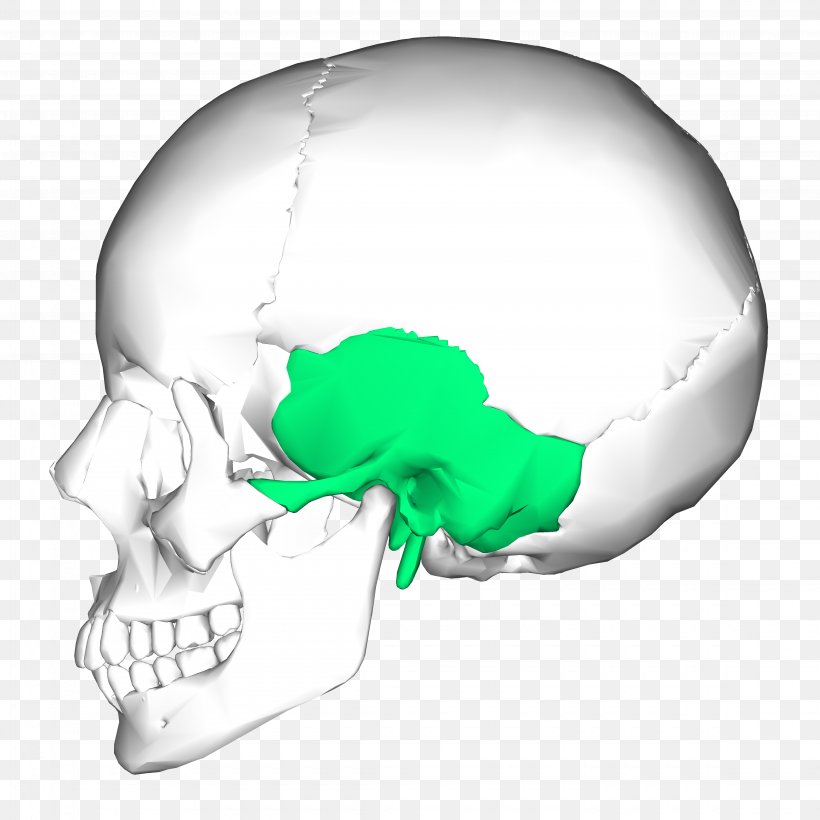
Which skull bone contains a protuberance?
external occipital protuberance foramen magnum allows passage of spinal cord external occipital protuberance bump at the back of the cranium another name for the external occipital protuberance inion 2 lateral portions of the occipital bone are the occipital condyles occipital condyles
How to pronounce occipital bone?
Here are 4 tips that should help you perfect your pronunciation of 'occipital bone':
- Break 'occipital bone' down into sounds : say it out loud and exaggerate the sounds until you can consistently produce them.
- Record yourself saying 'occipital bone' in full sentences, then watch yourself and listen. ...
- Look up tutorials on Youtube on how to pronounce 'occipital bone'.
What does occipital bone mean?
The occipital bone is the trapezoid-shaped bone at the lower-back of the cranium (skull). The occipital bone houses the back part of the brain and is one of seven bones that come together to form the skull. It is located next to five of the cranium bones. As a person ages, their occipital bones will fuse to the other bones of their skull.
What is occipital tumor?
Tumors developing in the posterior aspect of the brain are termed occipital lobe tumors. Both primary and secondary (metastatic) lesions were recognized in clinical practice and tumors of neural, skeletal, mesenchymal, and vascular origins have all been described. The principal symptom of an occipital lobe tumor is visual disturbance, with the severity depending on the extent of tumor spread ...
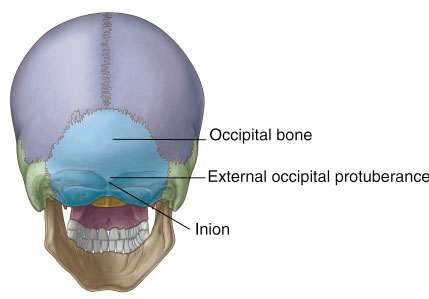
Is occipital protuberance normal?
