What causes increased DLCO?
The high D LCO values [123, 124] have been explained by hyperinflation, increased intrathoracic pressure, and a more likely cause, increases in pulmonary capillary blood volume or extravasation of red blood cells into the alveolus.
What does decreased DLCO mean?
DLCO values represent the ability of the lung to transfer gas from the inhaled air into the blood stream and acts as a surrogate marker of the extent of lung damage . DLCO values may decrease because of several clinical conditions including emphysema, interstitial lung diseases, or pulmonary fibrosis . Thus, impaired DLCO values in lung cancer patients may suggest not only lung damage but also the possibility of a co-existing comorbidity such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD ...
What is the normal range of intracranial pressure?
The normal intracranial pressure (ICP) ranges within 7 to 15 mm Hg while in the vertical position, it does not exceed −15 mm Hg. Overnight sleep monitoring is considered the “gold standard” in conscious patients.[1] The normal intracranial pressure (ICP) ranges within 7 to 15 mm Hg while in the vertical position, it does not exceed −15 mm Hg.
What is DLCO on pulmonary function test?
Measurement of diffusing capacity of the lungs for carbon monoxide (DLCO), also known as transfer factor, is the second most important pulmonary function test (PFT), after spirometry. Previously available only in hospital-based PFT labs, DLCO testing is now available at outpatient clinics using a portable device.

What does a low DLCO mean?
A low DLCO indicates one of the following: pulmonary interstitial thickening (diffuse parenchymal lung disease [DPLD]); a loss of vasculature, as seen in COPD; or pulmonary vascular disease (ie, chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension [CTEPH] or idiopathic pulmonary arterial hypertension [IPAH])
What does the DLCO tell you?
The DLCO measures the ability of the lungs to transfer gas from inhaled air to the red blood cells in pulmonary capillaries. The DLCO test is convenient and easy for the patient to perform.
Is DLCO high or low in COPD?
DLCO % predicted was significantly lower in COPD patients with more severe airflow limitation (stage II/IV), more symptoms (group B/D), and high exacerbation risk (group C/D). Lower DLCO % predicted was also found in exacerbation patients and non-survivors.
What is the normal value for DLCO and what are the units of measurement?
The mean values for DLCO and DLCO/VA were 28.05±5.07 ml/min/mmHg, 4.569±0.694 ml/min/mmHg/L for men and 20.79±4.03 ml/min/mmHg, 4.695±0.743 ml/min/mmHg/L for women, respectively.
What is a good DLCO score?
Normal DLCO: >75% of predicted, up to 140% Mild: 60% to LLN (lower limit of normal) Moderate: 40% to 60% Severe: <40%
How can I improve my DLCO?
No, it is not possible to improve your DLCO % which is simply how well your lungs exchange oxygen and carbon monoxide. It's the diffusing capacity of your lungs.
Is low DLCO life threatening?
Importantly, the low-DLCO patient group had a 2 1/2 times higher risk of mortality, compared with high-DLCO patients. These results were comparable with previous studies, reporting DLCO as a predictor of mortality in group 1 and group 2 PH patients.
Does DLCO increase with exercise?
During exercise, both groups exhibited increases in DLCO, D M and V C with exercise intensity. Athletes had a greater DLCO and greater D M at 80 and 90% of V ˙ O 2 max compared to non‐athletes.
Does exercise decrease DLCO?
Pulmonary diffusion (DLCO) increases during exercise due to greater pulmonary capillary volume (Vc) and membrane diffusing capacity (DM). However, after heavy exercise there is a reduction in resting DLCO.
What decreases DLCO?
