Medical Definition of Olive. Olive: In neuroanatomy, a rounded oval prominence on the surface of the medulla oblongata in the brain. There are two olives, corresponding to the two olivary bodies, one on each side of the medulla oblongata. Nerve fibers in the olivopontocerebellar pathway connect the olives to the pons and cerebellum .
What are the olivary bodies of the brain?
In anatomy, the olivary bodies or simply olives (Latin oliva and olivae, singular and plural, respectively) are a pair of prominent oval structures in the medulla oblongata, the lower portion of the brainstem.
Is olive oil good for the brain?
Olive oil nourishes the brain and protects it from degenerative disease. The benefits of olive oil are mainly due to its polyphenols, compounds with potent antioxidant properties.
What are the benefits of olive oil for the human body?
Olive oil’s beneficial effects on the human brain and body are likely related to the presence of the polyphenols hydroxytyrosol (HT) and Oleic acid (OA). HT protects cells that are under oxidative stress.
What are the two parts of the olive cell?
The olive consists of two parts: The inferior olivary nucleus (or 'complex'), which is a part of the olivo-cerebellar system and is mainly involved in cerebellar motor-learning and function.

What happens at the olives in medulla?
The olives contain the inferior olivary nucleus (the superior olivary nucleus is actually located in the pons). The olivary nucleus receives input from the motor and sensory cortices, and has important efferent connections with the cerebellum – these circuits are important in the control of movement.
What is the function of the olive in the brain?
The olive consists of two parts: The inferior olivary nucleus (or 'complex'), which is a part of the olivo-cerebellar system and is mainly involved in cerebellar motor-learning and function. The superior olivary nucleus, considered part of the pons and part of the auditory system, aiding the perception of sound.
What does the superior olive do?
The superior olivary complex (SOC) or superior olive is a collection of brainstem nuclei that functions in multiple aspects of hearing and is an important component of the ascending and descending auditory pathways of the auditory system.
Where is the olive nucleus?
brainstemThe olivary nuclei, which consist of the inferior olivary nucleus and superior olivary nucleus, are found in brainstem. The olivary nuclei are paired structures, with one inferior and one superior olivary nucleus on each side of the brainstem.
What happens at the inferior olive?
The inferior olivary nucleus (ION), is a structure found in the medulla oblongata underneath the superior olivary nucleus. In vertebrates, the ION is known to coordinate signals from the spinal cord to the cerebellum to regulate motor coordination and learning.
What is olive nucleus?
The inferior olivary nucleus is the part of the olivary body that assists in cerebellar motor learning and functioning. The cerebellum is located in the lower, back part of the brain. The superior olivary nucleus is the part of the olivary body that belongs to the auditory system and assists with sound perception.
Where are the olives in the brainstem?
superior medullaThe olive is a smooth ovoid prominence just below the pons. It is located in the superior medulla, lateral to the pyramid and ventrolateral sulcus. The hypoglossal nerve and ventrolateral sulcus separates it from the pyramid.
Where is the superior olive found?
caudal ponsThe superior olive is situated caudally near the facial nucleus in the tegmentum of the caudal pons.
What lies immediately medial to the olives?
The hypoglossal nerve (CN XII) exits the medulla through the anterolateral sulcus, just medial to the olive.
Does the cerebellum control movement?
Most movements are composed of a number of different muscle groups acting together in a temporally coordinated fashion. One major function of the cerebellum is to coordinate the timing and force of these different muscle groups to produce fluid limb or body movements.
What is the role of the inferior olivary nucleus?
Function. The inferior olivary nuclei are implicated in motor coordination. They may have oscillatory-pacemaking functions, and play a role in the pathogenesis of essential tremor.
What is a Purkinje cell?
Purkinje cells are a unique type of neuron-specific to the cerebellar cortex. They are remarkable (and instantly recognizable) for their massive, intricately branched, flat dendritic trees, giving them the ability to integrate large amounts of information and learn by remodeling their dendrites.
What is the function of the inferior olivary nuclei?
Function. The inferior olivary nuclei are implicated in motor coordination. They may have oscillatory-pacemaking functions, and play a role in the pathogenesis of essential tremor.
What is the main function of reticular formation?
The brainstem reticular formation (RF) represents the archaic core of those pathways connecting the spinal cord and the encephalon. It subserves autonomic, motor, sensory, behavioral, cognitive, and mood-related functions.
Where are pons present in the brain?
Your pons is one of the lowermost structures in your brain, located near the bottom of your skull. It's just above your medulla oblongata, which then connects to your spinal cord through the opening at the bottom of your skull.
What is the function of the pyramids of the medulla?
The two pyramids contain the motor fibers that pass from the brain to the medulla oblongata and spinal cord.
