What is the Order of reactivity of alkyl halides for SN2 reactions?
The order of reactivity of alkyl halides for Sn2 reactions relies on which of the halogen atoms is most weakly bonded to the carbon atom. The weaker the bond, the more easily it is broken, the lower the activation energy for the reaction and the faster the rate at which it will occur.
What is the Order of intermediate alkyl halides?
Intermediate is carbonation, so we must see carbonation stability. Therefore the order is : Benzylic > Allylic > Tertiary > Secondary > Primary > Vinylic Steric Hindrance is major point. More is the steric hindrance, less stable the alkyl halide is.Therefore the order is :
What is the Order of substitution for aryl halide?
This can be explained by which halogen atom is a better leaving group compared to the other. But in case of Aryl halides, where substitution occurs by SnAr mechanism, the order is reverse Ar-F>Ar-Cl>Ar-Br>Ar-I. Hope it helps. Can I listen to SiriusXM for 3 months for free right now? Yes, you can. Stream SiriusXM for 3 months for free.
What is the Order of reactivity of the leaving group?
In order for a leaving group to leave, it must be able to accept electrons. A strong bases wants to donate electrons; therefore, the better leaving group will be the better base. Giving the order of reactivity I>Br>Cl>F. An exception to this series is the SNAr reaction whereby the order of reactivity is reversed.
Which alkyl halide is more reactive?
Hence, correct answer is alkyl iodide.
What is the reactivity order of alkyl halides in Sn2?
So,order of reactivity of alkyl halide in Sn2 reaction is RI>RBr>RCl>RF.
What is the correct order of reactivity of alkyl halides in the SN1 reactions?
3o carbocations are more stable than others or stability order of carbocations is 3o>2o>1o, so, order of alkyl halides towards SN1 reaction is 3o>2o>1o.
What is the order of reactivity?
The reactivity series follows the order, from most reactive to least reactive:Cesium.Francium.Rubidium.Potassium.Sodium.Lithium.Barium.Radium.More items...•
Which alkyl halide is more reactive primary secondary or tertiary?
In S(N^1) reactions, primary alkyl halides are more reactive than tertiary alkyl halides.
Is SN1 first or second order?
The Rate Law Of The SN1 Reaction Is First-Order Overall.
What is reactivity of alkyl halide?
The high reactivity of alkyl halides can be explained in terms of the nature of C — X bond which is highly polarized covalent bond due to large difference in the electronegativities of carbon and halogen atoms.
Which is the most reactive alkyl halide in a SN1 reaction *?
Solution : Tertiary butyl chloride is most reactive in `S_(N^(1))` reaction. This is due to greater stability of `3^(@)`-carbocation formed in the first step.
Which of the following alkyl halide is most reactive towards SN1 reaction ch3 ch2 Cl CH3 Cl?
In (III), the carbocation generated is stabilised due to resonance. Hence, (III) is most reactive towards SN1 reaction.
What is the order of reactivity of halogens?
So the correct order of reactivity of halogens is F2>Cl2>Br2>I2.
Which of the following statement is correct order of reactivity?
So, the correct order of reactivity is Na>Mg>Zn>Fe.
What is the order of reactivity of halide with amine?
The order of reactivity of alkyl halides with ammonia is, R–I > R–Br > R–Cl.
What is the order of reactivity of SN2 reaction?
In general, the order of reactivity of alkyl halides in SN2 reactions is: methyl > 1° > 2°. The 3° alkyl halides are so crowded that they do not generally react by an SN2 mechanism.
What is order of reactivity of alkyl halide towards SN1 and SN2 reaction?
RI > RBr > RCl is the decreasing order in which alkyl halides react.>
What is the order of reactivity for SN1 and SN2 reaction?
The Mechanism Of The SN1 Is Stepwise. The SN2 reaction is concerted. That is, the SN2 occurs in one step, and both the nucleophile and substrate are involved in the rate determining step.
Which of the following is most reactive towards SN2 reaction CH3Br ch3 2chbr ch3 3cbr?
CH3Br is the most reactive in Sn2 reaction.
How are alkyl halides synthesized?
Alkyl halides can be synthesized from alcohols by treating with hydrogen halides, HX (where X=Cl / Br / I). It is a nucleophilic substitution reaction.
Which halide is more reactive?
Tertiary halides are more reactive under conditions that promote ionization of the alkyl halide and stabilize the resulting carbocation.
What is SN1 in a tertiary substitution reaction?
An SN1 reaction makes a carbocation intermediate that has to be stable enough that it hangs around long enough for the nucleophile to find ( by random motions and bumping around). Methyl, ethyl, etc are considered to be electron donating groups so the more of them that are attached to the carbocation, the more stable it is. Hence. Tertiary substitution reactions will proceed via SN1.
What alcohols react with Lucas' agent?
While, tertiary and secondary alcohols form stable carbocations, that's why they both react with Lucas' agent to form corresponding alkyl halides.
Why doesn't Lucas react with alcohol?
