
What is the origin of the atomic line spectrum?
• electrons are allowed to higher orbit with an input in energy. What is the origin of the Atomic Line spectrum ? The line emission line spectrum results from electrons dropping from higher energy level to lower energy levels.
What is an emission spectrum of an element?
Emission spectrum. Emission spectrum of a metal halide lamp. The emission spectrum of a chemical element or chemical compound is the spectrum of frequencies of electromagnetic radiation emitted due to an atom or molecule making a transition from a high energy state to a lower energy state.
What is a line emission line spectrum?
The line emission line spectrum results from electrons dropping from higher energy level to lower energy levels. Each time an electron drops, a proton of light is released whose energy correspond to the difference in energy between the two levels.
Why do different elements have different emission wavelengths?
There are many possible electron transitions for each atom, and each transition has a specific energy difference. This collection of different transitions, leading to different radiated wavelengths, make up an emission spectrum. Each element's emission spectrum is unique.
Who did the atomic emission spectrum of an element?
The Bohr Model for Hydrogen (and other one-electron systems) In 1913, a Danish physicist, Niels Bohr (1885–1962; Nobel Prize in Physics, 1922), proposed a theoretical model for the hydrogen atom that explained its emission spectrum.
What is the origin of spectrum?
In the physical sciences, the term spectrum was introduced first into optics by Isaac Newton in the 17th century, referring to the range of colors observed when white light was dispersed through a prism.
What causes the emission spectrum of an element quizlet?
What causes atomic emission spectra? When atoms absorb energy, electrons move into higher energy levels. These electrons then lose energy by emitting light when they return to lower energy levels.
What is the origin of spectral lines according to Bohr's atomic model?
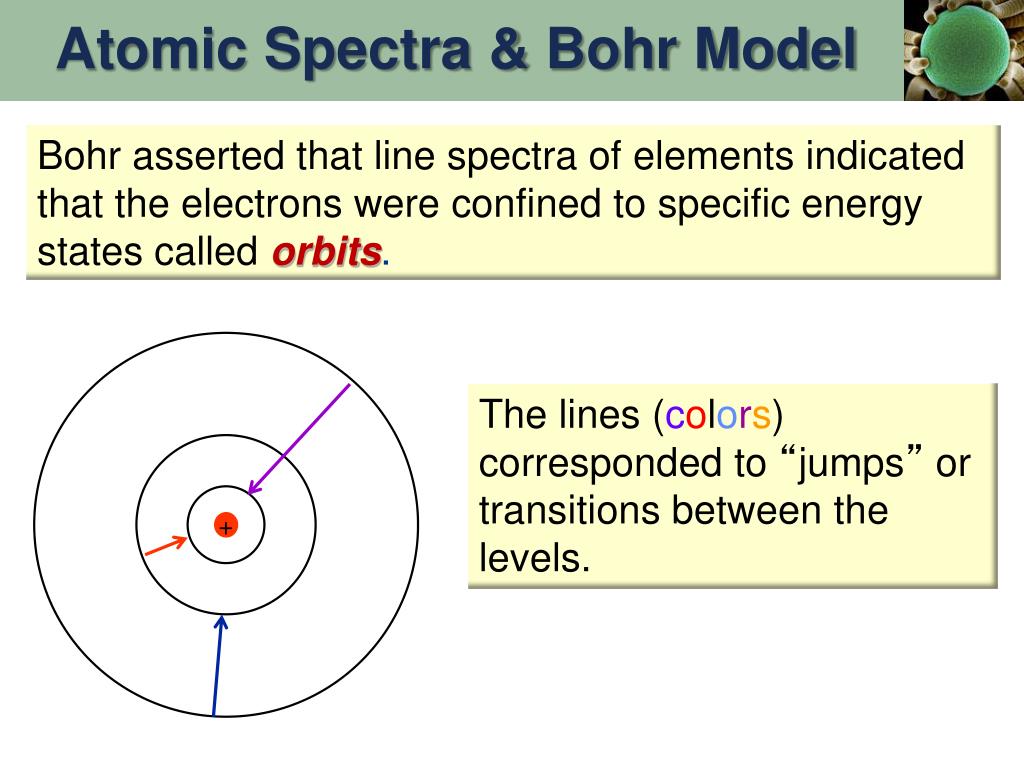
1 Answer. i. According to Bohr's third postulate, when an electron in a hydrogen atom jumps from higher energy level to the lower energy level, the difference of energies of the two energy levels is emitted as a radiation of particular wavelength called spectral line.
What do you mean by emission spectrum?
The emission spectrum of a chemical element or chemical compound is the spectrum of frequencies of electromagnetic radiation emitted due to an atom or molecule transitioning from a high energy state to a lower energy state.
