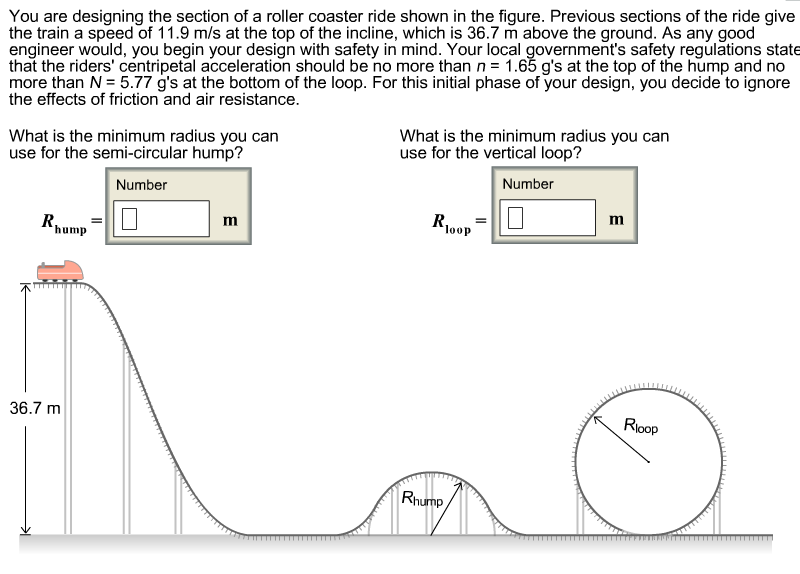
What forces are involved in a roller coaster? Neglecting friction and air resistance, a roller coaster car will experience two forces: the force of gravity (Fgrav) and the normal force (Fnorm). The normal force is directed in a direction perpendicular to the track and the gravitational force is always directed downwards.
Why are g forces important on a roller coaster?
G Forces vary depending on the element and the entry/exit into and out of it; some elements are more intense than others. G Forces create the airtime that riders experience. Ejector Airtime is where the rider feels they are being quickly ejected from the coaster. Floater Airtime is a smoother sensation where the rider feels they are weightless.
How does force affect roller coasters?
In roller coasters, friction is a force that opposes motion and significantly slows the cars as they move on the track. While it is easy to believe that friction is bad for the ride, it is one of the forces engineers consider in ensuring passengers have a safe ride. In the physics classroom, students often ignore the forces of friction and air resistance while considering idealized situations, according to Encyclopaedia Britannica.
What do forces do roller coasters use?
- Gravity. Gravity is also a force and it acts upon us every day, only we don't usually notice. ...
- 'g-forces' When on a roller coaster, the rider experiences 'g-forces'. These are the same forces that astronauts experience during a rocket launch, only smaller.
- Centripetal force. ...
How do engineers force a roller coaster to speed up?
They first begin with an idea of what they want the latest and greatest roller coaster to be. They then put this idea onto paper. The engineers must calculate the perfect angles, heights and directions that will allow the roller coaster to reach great speeds without going off of the track.

How do you find the normal force of a roller coaster?
11:1616:00Normal Force on a Hill, Centripetal Force, Roller Coaster Problem ...YouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipSo it becomes positive mv squared over r so for the roller coaster notice that the normal force isMoreSo it becomes positive mv squared over r so for the roller coaster notice that the normal force is mv squared over r minus mg it's the difference between the centripetal force. And the weight force.
Where is normal force greatest on a roller coaster?
bottomThe normal force is large at the bottom of the loop because in order for the net force to be directed inward, the normal force must be greater than the outward gravity force.
Why is normal force down roller coaster?
Explanation: For a roller coaster for example, there is a force between the roller coaster seat and the rider called the normal reaction force. this force acts down because the rider is upside down. So, at the bottom of the ride the seat's normal force acts up on the person.
What kind of force does a roller coaster have?
A roller coaster is a machine that uses gravity and inertia to send a train of cars along a winding track. The combination of gravity and inertia, along with g-forces and centripetal acceleration give the body certain sensations as the coaster moves up, down, and around the track.
Why is normal force 0 at the top of a loop?
Normal force equal to zero at the top is the limiting case for the largest possible radius, which is what you were asked to find. If the radius becomes larger than that, the car would require a negative force to stay on the track, meaning it would have to somehow "stick" to the track, which would be unusual...
How do I calculate normal force?
Normal force (Fn) can be calculated by the application of Newton's Second Law (F=m*a). On a flat surface, for example, Fn can be calculate by Fn=m*g. On a surface inclined with an angle X, Fn can be calculated by Fn=m*g*cosX.
