
What is a nephron, and what does it do?
A nephron is the structural and functional unit of the kidney. It regulates the concentration of water and minerals such as sodium by filtering the blood and reabsorbing the important nutrients. How does a nephron filter blood? A nephron consists of a filter called glomerulus and a tubule.
What are the parts of the nephron and their functions?
What are the functions of the different parts of the nephron?
- Bowman's Capsule. epithelial layer surrounding golmerulus.
- Glomerulus. ball of capillary involved in filtration of blood and keeps large particles ( blood and proteins) out of filtrate; creates urine.
- Proximal Convoluted Tubule.
- Loop of Henle.
- Distal Convoluted Tubule.
- Collecting Duct.
What are the essential functions of nephron?
nephron, functional unit of the kidney, the structure that actually produces urine in the process of removing waste and excess substances from the blood. There are about 1,000,000 nephrons in each human kidney. The most primitive nephrons are found in the kidneys ( pronephros) of primitive fish, amphibian larvae, and embryos of more advanced vertebrates.
What is the nephron also known as?
This component performs other functions under normal conditions in dialysis care. What Is Another Name Of Nephron? One side of the uriniferous tubule is also known as the nephron. There is a special kind of tubules in the kidney called tube nephron or uriniferous tubules.
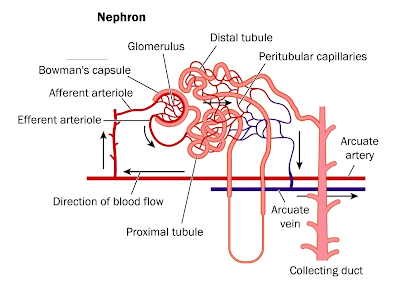
What is a nephron short answer?
nephron, functional unit of the kidney, the structure that actually produces urine in the process of removing waste and excess substances from the blood. There are about 1,000,000 nephrons in each human kidney.
What are the 3 functions of the nephron?
7.12 Filtration, reabsorption, and secretion The principal task of the nephrons is to balance the plasma to homeostatic set points and excrete potential toxins in the urine. They do this by accomplishing three key functions—filtration, reabsorption, and secretion.
What are the 4 functions of the nephron?
The nephron uses four mechanisms to convert blood into urine: filtration, reabsorption, secretion, and excretion. These apply to numerous substances.
Why is nephron so important?
Nephrons eliminate wastes from the body, regulate blood volume and pressure, control levels of electrolytes and metabolites, and regulate blood pH. Its functions are vital to life and are regulated by the endocrine system by hormones such as antidiuretic hormone, aldosterone, and parathyroid hormone.
What is structure of nephron?
Nephron Structure A nephron is a microscopic structural and functional unit of the kidney. It is made of a renal corpuscle and a renal tubule. The renal corpuscle consists of a network of capillaries called glomerulus and Bowman's capsule. The corpuscle and tubule both are connected. They are made of epithelial cells.
What are the two main parts of a nephron?
The Renal Corpuscle This structure is located in the renal cortex. You should also be aware that the nephron is composed of two main parts: the renal tubule and the renal corpuscle.
How many nephrons are in a kidney?
one millionEach kidney contains about one million tiny units called nephrons. Each nephron is made up of a very small filter, called a glomerulus, which is attached to a tubule. As blood passes through the nephron, fluid and waste products are filtered out.
What are the five main parts of the nephron?
Urinary: Nephronproximal convoluted tubule (found in the renal cortex)loop of Henle (mostly in the medulla)distal convoluted tubule (found in the renal cortex)collecting tubule (in the medulla)collecting duct (in the medulla)
What are the 3 parts of the nephron?
The glomerulus is the site in the nephron where fluid and solutes are filtered out of the blood to form a glomerular filtrate. The proximal and distal tubules, the loop of Henle, and the collecting ducts are sites for the reabsorption of water and ions.
What color is urine when your kidneys are failing?
When kidneys are failing, the increased concentration and accumulation of substances in urine lead to a darker color which may be brown, red or purple. The color change is due to abnormal protein or sugar, high levels of red and white blood cells, and high numbers of tube-shaped particles called cellular casts.
What causes kidney failure?
What causes kidney failure? High blood pressure and diabetes are the two most common causes of kidney failure. They can also become damaged from physical injury, diseases, or other disorders.
Can you live with one kidney?
Most people live normal, healthy lives with one kidney. However, it's important to stay as healthy as possible, and protect the only kidney you have.
What are the 5 main functions of a nephron?
Functions of Nephron The primary function of nephron is removing all waste products including the solid wastes, and other excess water from the blood, converting blood into the urine, reabsorption, secretion, and excretion of numerous substances.
What is the function of the nephron quizlet?