What causes the emission spectrum of an element Quizizz?
What causes the emission spectrum of an element? movement of electrons from a lower energy state to a higher energy state.
What is the emission spectrum of an element quizlet?
Each spectral line in an atomic emission spectrum of an element corresponds to exactly one wavelength of light emitted by the electrons of that element. a number used to calculate the radiant energy (E) absorbed or emitted by a body based on the frequency of radiation.
What is an emission spectrum quizlet?
What is an emission spectrum? In a emission spectrum (which is light), the energy is emitted by the electron as it drops to a lower energy level.
Who invented spectrum?
In the year 1800, Sir William Herschel was exploring the question of how much heat was contained by the different colors of visible light. He devised and experiment where he used a glass prism to separate sunlight into it's rainbow of colors.
What is meant by spectrum and how is it formed?
Likewise the other colour light waves bend with respect to the incident white light as they pass through the prism. Thus, the rays of different colours emerge alone and become distinct. This band of the coloured components of a light beam is called its spectrum.
What was spectrum before?
Time Warner Cable Bright HouseSpectrum (brand)Trade nameSpectrumIndustryTelecommunicationsPredecessorsTime Warner Cable Bright House NetworksFoundedJuly 22, 1999 (as Charter Communications) 2014 (as Charter Spectrum)HeadquartersStamford, Connecticut , U.S.5 more rows
Is spectrum owned by Verizon?
Verizon Buys Spectrum for $3.6 Billion It is worth mentioning that Verizon actually purchased 122 Spectrum mobile carrier licenses from Spectrum at this price. This purchase was part of Verizon's plan to expand its own mobile wireless carrier network. The deal was struck, and Verizon is now the owner of these licenses.
What is the principle of the atomic emission spectrum?
The principle of the atomic emission spectrum explains the varied colors in neon signs, as well as chemical flame test results (described below). The frequencies of light that an atom can emit are dependent on states the electrons can be in. When excited, an electron moves to a higher energy level or orbital.
Why is emission spectroscopy called optical emission spectroscopy?
Emission spectroscopy is often referred to as optical emission spectroscopy because of the light nature of what is being emitted.
How do atoms get excited?
There are many ways in which atoms can be brought to an excited state. Interaction with electromagnetic radiation is used in fluorescence spectroscopy, protons or other heavier particles in Particle-Induced X-ray Emission and electrons or X-ray photons in Energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy or X-ray fluorescence. The simplest method is to heat the sample to a high temperature, after which the excitations are produced by collisions between the sample atoms. This method is used in flame emission spectroscopy, and it was also the method used by Anders Jonas Ångström when he discovered the phenomenon of discrete emission lines in the 1850s.
Why is spectroscopy used in chemical analysis?
Each element's emission spectrum is unique. Therefore, spectroscopy can be used to identify elements in matter of unknown composition . Similarly, the emission spectra of molecules can be used in chemical analysis of substances.
What is the process of a particle becoming a higher energy quantum mechanical state?
Emission. In physics, emission is the process by which a higher energy quantum mechanical state of a particle becomes converted to a lower one through the emission of a photon, resulting in the production of light. The frequency of light emitted is a function of the energy of the transition. Since energy must be conserved, ...
What is the emission spectrum of a metal halide lamp?
The emission spectrum of a chemical element or chemical compound is the spectrum of frequencies of electromagnetic radiation emitted due to an atom or molecule making a transition from a high energy state to a lower energy state.
What is discontinuous spectrum?
Light consists of electromagnetic radiation of different wavelengths. Therefore, when the elements or their compounds are heated either on a flame or by an electric arc they emit energy in the form of light. Analysis of this light, with the help of a spectroscope gives us a discontinuous spectrum. A spectroscope or a spectrometer is an instrument which is used for separating the components of light, which have different wavelengths. The spectrum appears in a series of lines called the line spectrum. This line spectrum is called an atomic spectrum when it originates from an atom in elemental form. Each element has a different atomic spectrum. The production of line spectra by the atoms of an element indicate that an atom can radiate only a certain amount of energy. This leads to the conclusion that bound electrons cannot have just any amount of energy but only a certain amount of energy.
Who discovered that each element has its own unique spectrum?
In 1859, Gustav Kirchhoff recognized that each element and compound had its own unique spectrum and by studying the spectrum of an unknown source, you can determine its chemical composition. Kirchhoff’s laws also state that emitted power and absorbed the power of light at a given wavelength is the same for all bodies at the same temperature.
Who discovered that light can be separated into different colors?
In 1666, Sir Isaac Newton showed that white light from the sun could be separated into different colors of light; he also introduced the word ‘spectrum’.
What did Kirchhoff do with spectroscopy?
