainstem is located at the base of the skull. Within the brainstem is the pons, a specialized area that serves as a major relay center between the brain and the bladder (see the image below). The pons is responsible for coordinating the activities of the urinary sphincters and the bladder.
What muscle is used to control urine flow?
You use ring-shaped muscles called sphincter muscles to control urine flow. An outer layer of smooth muscle called the detrusor muscle surrounds the bladder. When your bladder is full, the muscles in the bladder wall can be tightened to squeeze out the urine. As you urinate, the bladder shrinks in size.
What is the cancer on the inside of the bladder called?
Superficial bladder cancer affects only the inside lining of the bladder. This is the transitional epithelium. Cancer here is called transitional cell carcinoma (TCC) or urothelial carcinoma. As the cancer grows, it can become invasive bladder cancer that goes into deeper layers of the bladder wall. Over time, it can grow into the fatty connective tissue.
What is the bladder wall made of?
The bladder wall is made of many layers, including: Urothelium or transitional epithelium. This is the layer of cells that lines the inside of the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra. Cells in this layer are called urothelial cells or transitional cells. Lamina propria.
What is the name of the tube that the kidneys use to make urine?
This is the liquid waste that’s made by the kidneys. Urine flows away from each kidney through a tube called a ureter. The ureters carry the urine into your bladder. The urine stays in your bladder until you let it pass out of your body through another tube called the urethra.
What are the functions of the bladder?
The bladder is an organ of the urinary system. It plays two main roles: 1 Temporary storage of urine – the bladder is a hollow organ with distensible walls. It has a folded internal lining (known as rugae), which allows it to accommodate up to 400-600ml of urine in healthy adults. 2 Assists in the expulsion of urine – the musculature of the bladder contracts during micturition, with concomitant relaxation of the sphincters.
What is the role of the bladder in the urinary system?
6 Clinical Relevance: Urine Retention. The bladder is an organ of the urinary system. It plays two main roles: Temporary storage of urine – the bladder is a hollow organ with distensible walls. It has a folded internal lining (known as rugae), which allows it to accommodate up to 400-600ml of urine in healthy adults.
Why is the detrusor muscle hypertrophic?
The fibers of the detrusor muscle often become hypertrophic (presenting as prominent trabeculae) in order to compensate for increased workload of the bladder emptying. This is very common in conditions that obstruct the urine outflow such as benign prostatic hyperplasia.
How much urine can a bladder hold?
It has a folded internal lining (known as rugae), which allows it to accommodate up to 400-600ml of urine in healthy adults.
What does the bladder look like when empty?
The appearance of the bladder varies depending on the amount of urine stored. When full, it exhibits an oval shape , and when empty it is flattened by the overlying bowel.
Why is my bladder emptying?
In males, the most common cause is obstruction due to prostate enlargement (BPH). Other causes include obstruction by a stone or large blood clot.
Which branch of the iliac artery supplies the arteries?
Arterial supply is via the superior vesical branch of the internal iliac artery. In males, this is supplemented by the inferior vesical artery, and in females by the vaginal arteries. In both sexes, the obturator and inferior gluteal arteries may also contribute small branches.
What is the bladder anatomy page?
WebMD's Bladder Anatomy Page provides a detailed image and definition of the bladder and describes its function, location in the body, and conditions that affect the bladder.
Where is the urinary bladder located?
All rights reserved. Prev. Next. The urinary bladder is a muscular sac in the pelvis, just above and behind the pubic bone. When empty, the bladder is about the size and shape of a pear. Urine is made in the kidneys and travels down two tubes called ureters to the bladder. The bladder stores urine, allowing urination to be infrequent and controlled.
Why does urine not exit the bladder?
Urinary retention: Urine does not exit the bladder normally due to a blockage or suppressed bladder muscle activity. The bladder may swell to hold more than a quart of urine. Cystocele: Weakened pelvic muscles (usually from childbirth) allow the bladder to press on the vagina. Problems with urination can result.
How to treat bladder cancer?
Bladder Treatments. Cystoscopy: A narrow tube is passed through the urethra into the bladder. A light, camera, and tools allow a doctor to diagnose and treat bladder problems. Surgery: Bladder cancer generally requires surgery. Some cases of urinary incontinence and cystocele may also be treated with surgery.
What causes pain in the bladder?
Cystitis: Inflammation or infection of the bladder causing acute or chronic pain, discomfort, or urinary frequency or hesitancy. Urinary stones: Stones (calculi) may form in the kidney and travel down to the bladder. If kidney stones block urine flow to or from the bladder, they can cause severe pain.
How many ml of urine does the bladder hold?
