What is the normal range for PAO2?
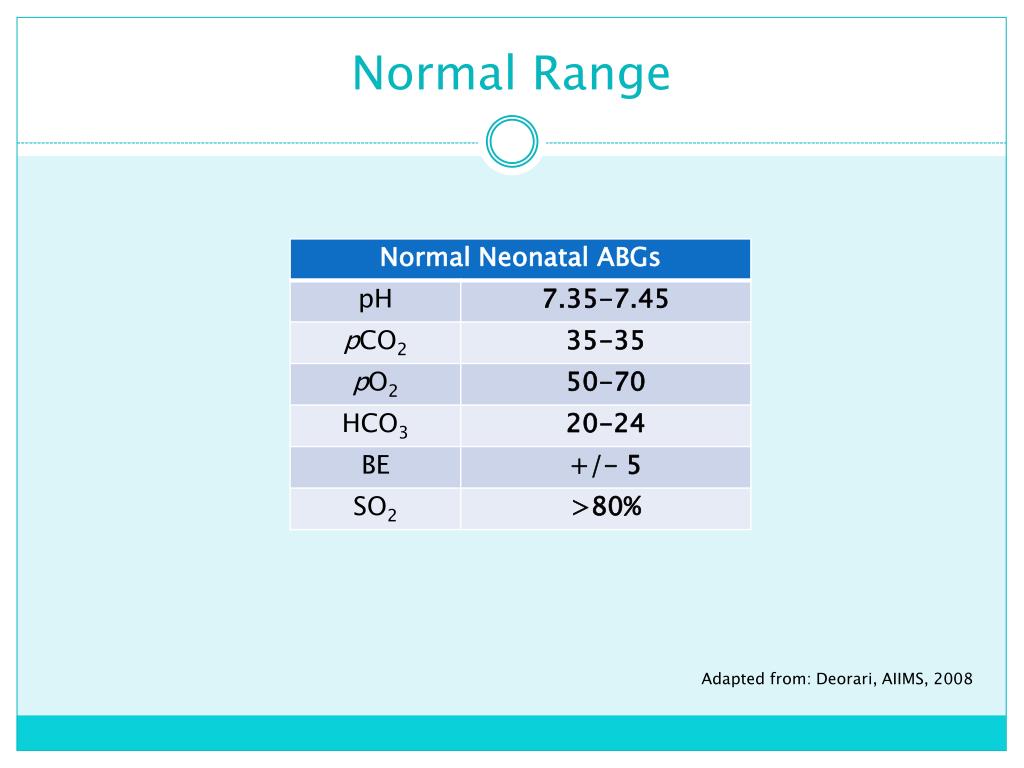
May 06, 2020 · Normal PaO2/FiO2 is >400 mmHg. Approximate PaO2 by multiplying FiO2 by 5 (eg, FiO2 = 21%, then PaO2 = 100 mmHg) Similarly, what should PaO2 be on 100 oxygen? A patient's PaO2 (at sea level) should be 5 x the inspired oxygen percentage (FIO2). For example, a patient on room air is breathing 21% oxygen and so the PaO2 should be ~ 105 mmHg.
What causes low PaO2?
Nov 03, 2020 · at sea level, the normal PaO2/FiO2 ratio is ~ 400-500 mmHg (~55-65 kPa) MD Calc is an example of an online P/F ratio calculator – however it is quite easy to do “in your head” P/F ratio is a widely used clinical indicator of hypoxaemia, …
What are the normal ranges for PaO2 and PaCO2?
Jun 12, 2020 · A patient's PaO2 (at sea level) should be 5 x the inspired oxygen percentage (FIO2). For example, a patient on room air is breathing 21% oxygen and so the PaO2 should be ~ 105 mmHg. A patient on 100% oxygen should have a PaO2 of ~500 mmHg. A patient on 40% FIO2 should have a PaO2 of ~200 mmHg.
What is the formula for PAO2?
