Why do we have an optic chiasm?
The optic nerve connects the eye to the brain. The optic chiasm is believed to be a turning point in evolution for biologists. Crossing and uncrossing optic nerve fibres travelling through the optic chiasm are believed to have evolved in such a way to help with binocular vision and eye-hand coordination.
What does optic chiasm mean?
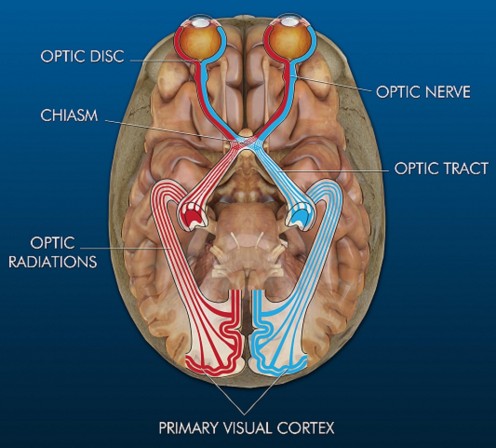
The optic chiasm or optic chiasma is the part of the brain where the optic nerves partially cross. The optic chiasm is located at the bottom of the brain immediately below the hypothalamus. U.S. National Library of Medicine (0.00 / 0 votes) Rate this definition: Optic Chiasm The X-shaped structure formed by the meeting of the two optic nerves.
What is the function of the optic chiasma in the brain?
The optic chiasm, by allowing and facilitating the decussation of part of the optical fibers, allows both hemispheres of the brain to receive visual information from both eyes: if it were not produced (or a decussation of all the fibers were produced), the information received by each eye would be processed only by one of them, without a good integration of the material.
What does optic chiasma mean?
optic chiasma, optic chiasm, chiasma opticum noun. the crossing of the optic nerves from the two eyes at the base of the brain.
What is the function of the optic chiasm quizlet?
The purpose of the optic chiasm is to ensure that visual signals go to both hemispheres of brain. The majority of neural signals are sent to the thalamus for processing and are then distributed into areas of the occipital lobe.
Where is the optic chiasm located and what is its function?
The optic chiasm, or optic chiasma, is the part of the brain where the optic nerves cross and is therefore of primary importance to the visual pathway. It is located at the base of the brain inferior to the hypothalamus, and approximately 10 mm superior to the pituitary gland within the suprasellar cistern.
What happens if optic chiasm is damaged?
Damage to the retina or one of the optic nerves before it reaches the chiasm results in a loss of vision that is limited to the eye of origin. In contrast, damage in the region of the optic chiasm—or more centrally—results in specific types of deficits that involve the visual fields of both eyes (Figure 12.8).
What is the difference between optic nerve and optic chiasm?
The optic nerves exit the orbit and pass through the optic canals (in the skull base) and into the intracranial space. A portion of each optic nerve crosses the midline above the pituitary gland to form the optic chiasm.
Where is the optic chiasm located quizlet?
- At the optic chiasm, the optic nerve fibers from the nasal halves of the retinas cross to the opposite sides, where they join the fibers from the opposite temporal retinas to form the optic tracts.
Is the optic chiasm part of the cerebrum?
The optic chiasm is found in all vertebrates, although in cyclostomes (lampreys and hagfishes), it is located within the brain....Optic chiasmSystemVisual systemFunctionTransmit visual information from the optic nerves to the occipital lobes of the brainIdentifiersLatinchiasma opticum10 more rows
Where is the optic nerve located?
of the eyeThe optic nerve begins at the optic disk, a structure that is 1.5 mm (0.06 inch) in diameter and is located at the back of the eye. The optic disk forms from the convergence of ganglion cell output fibres (called axons) as they pass out of the eye.
Where is the optic tract located?
the brainThe optic tract is an extension of the optic nerve located in the brain. It begins at the area where information from the left eye and right eye cross (or “decussate”) to create a complete visual picture.
What is the function of optic chiasm?
The function of Optic Chiasm: The optic chiasm plays a crucial role in visual input information retinotopic depiction and is situated above the pituitary gland, anterior to the pituitary stalk, and inferior to the hypothalamus. At optic chiasm stage, it is estimated that 53% of optic nerve axons, predominantly nasal hemiretine, ...
Why is the optic chiasm important?
The optic chiasm is believed to be a turning point in evolution for biologists. Crossing and uncrossing optic nerve fibres travelling through the optic chiasm are believed to have evolved in such a way to help with binocular vision and eye-hand coordination.