They are responsible for removal of waste products and reabsorption of nutrients. Nephrons that have longer loops of Henle that extend deep into the medulla. Their primary function is concentration of the urine.
What 3 processes occur to the nephron can regulate the concentration of water?
Urine formation occurs during three processes: Filtration. Reabsorption. Secretion.
What is the main function of a nephron?
A nephron is the structural and functional unit of the kidney. It regulates the concentration of water and minerals such as sodium by filtering the...
How does a nephron filter blood?
A nephron consists of a filter called glomerulus and a tubule. The glomerulus filters the fluid and waste products holding back the blood cells and...
What are the two main parts of a nephron structure?
The two main parts of a nephron structure include: Renal tubule Renal corpuscle
Where are the nephrons located?
The nephrons are located in the cortex and medulla of the kidney. The cortex contains the renal corpuscle, distal convoluted tubule and proximal co...
What is the cup-shaped structure surrounding the renal corpuscle called?
The cup-shaped structure surrounding the renal corpuscle is known as the Bowman’s capsule or glomerulus that helps in blood filtration.
What is Nephron?
A nephron is the basic structural and functional unit of the kidney. They are the microscopic structure composed of a renal corpuscle and a renal tubule. The word nephron is derived from the Greek word – nephros, meaning kidney. There are about millions of nephrons in each human kidney.
What is the structure of the nephron?
Structure of Nephron. The mammalian nephron is a long tube-like structure, its length varying from 35–55 mm long. At one end, the tube is closed, folded and expanded, into a double-walled, a cuplike structure called the Bowman’s capsule or renal corpuscular capsule, which encloses a cluster of microscopic blood vessels called the glomerulus.
What is the name of the tubule that is located in the glomerulus?
Renal Tubule. The renal tubule is a long and convoluted structure that emerges from the glomerulus and can be divided into three parts based on function. The first part is called the proximal convoluted tubule (PCT) due to its proximity to the glomerulus; it stays in the renal cortex.
What is the structure of the glomerulus called?
The capillaries of the glomerulus are enclosed by a cup-like structure called Bowman’s capsule. This structure extends to form highly coiled tubules called PCT. PCT continues to form the loop of Henle which ascends to DCT, which in turn opens into the collecting duct.
Where does reabsorption take place?
Maximum reabsorption takes place in PCT of the nephron.PCT is the region of renal tubule where reabsorption of essential substances like glucose, proteins, amino acids, a major portion of electrolytes and water takes place. The surface area for reabsorption is facilitated by the lining of the simple cuboidal epithelium in them. Reabsorption takes place at the expense of energy, i.e., the process is active.PCT selectively secretes ions such as hydrogen, ammonia, and potassium into the filtrate and absorbs HCO 3– from it. Thus, PCT maintains the electrolyte and acid-base balance of the body fluids.
Where does ultrafiltrate go in the body?
The obtained ultrafiltrate is urine, which travels down via the collecting duct to the bladder, where it will be stored and released through the urethra.
Which segment of the renal system empties its contents into collecting ducts?
But reabsorption is limited in this segment. The DCT, which is the last part of the nephron, connects and empties its contents into collecting ducts that line the medullary pyramids. The collecting ducts amass contents from multiple nephrons and fuse together as they enter the papillae of the renal medulla.
What is the nephron in a britannica?
Nephron, functional unit of the kidney, the structure that actually produces urine in the process of removing waste ...
Where are nephrons found?
The nephrons found in the kidneys ( mesonephros) of amphibians and most fish, and in the late embryonic development of more advanced vertebrates, are only slightly more advanced in structure. The most advanced nephrons occur in the adult kidneys, or metanephros, of land vertebrates, such as reptiles, birds, and mammals.
What is the name of the capsule that encloses a cluster of microscopic blood vessels called?
This structure, called the renal corpus cular capsule, or Bowman’s capsule, encloses a cluster of microscopic blood vessels—capillaries—called the glomerulus. The capsule and glomerulus together constitute the renal corpuscle.
How long is a nephron?
Each nephron is a long tubule (or extremely... Each nephron in the mammalian kidney is a long tubule, or extremely fine tube, about 30–55 mm (1.2–2.2 inches) long. At one end this tube is closed, expanded, and folded into a double-walled cuplike structure.
How many nephrons are there in the human body?
There are about 1,000,000 nephrons in each human kidney. The most primitive nephrons are found in the kidneys ( pronephros) of primitive fish, amphibian larvae, and embryos of more advanced vertebrates.
Which organ contains blood vessels and a special tubule?
nephron of the kidney. Each nephron of the kidney contains blood vessels and a special tubule. As the filtrate flows through the tubule of the nephron, it becomes increasingly concentrated into urine. Waste products are transferred from the blood into the filtrate while nutrients are absorbed from the filtrate into the blood.