Is normal force always upwards?
Newton's third law says that for every force, there is an equal and opposite force: for an object on a non-inclined plane, the force of gravity is straight down and the normal force is straight up.
Is normal force equal to weight?
The normal force is usually symbolized by N . In many cases the normal force is simply equal to the weight of an object, but that's only when the normal force is the only thing counteracting the weight. That is not always true, and one should always be careful to calculate any force by applying Newton's second law.
What is the most common type of force experienced on roller coasters?
3:217:22Roller Coaster Forces: Explained - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipThis type of force is usually most common on roller coasters a ride which boasts a maximum g-forceMoreThis type of force is usually most common on roller coasters a ride which boasts a maximum g-force of 5 and allows guests to experience 5 GS of positive force at some point during their ride.
At which position does the roller coaster have the greatest potential energy?
highest pointGravitational potential energy is greatest at the highest point of a roller coaster and least at the lowest point. Kinetic energy is energy an object has because of its motion and is equal to one-half multiplied by the mass of an object multiplied by its velocity squared (KE = 1/2 mv2).
Why do you feel heavier at the bottom of a roller coaster?
As you approach the bottom of the ride, you feel “heavier” because the normal force of your seat has to increase, and the centripetal force is now pulling you up.
What is the normal force acting on the car at the top of the hill?
On top of a hill The only forces acting on the rider are the upward normal force n exerted by the car and the downward force of gravity w, the rider's weight. These add together, as vectors, to provide the net force Fnet which is the centripetal force Fc, directed toward the center of the circle.
How do you find the normal force at the bottom of a loop?
6:427:37Vertical Loop Example | Find The Normal Force and Min Speed NeededYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipFG is our mass mg FC is MV squared over R which is given these M's will do a wonderful thing andMoreFG is our mass mg FC is MV squared over R which is given these M's will do a wonderful thing and cancel out and then V will just become the square root of G.
What is the theory of roller coaster movement?
That doesn’t mean he started working out how to thrill people, but he developed his Laws of Motion that are fundamental to coaster design. When a rider is on a coaster, Newton’s Laws of Motion are probably the last thing on their mind, but every physical thrilling element of the ride relies completely on physics.
What is the kinetic energy of a coaster train?
The coaster rails control the angle of descent meaning the steeper the first drop, the greater the kinetic energy. The kinetic energy at the bottom of the drop determines how far the coaster train can travel along the track and through inversions, banked turns and airtime hills.
How much does a rider weigh at a 4G ride?
If a theme park says a coaster rider will experience, for example, 4G, the rider will briefly experience four times the force of gravity. In simpler terms, if a rider person weighs 100 kg while standing still, they would momentarily weigh 400 kg at the 4G point of the ride. G Forces vary depending on the element and the entry/exit into and out ...
What is the difference between ejector and floater?
G Forces create the airtime that riders experience. Ejector Airtime is where the rider feels they are being quickly ejected from the coaster. Floater Airtime is a smoother sensation where the rider feels they are weightless.
How fast is Kingda Ka?
Kingda Ka at Six Flags Great Adventure exerts high linear G’s when it accelerates from 0 to 128 mph in around 3.5 seconds. Linear G forces push against riders during high-speed launches. Linear G’s force riders back against their seat.
What happens when a train accelerates down the first drop and climbs up the second element?
In this situation, when the train accelerates down the first drop and climbs up the second element, it would roll back. Even though, theoretically, the train has the kinetic energy to get up the same size hill as the first drop, some kinetic energy would be lost yet again due to friction and air resistance.
What does positive G mean in riding?
Positive G is when riders feel heavier from pressure bearing down, as if they are being pushed down into the seat.
What is the feeling of weight on a roller coaster?
This is the feeling of weight. At every point on a roller coaster ride, gravity is pulling you straight down. The other force acting on you is acceleration. When you are riding in a coaster car that is traveling at a constant speed, you only feel the downward force of gravity.
What happens when you ride a roller coaster?
When you ride a roller coaster, all the forces we've discussed are acting on your body in different ways. Newton's first law of motion states that an object in motion tends to stay in motion. That is, your body will keep going at the same speed in the same direction unless some other force acts on you to change that speed or direction. ...
What happens when a coaster slows down?
When the coaster speeds up, the seat in the cart pushes you forward, accelerating your motion. When the cart slows down, your body naturally wants to keep going at its original speed. The harness in front of you accelerates your body backward, slowing you down. We'll talk more about the forces on your body on the next page.