External occipital protuberance is normal anatomical entity, rarely it may show hyperostosis and may get prominent and causing pain and examination reveals presence of tender bony swelling. However, such occurrence is extremely uncommon.
Do females have an occipital protuberance?
The spine type (Type 3) EOP is found to be 63.4% in males and to be 4.2% in females. On the other hand, studies of dry-skull remains revealed the incidence of Type 1 EOP to be 67.5% in females and Type 3 EOP to be 55.2% in males.
Can you feel the occipital protuberance?
The bony skull bump — known as an external occipital protuberance — is sometimes so large, you can feel it by pressing your fingers on the base of your skull.
What is the occipital protuberance What is the difference between males and females?
Males tend to have a blunter, more rounded surface here, females a sharper border. These are attachments for the neck muscles on the occipital bone at the rear of the skull.
Why is the occipital protuberance important?
The internal occipital protuberance separates these cavities dorsally and provides attachment for the tentorium cerebelli, the tent-shaped extension of the dura mater that forms a partition between the cerebrum and cerebellum.
Why does my skull protrude at the back?
A bump on the back of the head has many possible causes, including injuries, cysts, fatty growths, inflamed hair follicles, and bone spurs. Bumps on this part of the body can be hard or soft, and they can vary in size.
Is it normal to have a bump at the base of your skull?
In addition, each human skull has a natural bump on the back of the head. This bump, called an inion, marks the bottom of the skull where it attaches to the neck muscle.
Why do I have a bump on the base of my skull?
Skull Base Osteoma Osteomas are benign bony outgrowths (new bone growth) mostly found on the skull and facial bones. If the bone tumor grows on another bone, it is called homoplastic osteoma. If it grows on tissue, it is called eteroplastic osteoma. Skull base osteomas are slow growing and generally cause no symptoms.
Why do I feel a bump on my skull?
A bump is any size of lump, protrusion, puffiness, or localized swelling either under or on top of the skin of your head. Many head bumps are caused by a direct injury or force, though some can form without prior trauma to the area, such cysts, infections, or bone spurs.
What gender has a bigger head?
MEN HAVE BIGGER HEADS AND LONGER ARMS AND LEGS than women, relative to body size. Sources differ on comparative limb length but they all agree women have smaller, lighter heads & necks. Did you know a human head weighs about 5kg?
How can you tell a male from a female skeleton?
Within the same population, males tend to have larger, more robust bones and joint surfaces, and more bone development at muscle attachment sites. However, the pelvis is the best sex-related skeletal indicator, because of distinct features adapted for childbearing.
What causes enlarged external occipital protuberance?
Children use these devices with their head tilted down and poor posture resulting in increased stress on the skull from attached structures and develop an exostosis at the external occipital protuberance (EOP). This is more commonly known as a bone spur, or excess bone formation on the surface of another bone.
Does everyone have an occipital bun?
An occipital bun is a prominent bulge or projection of the occipital bone at the back of the skull. It is important in scientific descriptions of classic Neanderthal crania. While common among many of humankind's ancestors, primarily robust relatives rather than gracile, the protrusion is rare in modern Homo sapiens.
What is prominent in female skull?
When viewed in profile, female skulls have a rounded forehead (frontal bone). Male frontal bones are less rounded and slope backwards at a gentler angle. This ridge along the brow is prominent in males and much smoother in females.
Is there a difference between a male and female skull?
Overall, the male skull tends to be larger, have a lower, sloping forehead, larger muscle attachment sites and smaller, squarer eye sockets when compared to females. There is overlap between the sexes and it is not uncommon for individuals to exhibit a mixture of 'masculine' and 'feminine' features.
Are female skulls thicker?
According to a new imaging study of 3,000 people using the latest in imaging analysis techniques, women's skulls are thicker than men's, and both shrink slowly in adulthood. The average skull thickness for men is 6.5 millimeters, and the average for women is 7.1 mm.