What is the nephron?
Anatomical terminology. The nephron is the minute or microscopic structural and functional unit of the kidney. It is composed of a renal corpuscle and a renal tubule. The renal corpuscle consists of a tuft of capillaries called a glomerulus and an encompassing Bowman's capsule. The renal tubule extends from the capsule.
What is the function of the nephron?
The nephron is the functional unit of the kidney. This means that each separate nephron is where the main work of the kidney is performed. A nephron is made of two parts: a renal corpuscle, which is the initial filtering component, and. a renal tubule that processes and carries away the filtered fluid.
What percentage of juxtamedullary nephrons are in the human kidney?
The juxtamedullary nephrons comprise only about 15% of the nephrons in the human kidney. : 24 However, it is this type of nephron which is most often depicted in illustrations of nephrons.
What is the tubule of the renal system?
The renal tubule is the portion of the nephron containing the tubular fluid filtered through the glomerulus. After passing through the renal tubule, the filtrate continues to the collecting duct system .
What are the four mechanisms used to make a blood filtration system?
The four mechanisms used to create and process the filtrate (the result of which is to convert blood to urine) are filtration, reabsorption , secretion and excretion. Filtration or ultrafiltration occurs in the glomerulus and is largely passive: it is dependent on the intracapillary blood pressure. About one-fifth of the plasma is filtered as the blood passes through the glomerular capillaries; four-fifths continues into the peritubular capillaries. Normally the only components of the blood that are not filtered into Bowman's capsule are blood proteins, red blood cells, white blood cells and platelets. Over 150 liters of fluid enter the glomeruli of an adult every day: 99% of the water in that filtrate is reabsorbed. Reabsorption occurs in the renal tubules and is either passive, due to diffusion, or active, due to pumping against a concentration gradient. Secretion also occurs in the tubules and collecting duct and is active. Substances reabsorbed include: water, sodium chloride, glucose, amino acids, lactate, magnesium, calcium phosphate, uric acid, and bicarbonate. Substances secreted include urea, creatinine, potassium, hydrogen, and uric acid. Some of the hormones which signal the tubules to alter the reabsorption or secretion rate, and thereby maintain homeostasis, include (along with the substance affected) antidiuretic hormone (water), aldosterone (sodium, potassium), parathyroid hormone (calcium, phosphate), atrial natriuretic peptide (sodium) and brain natriuretic peptide (sodium). A countercurrent system in the renal medulla provides the mechanism for generating a hypertonic interstitium, which allows the recovery of solute-free water from within the nephron and returning it to the venous vasculature when appropriate.
What are the parts of the nephron?
A nephron is made of two parts: 1 a renal corpuscle, which is the initial filtering component, and 2 a renal tubule that processes and carries away the filtered fluid.
What is the proximal tubule?
The proximal tubule as a part of the nephron can be divided into an initial convoluted portion and a following straight (descending) portion. Fluid in the filtrate entering the proximal convoluted tubule is reabsorbed into the peritubular capillaries, including more than half of the filtered salt and water and all filtered organic solutes (primarily glucose and amino acids ).

Overview
The nephron is the minute or microscopic structural and functional unit of the kidney. It is composed of a renal corpuscle and a renal tubule. The renal corpuscle consists of a tuft of capillaries called a glomerulus and a cup-shaped structure called Bowman's capsule. The renal tubule extends from the capsule. The capsule and tubule are connected and are composed of epithelial cells with a lumen. A healthy adult has 1 to 1.5 million nephrons in each kidney. Blood i…
Structure
The nephron is the functional unit of the kidney. This means that each separate nephron is where the main work of the kidney is performed.
A nephron is made of two parts:
• a renal corpuscle, which is the initial filtering component, and
• a renal tubule that processes and carries away the filtered fluid.
Functions
The nephron uses four mechanisms to convert blood into urine: filtration, reabsorption, secretion, and excretion. These apply to numerous substances. The structure and function of the epithelial cells lining the lumen change during the course of the nephron, and have segments named by their location and which reflects their different functions.
The proximal tubule as a part of the nephron can be divided into an initial convoluted portion an…
Clinical significance
Patients in early stages of chronic kidney disease have show an approximate 50% reduction in number of nephrons, comparable to the nephron loss that occurs with aging (between ages 18-29 and 70-75).
Diseases of the nephron predominantly affect either the glomeruli or the tubules. Glomerular diseases include diabetic nephropathy, glomerulonephritis and IgA nephropathy; renal tubular dise…
Additional images
• Distribution of blood vessels in cortex of kidney. (Although the figure labels the efferent vessel as a vein, it is actually an arteriole.)
• Glomerulus is red; Bowman's capsule is white.
• Kidney tissue
• Glomerulus
See also
• Nephrology
• Urology