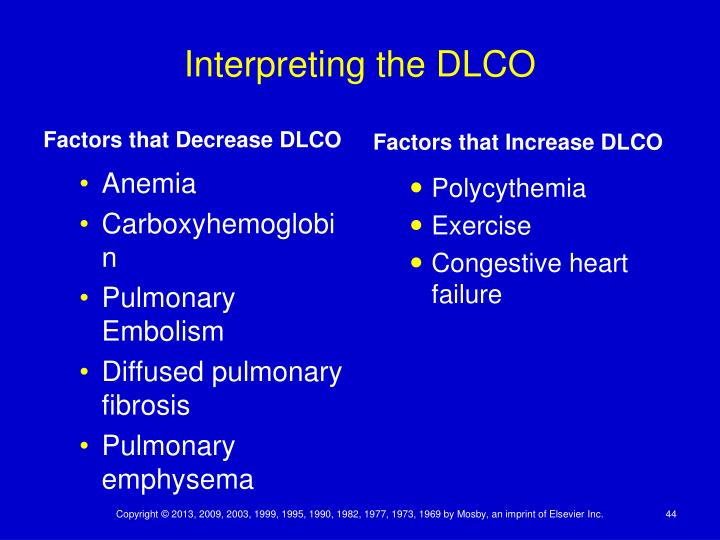
There are several conditions that can decrease the DLCO. These include cigarette smoking, emphysema, interstitial lung disease, anemia, decreased lung volume, heart failure, pulmonary vascular disease (pulmonary emboli and pulmonary hypertension), and others.
Does DLCO decrease with age?
These data suggest that at rest and during exercise, lung diffusing capacity and its component parts (i.e., DLCO, DmCO, and Vc) are decreased with age.
What is DLCO in pulmonary hypertension?
Exercise pulmonary hypertension is an underappreciated form of physical limitation related to early pulmonary vascular disease. A low diffusing capacity of lungs for carbon monoxide (DLco) can be seen in patients with resting pulmonary hypertension as well as parenchymal lung disease.
What does a high DLCO mean?
Conclusion: A high DLCO on a PFT is most frequently associated with large lung volumes, obesity, and asthma. Other conditions are much less common. A clinical condition, which typically reduces DLCO, may deceptively normalize DLCO in such patients.
What causes decreased DLCO?
There are several conditions that can decrease the DLCO. These include cigarette smoking, emphysema, interstitial lung disease, anemia, decreased lung volume, heart failure, pulmonary vascular disease (pulmonary emboli and pulmonary hypertension), and others.
What are three factors that can influence the value of DLCO?
Factors affecting DLCOHemoglobin: DLCO CORR.Lung volume: DL/VA.V/Q mismatch:Pulmonary capillary bed:Alveolar capillary membrane thickness:
What happens to DLCO in restrictive lung disease?
Restrictive lung diseases such as pulmonary fibrosis most often decrease diffusing capacity (DLCO) because of scarring and thickening of the area between the alveoli and capillaries.
What is the normal DLCO?
See below: The DLCO should be between 80 and 120% of normal for you. The normals are calculated based on biographical data entered at the time of the test.
How do we measure normal?
Percent of predicted: We measure "normal" by measuring what you do relative to others of your age, gender, ethnicity, and body size. If you are 75% or more, it is considered normal.
What is DLCO in spirometry?
Diffusing Capacity of Lung for Carbon Monoxide (DLCO) is a measure of the efficiency of lung gas transfer. This test is used to further characterise a respiratory defect following spirometry and lung volume testing, to provide evidence supporting a specific respiratory pathology.
How long do you hold your breath for DLCO?
The patient inhales a mixture of helium (10%), carbon monoxide (0.3%), oxygen (21%) and nitrogen (68.7%), hold their breath for ten seconds and then exhale fully. The levels of exhaled helium and carbon monoxide are used to calculate DLCO. The results may need to be corrected for the patient’s haemoglobin.
What is the purpose of a diffusion lung capacity test?
This test gives the doctor an idea of how much oxygen a person breathes in and how well the gas exchange system is working. This test is also known as diffusion lung capacity ...
What is the diagnosis of high red blood cell count?
They will often order other pulmonary function tests to help with the diagnosis, such as spirometry and lung volume tests.
What is a lung diffusion test?