Additional images
Position of external occipital protuberance (shown in red). Animation.
External links
Wikimedia Commons has media related to External occipital protuberance.
What is external occipital protuberance?
Ask U.S. doctors your own question and get educational, text answers — it's anonymous and free!
How to know if the lump on the back of the head is a external occipital protuberance?
Examine: occasional an X-ray if some question. Cysts and lipomas can occur there also along with some othe R masses
What is the occipital lymph node?
Occipital Lymph node: Probably a lymph node reacting to a scalp injury or infection, even dandruff or seborrheic dermatitis, but just to be absolutely sure it isn't somethi ... Read More
What does it mean when your occipital area is swollen?
Occipital pain: Pain with swelling at this location can be a simple scalp or muscle condition or can be a more serious condition such as irritation of the greater occ... Read More
Is occipital lymph node enlargement common in children?
Dont worry: Occipital lymph node enlargement is very common in young children . They tend to be associated with infections on the scalp or inflammation on the sca ... Read More
What is the internal occipital protuberance?
This point is called the internal occipital protuberance and runs from the superior angle of the bone to a deep grove, called the sagittal sulcus, which hides part of the superior sagittal sinus and is attached to the falx cerebri.
What is the opening in the occipital bone?
At the base of your skull there is a large oval opening in the occipital bone that is called the foramen magnum. This opening allows for passage of the spinal cord. The occipital bone is the only cranial bone to connect to ...
What is the role of the occipital bone in the brain?
The most important role it plays is in protecting your brain. Specifically, it protects the brain’s visual processing center. It also acts as the connecting pathway from the brain to the spine. As the occipital bone connects with the first vertebra—the area called the atlas—it forms the atlantooccipital joint.
How long does it take for the occipital bone to harden?
When a person is born, their occipital bone is not completely hardened, and it takes up to six years for the hardening to fully complete. 2 Any problems with the development of occipital bone can lead to health issues.
Why is the occipital bone important?
It is therefore important to investigate the cause of head and spine symptoms you may be experiencing, especially pain and problems with function and movement.
Where is the squamous part of the occipital bone?
The squamous part of the largest part of the occipital bone. It is situated above and behind the foramen magnum and curved downward on each side. There are two curved lines on each side: the highest nuchal line and the superior nuchal line.
Where is the basilar part?
Basilar Part. The basilar part is at the front of the foramen magnum and sits next to the dense area of the temporal bone of your skull surrounding the inner ear. Towards the front, the basilar part fuses to the sphenoid bone to form the tribasilar bone during puberty.
What is external occipital protuberance?
External occipital protuberance is a midline bony prominence in the occipital bone that ligamentum nuchae and trapezius muscle attach to its tip. The tentorium cerebelli attaches to its internal surface. Exaggerated external occipital protuberance also is known as an occipital spur.
Which region of the occipital region is associated with osseous proliferation?
Osseous proliferation at the posterior occipital region is related to prominent external occipital protuberance.
What is the occipital bun?
An occipital bun, also called occipital spurs, occipital knob, chignon hooks, PBS head or inion hooks, is a prominent bulge or projection of the occipital bone at the back of the skull.
Why do people with narrow heads have occipital buns?
A study conducted by Lieberman, Pearson and Mowbray provides evidence that individuals with narrow heads ( dolichocephalic) or narrow cranial bases and relatively large brains are more likely to have occipital buns as a means of resolving a spatial packing problem.
Which hemisphere has neuroplasticity?
Assuming that the left parietal and occipital lobe did not function correctly, and the right hemisphere may have experienced neuroplasticity and adaption, where neurogenesis and regeneration, where normal healing without neurodegeneration is factually called adult neurogeneration.
Do humans have occipital buns?
There are still some human populations which often exhibit occipital buns. A greater proportion of early modern Europeans had them, but extremely prominent occipital buns in modern populations are now fairly infrequent, but exist frequently in certain populations.