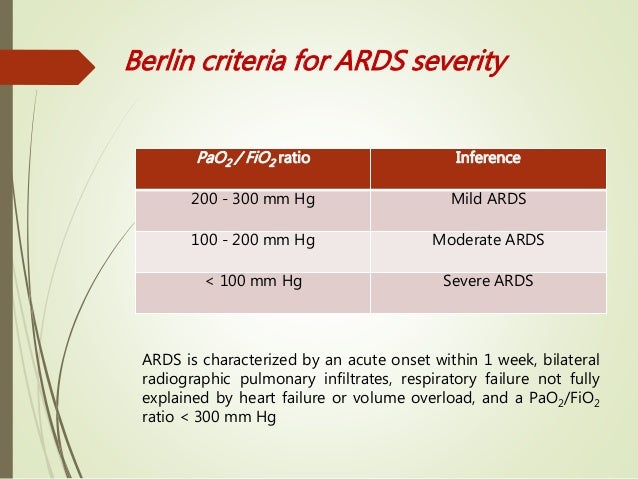
Patients were classified into four disease groups (normal, mild hypoxemia, acute lung injury and acute respiratory distress syndrome) according to their PaO2/FiO2 ratio. On each occasion the patients were studied using four to eight different FiO2 values, achieving arterial oxygen saturations in the range 85-100%.

What does PaO2 FiO2 ratio indicate?
In critically ill patients the PaO2/FIO2 ratio is an indicator of oxygenation status and is one of the diagnostic criteria for acute respiratory distress syndrome in adults (ARDS) [1–4].Sep 26, 2014
What is considered normal for the PaO2 FiO2 ratio quizlet?
A normal PaO2/FiO2 ratio while breathing room air is approximately 400 to 500 mm Hg.
Is PaO2 the same as FiO2?
As we all agree [1,2,3], the ratio of the partial pressure of arterial oxygen (PaO2) to the fraction of inspired oxygen (FiO2), or P/F ratio, can be significantly improved for better reflection of acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) severity by incorporating a wide range of either applied or measured pressures ...Sep 22, 2021
What is the formula for PF ratio?
The P/F ratio equals the arterial pO2 (“P”) from the ABG divided by the FIO2 (“F”) – the fraction (percent) of inspired oxygen that the patient is receiving expressed as a decimal (40% oxygen = FIO2 of 0.40).
What method's is are used to measure O2 consumption?
Oxygen consumption is determined by spirometry, from a resting subject, for 5–10 min. The determination of oxygen consumption represented a limitation for the use of the Fick method, in the first years of this technique application.
What is FiO2 on a ventilator?
FiO2: Percentage of oxygen in the air mixture that is delivered to the patient. Flow: Speed in liters per minute at which the ventilator delivers breaths.May 7, 2021
What happens when oxygen consumption and supply are mismatched?
When oxygen consumption and supply are mismatched, cell damage, and death occur.[5] . The key is recognizing the cause and, thus, the appropriate route of treatment. Inhaled atmospheric gas is 21% oxygen. The amount of oxygen inhaled, i.e., FiO2 is not equivalent to the oxygen which participates in gas exchange at the alveolar level.
What is the concentration of oxygen in room air?
The gas mixture at room air has a fraction of inspired oxygen of 21% , meaning that the concentration of oxygen at room air is 21% . The percentage of oxygen at different altitudes remains the same, meaning the FiO2 of air in the atmosphere remains 21% irrespective of the altitude of an individual. [1]
What is the purpose of FiO2?
In the setting of critically ill patients, FiO2 is routinely used to assess the lungs' capacity for gas exchange. , using the PaO2/FiO2 (P/F) ratio, where PaO2 represents the partial pressure of oxygen.
What can affect FiO2?
Another factor that can alter FiO2 is humidity . Dry air, aside from being uncomfortable for patients, has the potential to increase airway resistance by inducing acute damage and inflammation. Dry air can also cause increased water loss and decreased mucociliary clearance.
What is the meaning of FiO2?
To understand FiO2, it is crucial to understand a few other terms: Hypoxemia: Is defined as a decrease in the partial pressure of oxygen in the blood. [2] PaO2: Partial pressure of oxygen of arterial as measured by an arterial blood gas sample. [3] PAO2: Partial pressure of oxygen of the alveoli, a calculated value.
Is FiO2 equivalent to oxygen?
The amount of oxygen inhaled, i.e., FiO2 is not equivalent to the oxygen which participates in gas exchange at the alveolar level . Several factors need merit consideration and are summarized by the alveolar gas equation. The equation takes into account the barometric pressure (P), water vapor pressure (P), and the gas exchange ratio (Rq).
Can FiO2 be adjusted based on Spo2?
FiO2 can be adjusted based on Spo2; however, when to start supplemental oxygen is widely contested.