What is the purpose of the optic chiasm stage?
This decussation is intended to combine visual input data from two halves of each retina receiving light from the same part of the visual field.
How does optic chiasma help with vision?
What is the optic chiasma and how does it helps with vision? The optic chiasm is an X-shaped structure created through the crossing of the brain's optic nerves. The optic nerve connects the eye to the brain. The optic chiasm is believed to be a turning point in evolution for biologists. Crossing and uncrossing optic nerve fibres travelling ...
What is the most common disease that affects the optic chiasm?
A pituitary adenoma is the most prevalent disease affecting the optic chiasm. Pituitary adenomas are benign tumours. They do not affect at all in most cases, but in some instances, they may influence vision, sometimes causing vision loss. As pituitary adenomas grow in size, they can put pressure on essential structures in the body, such as the optic nerve. Pressing the optic nerve can cause blindness, so eye doctors must detect pituitary tumours before vision damage is caused.
Where does the optic chiasm cross?
Anatomy of Optic Chiasm: Nerve fibres from half of each retina at the optic chiasm cross over to the brain's opposite side. The other half of the retina's fibres travel to the same part of the brain. Each half of the brain gets visual signals from both eyes ' visual areas because of this intersection. The optic chiasm stretches at the level of the ...
Which part of the optic tract lies between the hypothalamus and the cerebral peduncle?
The hypothalamus supraoptic nucleus surmounts the lateral edge of the optic tract. Besides, the optic tract lies medially between the lateral hypothalamus and the cerebral peduncle, and laterally the amygdala's medial nucleus.
Where is the optic chiasma?
The optic chiasma, or optic chiasm, is the point in the brain where the optic nerves intersect. At this junction, approximately half of the fibers from each optic nerve cross over to the other side of the brain.
What are the two bundles of nerve fibers that form after the partial crossover of nerve fibers at the optic?
After the partial crossover of nerve fibers at the optic chiasma, the resulting two bundles of fibers are called the optic tracts. Each optic tract contains nerve fibers from both eyes — parts of the retina that correspond to specific parts of the visual field. The optic tracts then relay this “binocular” information to the visual cortex of the brain.
Where do optic nerves come from?
Long, threadlike nerve fibers, called axons, come together from the retinas to form the optic nerves of each eye. Once the optic nerves meet at the optic chiasm, axons from half of each retina cross over to the opposite side of the brain. The axons from the other half of the retina remain on the same side of the brain.
What is the best way to make sure all parts of the eye are working as they should?
A comprehensive eye exam is the best way to make sure all parts of the eye — internal and external — are looking and working as they should.
Why is optic chiasm so hard to detect?
Why Diseases of the Optic Chiasm May Be Hard to Detect. When a disease or lesion affects the optic nerve before it reaches the optic chiasm in the brain, the defect in the vision will show up in only one eye and can affect the entire field of that eye.
What diseases affect optic chiasm?
These include: 2. Inflammatory disorders such as multiple sclerosis. Infections such as tuberculosis. Benign (noncancerous) tumors and cysts. Cancerous tumors. Vascular (blood vessel) disorders.
How does pituitary adenoma affect optic chiasm?
How Pituitary Adenoma Affects the Optic Chiasm. The most common disorder affecting the optic chiasm is a pituitary adenoma. 3 Pituitary adenomas are benign tumors. In most cases, they have no impact at all, but in some cases, they can affect vision, sometimes causing vision loss.
What is the X-shaped structure formed by the crossing of the optic nerves in the brain?
Updated on July 26, 2020. The optic chiasm is an X-shaped structure formed by the crossing of the optic nerves in the brain. The optic nerve connects the brain to the eye. To biologists, the optic chiasm is thought to be a turning point in evolution. 1 It is thought that the crossing and uncrossing optic nerve fibers that travel through ...
What happens if you have a chiasm after a chiasm?
If the disease affects the optic tract after the chiasm, the person will have a defect in their vision in both eyes, but the defect will alter the same half of the visual field.
Where do nerve fibers from the other half of the retina travel?
The fibers from the other half of the retina travel to the same side of the brain.
Can chiasm affect both eyes?
If the disease affects at the chiasm, then the temporal visual fields will be affected in both eyes and anything further back in the brain behind the chiasm both eyes' visual field will also be affected but will be affected on the same side.
What is optic chiasm?
Optic chiasm. From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia. Jump to navigation Jump to search. Part of the brain where the optic nerves cross. For other meanings of "chiasm", see Chiasm. This article is about the optic tract. For the general definitions, see Chiasm (anatomy). Optic chiasm.