The bladder is lined by layers of muscle tissue that stretch to hold urine. The normal capacity of the bladder is 400-600 mL. During urination, the bladder muscles squeeze, and two sphincters (valves) open to allow urine to flow out. Urine exits the bladder into the urethra, which carries urine out of the body.
What is the first part of a urine test?
The first part of the test is a dipstick. If this is abnormal the urine should be looked at under a microscope. Cystoscopy: A narrow tube is passed through the urethra and into the bladder. A light, camera, and tools allow a doctor to diagnose and treat bladder problems.
What is the sphincter of the bladder?
The bladder sphincter is made up of two muscles, the internal and external sphincter muscles. The internal sphincter muscle is located at the opening of the bladder to the urethra. It is a smooth, involuntary muscle. Because of its location, it is also primary muscle prohibiting the release of urine. The external sphincter muscle surrounds the area ...
What muscle controls the flow of urine?
The external sphincter muscle surrounds the area of the urethra outside the bladder. It is the secondary muscle in control of urine flow. It is made of skeletal muscle and is a voluntary muscle.
What is urge incontinence?
One form of urge incontinence occurs when the urethra can’t hold back urine in the bladder and the bladder sphincters relax uncontrollably.
How do both muscles function?
Both muscles function in a similar fashion. When one relaxes the voluntary muscle, the involuntary muscle relaxes as well. When these muscles are relaxed, they open up allowing for urine to flow out of the bladder through the urethra and out the body. When these muscles are contracted, they keep urine in the bladder.
What is the bladder sphincter made of?
The bladder sphincter is made up of two muscles that control the release of urine from the bladder through the urethra. If the bladder were a reservoir, then the bladder sphincter would be the dam that holds back water and controls when it is released. The bladder sphincter is made up of two muscles, the internal and external sphincter muscles.
Which muscle is responsible for the release of urine?
Because of its location, it is also primary muscle prohibiting the release of urine. The external sphincter muscle surrounds the area of the urethra outside the bladder. It is the secondary muscle in control of urine flow. It is made of skeletal muscle and is a voluntary muscle. Both muscles function in a similar fashion.
Where is the internal sphincter located?
The internal sphincter muscle is located at the opening of the bladder to the urethra. It is a smooth, involuntary muscle. Because of its location, it is also primary muscle prohibiting the release of urine.
What muscles are used to keep urine in the bladder?
The urinary tract includes two sets of muscles that work together as a sphincter, closing off the urethra to keep urine in the bladder between your trips to the bathroom. The internal sphincter muscles of the bladder neck and urethra stay closed until your brain sends signals to urinate. The external sphincter muscles surround ...
What organs carry urine to the bladder?
Ureters. Thin tubes of muscle that connect your kidneys to your bladder and carry urine to the bladder. Bladder. A hollow, muscular, balloon-shaped organ that expands as it fills with urine. The bladder sits in your pelvis between your hip bones. A normal bladder acts like a reservoir.
What is the urinary tract?
The urinary tract is the body’s drainage system for removing urine, which is made up of wastes and extra fluid. For normal urination to occur, all body parts in the urinary tract need to work together, and in the correct order.
How does urination occur?
Then it signals the muscular bladder wall to tighten, squeezing urine through the urethra and out of your bladder.
How can you keep your urinary tract healthy?
You can help keep your urinary tract healthy by following some basic tips.
How to promote bowel movement and bladder health?
You can keep your urinary tract healthy by sticking to an eating plan that includes lean proteins, whole grains, fiber -rich breads, nuts, colorful berries, fruits, and vegetables to promote regular bowel movements. living a healthy lifestyle.
How many cups of urine does a normal bladder hold?
A normal bladder acts like a reservoir. It can hold 1.5 to 2 cups of urine. Although you do not control how your kidneys function, you can control when to empty your bladder. Bladder emptying is known as urination. Urethra. A tube located at the bottom of the bladder that allows urine to exit the body during urination.
The Relationship Between Bladder Muscles and OAB
Overactive bladder is a common issue for adults, especially as they age. According to the Urology Care Foundation, about 30% of men and 40% of women have symptoms of an overactive bladder.
Relaxation Techniques and Exercises for OAB
Various treatment options are available to treat overactive bladder. For example, in addition to medication, lifestyle changes may help reduce the symptoms. Exercises that relax and strengthen the bladder are also useful.
Muscles of the Bladder
Different muscles make up the bladder and surrounding area, including the following.
What Happens to the Bladder Muscles During an OAB Flare-Up?
During a flare-up of overactive bladder, the detrusor muscles may contract and squeeze erratically even if the bladder is not full. The contraction is involuntary and produces the sudden urge to go to the bathroom.
Resources
Overactive Bladder Living How Can Kegel Exercises Help Overactive Bladder?