Which nerve separates the olive from the pyramid?
The hypoglossal nerve and ventrolateral sulcus separates it from the pyramid. The posterolateral sulcus of the spinal cord separates the olive from the inferior cerebellar peduncle, which forms the lateral surface of the medulla.
Which oval prominence contains the inferior olivary nucleus?
The olive is the ventral oval prominence in the medulla oblongata which contains the inferior olivary nucleus, implicated in motor co-ordination.
Where is the facial nerve located?
The facial nerve arises at the just above the olive, inferior to the pons. The posterior inferior cerebellar artery arises anterior to the caudal olive in the premedullary cistern, from the vertebral artery.
What is the olivary body?
Sometimes called ‘ olives ,’ olivary bodies are a pair of distinct, oval structures, situated one on each side of the anterior (front) surface of the medulla oblongata. The medulla oblongata is the lower part of the brain stem. The brain stem assists in the management of certain senses and the regulation of the cardiac (heart) ...
What is the function of the olivary body?
The olivary body works specifically in the areas of motor (movement) learning function, as well as auditory (sound) perception. The olivary bodies are composed of nerve tissue and measure about 1.25 cm in length. The inferior olivary nucleus is the part of the olivary body that assists in cerebellar motor learning and functioning.
Where is the cerebellum located?
The cerebellum is located in the lower, back part of the brain. The superior olivary nucleus is the part of the olivary body that belongs to the auditory system and assists with sound perception. Last medically reviewed on January 21, 2018.
Which organ controls the size of blood vessels?
The medulla oblongata contains the respiratory, vomiting, and vasomotor centers, which control the size of blood vessels. It deals with involuntary functions such as breathing, blood pressure, and heart rate. The olivary body works specifically in the areas of motor (movement) learning function, as well as auditory (sound) perception.
What is the Latin name for the olive?
Medulla. Identifiers. Latin. oliva. MeSH. D009847. Anatomical terms of neuroanatomy. In anatomy, the olivary bodies or simply olives (Latin oliva and olivae, singular and plural, respectively) are a pair of prominent oval structures in the medulla oblongata, the lower portion of the brainstem. They contain the olivary nuclei .
What nerve is between the olive and the pons?
In the depression between the upper end of the olive and the pons lies the vestibulocochlear nerve . In humans, it measures about 1.25 cm. in length, and between its upper end and the pons there is a slight depression to which the roots of the facial nerve are attached.
What is the smallest olivary structure?
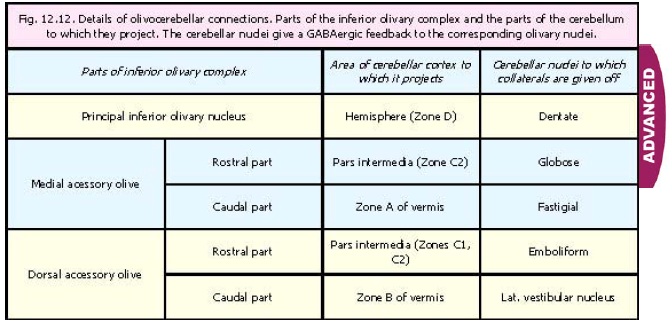
The dorsal accessory olivary nucleus (DAO) is the smallest, and appears on transverse section as a curved lamina behind the primary olivary nucleus. Small additional inferior olivary structures consist of the dorsal cap of Kooy and the ventrolateral outgrowth.
What is the inferior olive?
The inferior olive in itself is divided to 3 main nuclei: The primary olivary nucleus (PO) which consist of the major laminar structure. The medial accessory olivary nucleus (MAO) lies between the primary olivary nucleus and the pyramid, and forms a curved lamina, the concavity of which is directed laterally.
Where is the olivary body located?
The olivary body is located on the anterior surface of the medulla lateral to the pyramid, from which it is separated by the antero-lateral sulcus and the fibers of the hypoglossal nerve .
Which part of the cerebellar system is involved in motor learning?
The inferior olivary nucleus (or 'complex'), which is a part of the olivo-cerebellar system and is mainly involved in cerebellar motor-learning and function.
What are the benefits of olive oil?
Olive Oil Benefits: Take the Next Step. Olive oil nourishes the brain and protects it from degenerative disease. The benefits of olive oil are mainly due to its polyphenols, compounds with potent antioxidant properties. But when buying olive oil, quality matters.
Where does olive oil come from?
Olive oil comes from the fruit of the olive tree ( Olea europae) which originally comes from the Mediterranean Basin.
Why is olive oil not considered virgin?
The olive oils that failed to meet extra virgin standards did so for one or more of these reasons: Oxidation by exposure to elevated temperatures, light and/or aging. Adulteration with cheaper refined olive oil. Poor-quality oil made from damaged and overripe olives, processing flaws, and/or improper oil storage.