Where is the optic chiasm located?
It is located at the bottom of the brain immediately inferior to the hypothalamus. The optic chiasm is found in all vertebrates, although in cyclostomes ( lampreys and hagfishes ), it is located within the brain. This article is about the optic chiasm of vertebrates, which is the best known nerve chiasm, but not every chiasm denotes a crossing ...
What are the signals that guide the crossing of the optic nerve?
During development, the crossing of the optic nerves is guided primarily by cues such as netrin, slit, semaphorin and ephrin; and by morphogens such as sonic hedgehog (Shh) and Wnt . This navigation is mediated by the neuronal growth cone, a structure that responds to the cues by ligand - receptor signalling systems that activate downstream pathways inducing changes in the cytoskeleton. Retinal ganglion cell (RGC) axons leaving the eye through the optic nerve are blocked from exiting the developing pathway by Slit2 and Sema5A inhibition, expressed bordering the optic nerve pathway. Ssh expressed at the central nervous system midline inhibits crossing prior to the chiasm, where it is downregulated. The organization of RGC axons changes from retinotopic to a flat sheet-like orientation as they approach the chiasm site.
What is the X shape of the optic chiasm?
Visual pathway with optic chiasm (X shape) is shown in red (image from Andreas Vesalius ' Fabrica, 1543). The optic chiasm, or optic chiasma ( / ɒptɪk kaɪæzəm /; Greek: χίασμα, "crossing", from the Greek χιάζω, "to mark with an X", after the Greek letter " Chi "), is the part of the brain where the optic nerves cross.
How did the optic chiasm evolve?
Since all vertebrates, even the earliest fossils and modern jawless ones, possess an optic chiasm, it is not known how it evolved. A number of theories have been proposed for the function of the optic chiasm in vertebrates (see theories ). According to the axial twist hypothesis the optic chiasm develops as a consequence of a twist in the early embryo.
Where do RGC axons cross?
Most RGC axons cross the midline at the ventral diencephalon and continue to the contralateral superior colliculus. The number of axons that do not cross the midline and project ipsilaterally depends on the degree of binocular vision of the animal (3% in mice and 45% in humans do not cross).
Which type of chiasm is the best known?
This article is about the optic chiasm of vertebrates, which is the best known nerve chiasm, but not every chiasm denotes a crossing of the body midline (e.g., in some invertebrates, see Chiasm (anatomy) ). A midline crossing of nerves inside the brain is called a decussation (see Definition of types of crossings ).
The optic chiasm: what is it and where is it found?
The optic chiasm is a part of the brain that is of great importance when it comes to processing visual information coming from the retina, being the point where the optic nerves of both eyes meet.
Function
The optic chiasm, by allowing and facilitating the decussation of part of the optical fibers, allows both hemispheres of the brain to receive visual information from both eyes: if it were not produced (or a decussation of all the fibers were produced), the information received by each eye would be processed only by one of them, without a good integration of the material..
Consequences of your injury
Head injuries, surgeries or cerebrovascular accidents, together with some diseases and disorders such as tumors, can be the reason that the optic chiasm or the nerve pathways that circulate through it are injured. Although it is not frequent, given its position within the skull, this injury can cause a great effect on our visual system.
Bibliographic references
Adel K. Afifi. (2006). Functional neuroanatomy: Text and atlas. México D.F .: McGraw Hill p.324

Anatomy of The Optic Chiasm
Diseases of The Optic Chiasm
- There are a number of disorders that can affect the optic chiasm. These include:2 1. Inflammatory disorders such as multiple sclerosis 2. Infections such as tuberculosis 3. Benign (noncancerous) tumors and cysts 4. Cancerous tumors 5. Vascular (blood vessel) disorders
How Pituitary Adenoma Affects The Optic Chiasm
- The most common disorder affecting the optic chiasm is a pituitary adenoma.3Pituitary adenomas are benign tumors. In most cases, they have no impact at all, but in some cases, they can affect vision, sometimes causing vision loss. As they grow in size, pituitary adenomas can put pressure on important structures in the body, such as the optic nerve. Putting pressure on the op…
Why Diseases of The Optic Chiasm May Be Hard to Detect
- When a disease or lesion affects the optic nerve before it reaches the optic chiasm in the brain, the defect in the vision will show up in only one eye and can affect the entire field of that eye. People that suffer from a one-sided defect sometimes do not notice it until one eye is covered. This is because, when both eyes are open, the overlapping visual fields of each eye will mask th…