The reason why the Lucas' reagent doesn't react with primary alcohols is because primary alcohols do not form (if at all) stable carbocations. All the factors that help stabilize carbocations (such as neighboring carbon atoms, neighboring carbon-carbon multiple bonds and neighboring atoms with lone pair electrons) are absent in primary alcohols. That means, no stable carbocations, the harder the reaction becomes and the slower the SN1 reaction will be. Sometimes it takes days for Lucas reagents to react with primary alcohols. And who has days?
Which reaction is faster, E2 or SN2?
With 3rd degree alkyl halides, E2 reactions are favored over SN2 reactions. Tertiary Alkyl Halides undergo the fastest E2 reactions. The greater the alkyl substitution, the faster the reaction, since in the Transiton stage, a double bond is formed partially. A greater substituted alkene is lower in energy. Hence the activating energy is reduced, making the reaction faster.
Which carbon will undergo SN2?
So a primary carbon will more likely undergo SN2 whereas a tertiary carbon will more likely do SN1 and a secondary carbon could go either way, depending on the relative strength of the nucleophile and the leaving group.
Why are alkyl halides reactive?
The alkyl halides are very reactive due to highly polarized [CX] bonds with a large difference in electronegativities of carbon and halogen atoms.
What is the chain of hydrocarbons in which hydrogen are replaced by halogens?
Hint: We know that alkyl halides are the chain of hydrocarbons in which hydrogen are replaced by halogens. The reactivity of the alkyl halide is decided by the ease with which the halide leaves the substrate.
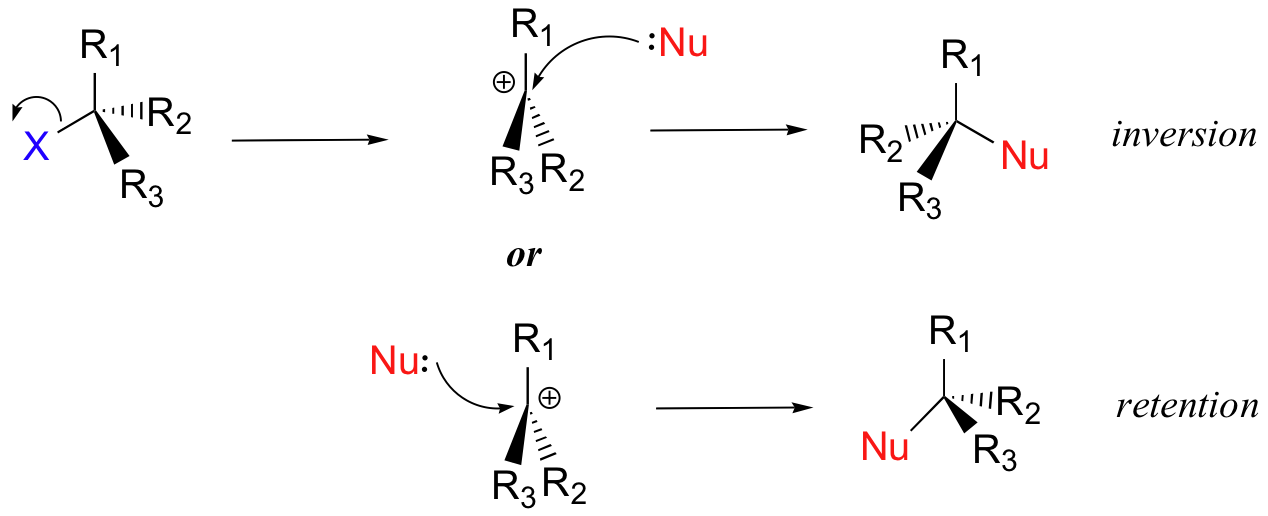
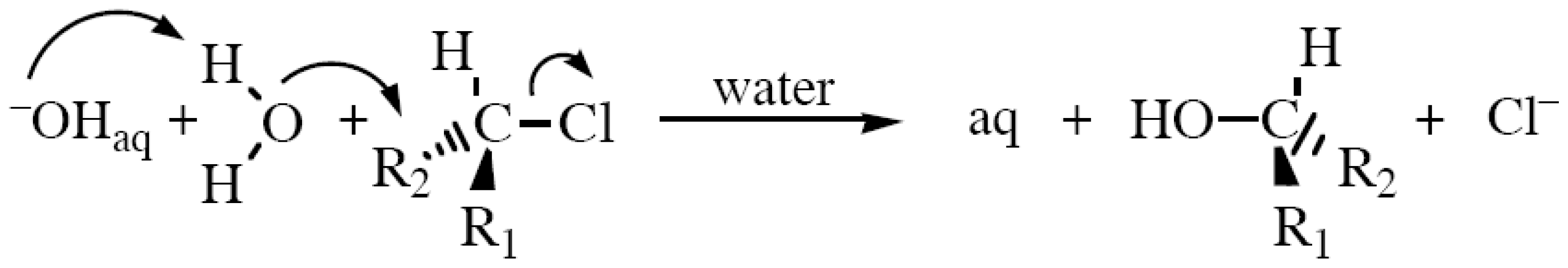
Which electron pair attacks the substrate?
The electron pair from the nucleophile (nuc) attacks the substrate(R-LG) forming a new bond, while the leaving group (LG) departs with an electron pair. The principal product in this case is R-nuc.