The lung diffusion test is one type of pulmonary function test. The test is quick and harmless. The lungs function by taking in oxygen during inhalation. The body then exchanges the oxygen for carbon dioxide, which is a waste product of respiration and exhales it.
Why do doctors use diffusion capacity?
A doctor will often recommend lung diffusion capacity testing in addition to other pulmonary function tests to gain an overall clinical picture of how well a person’s lungs are working.
How do diffusion tests check for lung damage?
Lung diffusion tests check for lung damage by measuring how well the lungs exchange gases.
What is DLCO used for?
Diagnostic: Doctors may use DLCO to diagnose medical conditions such as emphysema. Treatment Monitoring: Diffusing capacity may be monitored to determine whether a condition has worsened, or if it has improved with treatment.
Why is my DLCO high?
Causes of High Diffusing Capacity. Rarely, DLCO may instead be high. This may occur with asthma, polycythemia vera (a disease with an elevated hemoglobin level), and congenital diseases that cause blood to be shunted from the left side of the heart to the right side of the heart. 2 With these conditions, however, there are often other signs, ...
What is diffusing capacity?
Diffusing capacity is a measure of how well oxygen and carbon dioxide are transferred (diffused) between the lungs and the blood , and can be a useful test in the diagnosis and to monitor treatment of lung diseases. Diffusing capacity can also be important prior to lung surgery as a predictor of how well the surgery will be tolerated.
How many mechanisms are there for diffusing capacity?
There are two separate mechanisms by which diffusing capacity may be reduced. 2
Does emphysema decrease DLCO?
In contrast, obstructive lung diseases such as emphysema may decrease DLCO by reducing the surface area through which gas can be exchanged.
Why is learning all the different normal values important for respiratory therapy students?
Learning all the different normal values is an important step for Respiratory Therapy Students when it comes to making informed clinical decisions.
Do TMC questions include normal patient values?
Not to mention, questions and problems found on both the TMC Exam and Clinical Sims will include normal patient values. That means you will be required to know the normal ranges in order to select the correct answer.
What is a high DLCO?
For example, high DLCO is associated with asthma, obesity and intrapulmonary hemorrhage. Normal spirometry and lung volumes with low DLCO can be present in pulmonary vascular diseases, early ILD or emphysema. An obstructive ventilatory defect with low DLCO suggests emphysema or lymphangiomyomatosis.
Why is maximal inspiratory flow largely decreased with an extrathoracic airway obstruction?
The maximal inspiratory flow is largely decreased with an extrathoracic airway obstruction because there is a negative pressure inside the airways during inspiration. Inspiratory flows are not affected by intrathoracic lesions; the negative pleural pressure maintains the intrathoracic airways open.
What is maximal flow volume curve?
The maximal flow-volume curves are a great asset to detect mild airflow obstruction (Figure 2). There is an inspiratory and expiratory loop. [2]
How to measure lung volume?
There are 2 methods to measure lung volumes: body plethysmography and gas dilution methods (nitrogen washout and inert gas dilution). Gas dilution method uses an inert gas (poorly soluble in alveolar blood and lung tissues), either nitrogen or helium. The subject breathes a gas mixture until equilibrium is achieved. The volume and mixture of gas exhaled after the equilibrium have been achieved permit the calculation of FRC. In body plethysmography, the subject sits inside a body box and breathes against a shutter valve. FRC is calculated using Boyle Law (at a given temperature, the product of gas volume and pressure is constant). FRC calculated by body plethysmography is usually larger in subjects with obstructive lung disease and air trapping than FRC calculated using gas dilution methods. Body plethysmography is considered the gold standard for lung volumes measurement.
Is lung volume measurement required for obstructive ventilatory defects?
Measurement of lung volumes is not mandatory to identify obstructive ventilatory defects. Lung volumes are helpful when the FEV and FVC are equally decreased, and FEV/FVC ratio is normal or almost normal. The pattern usually reflects the failure of the patient to completely inhale or exhale. The flow-volume curve should be concave. Additionally, the TLC should be normal and RV abnormally increased.