What does "light" mean on olive oil?
Modifiers on the label like “lite, light, extra light, or pure” mean you are not getting genuine EVOO. Also, be forewarned that “light” in this case means lighter in taste, not lighter in calories.
How many grades of olive oil are there?
The method of extracting oil from olives has not changed much in thousands of years except that the tools are now stainless steel instead of stone. There are four grades of virgin olive oil. The lowest grade is not fit for human consumption and is designated for other uses, like making soap.
What is UP olive oil?
There’s a relatively new category of olive oil beyond extra virgin — Ultra Premium (UP).
How many phenolic compounds are in olive oil?
Olive oil contains over 30 phenolic compounds that are potent antioxidants and free radical scavengers.
What is the brain inflammation in MS?
The brain inflammation present in MS patients is thought to be driven by changes in the gut microbiome. Scientists now understand that the gut microbiome plays a significant role in both the progression and severity of MS.
Is OA a monounsaturated fatty acid?
OA is a monounsaturated omega-9 fatty acid that is generally higher in olive oil than vegetable fats. It has beneficial effects on blood cholesterol levels. In the current study of an animal model of MS, EVOO, as well as OA or HT alone, demonstrated potent anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects.
Is olive oil a chemical?
Answering this question is not easy. First of all, olive oil is a complex blend of various chemicals. It would be nice to know which are most advantageous and whether they influence brain health directly or indirectly.
Does olive oil affect the brain?
Olive oil modifies how your gut microbiome communicates with your brain. Olive oil’s beneficial effects on the human brain and body are likely related to the presence of the polyphenols hydroxytyrosol (HT) and Oleic acid (OA).
What is the active ingredient in olive leaf extract?
Olive leaf extract comes from the leaves of an olive plant. It contains an active ingredient called oleuropein. . This nutrient is thought to contribute to the anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties of olive leaf extract.
How to treat herpes with olive leaf extract?
To treat herpes with olive leaf extract, drop 1 to 2 droplets on a cotton ball and place on the sore. One study found that olive leaf extract’s antiviral and antimicrobial factors reduce the ability of the herpes virus to invade surrounding cells.
Why is Mediterranean diet important?
You may have heard how a Mediterranean diet has been linked to a decrease in chronic diseases, especially cardiovascular disease. This is thought to be due to the focus on olive oil, leaves, and fruit in the diet. It’s been used as traditional medicine for centuries in countries like Greece, Morocco, and Tunisia.
Does olive leaf extract help with herpes?
These properties mean that olive leaf extract may help with weight loss, heart health, and herpes breakouts. Read on to learn how olive leaf extract can benefit you, dosage information, and more.
Does olive leaf extract lower blood pressure?
Olive leaf extract may help lower systolic and diastolic blood pressure. A 2017 study found that olive leaf extract successfully lowered blood pressure. A lower blood pressure can reduce your risk of stroke and heart attack.
Can you take olive leaf extract with blood thinners?
If you take any blood pressure medication or blood thinners or have diabetes, check with your doctor before taking olive leaf extract. It’s possible to develop severe respiratory allergic reactions.
Which layer of the brain is thick and tough?
The outermost layer, the dura mater, is thick and tough. It includes two layers: The periosteal layer of the dura mater lines the inner dome of the skull (cranium) and the meningeal layer is below that. Spaces between the layers allow for the passage of veins and arteries that supply blood flow to the brain.
What is the brain made of?
Weighing about 3 pounds in the average adult, the brain is about 60% fat. The remaining 40% is a combination of water, protein, carbohydrates and salts. The brain itself is a not a muscle. It contains blood vessels and nerves, including neurons and glial cells.
How does the brain work?
The brain sends and receives chemical and electrical signals throughout the body. Different signals control different processes, and your brain interprets each. Some make you feel tired, for example, while others make you feel pain.
How many nerves are in the cranium?
Inside the cranium (the dome of the skull), there are 12 nerves, called cranial nerves:
How many halves are there in the cerebral cortex?
The cerebral cortex is divided into two halves, or hemispheres. It is covered with ridges (gyri) and folds (sulci). The two halves join at a large, deep sulcus (the interhemispheric fissure, AKA the medial longitudinal fissure) that runs from the front of the head to the back.
Why are the two different shades of gray on a neuron scan?
Gray matter is primarily responsible for processing and interpreting information, while white matter transmits that information to other parts of the nervous system.
Which part of the brain controls movement?
The largest part of the brain, the cerebrum initiates and coordinates movement and regulates temperature. Other areas of the cerebrum enable speech, judgment, thinking and reasoning, problem-solving, emotions and learning. Other functions relate to vision, hearing, touch and other senses.