Together with Bunsen, Kirchhoff established spectroscopy as a scientific tool for probing the atomic and molecular structures and founded the field of spectrochemical analysis for examining the composition of materials.
What is AES in science?
AES is a qualitative technique, it allows scientists to figure out what metal they are looking at, and it only concerns visible light. It is an incredibly powerful means of determining the elemental composition of samples based on the emission of light.
When was AES first used?
Atomic Emission Spectroscopy (AES) has a long history; as far back as the 1550s , where qualitative applications based on the color of flames were used in the smelting of ores. It is based on the physical and chemical principle of atoms that, after being heated by a flame, return to a normal energy state and give off excess energy in the form of light.
Who invented the AES?
Very early in its history, AES was understood to be a very powerful tool, but it was not utilized extensively until the 1930s. Although the quantitative application based on atomic emission from electric sparks was developed by Sir Norman Lockyer, a British scientist and astronomer credited with discovering helium in the 1870s, it was Henrik Lundegårdn who pioneered the technique.
What is the photoelectric effect?
The breakthrough came with the discovery and implementation of the photoelectric effect, which describes the emission of electrons when light hits material; these emitted electrons are known as photo electrons. The effect can be attributed to the transfer of energy from light to the electron.
How many electrons are in an atomic orbital?
an atomic orbital may describe at most 2 electrons, each with opposite spin direction
What did Einstein propose to explain the photoelectric effect?
To explain the photoelectric effect, Einstein proposed that light could be described as quanta of energy that behave as if they were particles (E=hv)
How do atoms lose energy?
When atoms absorb energy, their electrons move to higher energy levels. They lose energy by emitting light when they return to lower energy levels
Which type of mechanics describes the motion of subatomic particles and atoms as waves?
Classical mechanics describes the motion of bodies larger than atoms, while quantum mechanics describes the motion of subatomic particles and atoms as waves
What is the atomic line spectrum?
Light emits light at all wavelength. Excitation of certain elements or the electrical excitation of certain elements give rise to an atomic line spectrum unique to that atom. • electrons are allowed to higher orbit with an input in energy.
What is the purpose of emission spectra?
Excited gaseous elements produce characteristic spectra that can be used to identify the elements as well as to determine how much elements is present in a sample.
What happens when an electron transitions from a high energy level to a lower energy level?
Transition of the electron from a high energy level to a lower energy level results in a photon emission which has a frequency related to the energy difference between the transition.

Overview
The emission spectrum of a chemical element or chemical compound is the spectrum of frequencies of electromagnetic radiation emitted due to an electron making a transition from a high energy state to a lower energy state. The photon energy of the emitted photon is equal to the energy difference between the two states. There are many possible electron transitions for each atom, and each t…
Emission
In physics, emission is the process by which a higher energy quantum mechanical state of a particle becomes converted to a lower one through the emission of a photon, resulting in the production of light. The frequency of light emitted is a function of the energy of the transition.
Since energy must be conserved, the energy difference between the two states equals the energy carried off by the photon. The energy states of the transitions can lead to emissions over a very l…
Origins
When the electrons in the atom are excited, for example by being heated, the additional energy pushes the electrons to higher energy orbitals. When the electrons fall back down and leave the excited state, energy is re-emitted in the form of a photon. The wavelength (or equivalently, frequency) of the photon is determined by the difference in energy between the two states. These emitted …
Emission spectroscopy
Light consists of electromagnetic radiation of different wavelengths. Therefore, when the elements or their compounds are heated either on a flame or by an electric arc they emit energy in the form of light. Analysis of this light, with the help of a spectroscope gives us a discontinuous spectrum. A spectroscope or a spectrometer is an instrument which is used for separating the components of …
History
In 1756 Thomas Melvill observed the emission of distinct patterns of colour when salts were added to alcohol flames. By 1785 James Gregory discovered the principles of diffraction grating and American astronomer David Rittenhouse made the first engineered diffraction grating. In 1821 Joseph von Fraunhofer solidified this significant experimental leap of replacing a prism as the source of wavelength dispersion improving the spectral resolution and allowing for the dispersed w…
Experimental technique in flame emission spectroscopy
The solution containing the relevant substance to be analysed is drawn into the burner and dispersed into the flame as a fine spray. The solvent evaporates first, leaving finely divided solid particles which move to the hottest region of the flame where gaseous atoms and ions are produced. Here electrons are excited as described above. It is common for a monochromator to be used to allow for easy detection.
Emission coefficient
Emission coefficient is a coefficient in the power output per unit time of an electromagnetic source, a calculated value in physics. The emission coefficient of a gas varies with the wavelength of the light. It has units of ms sr . It is also used as a measure of environmental emissions (by mass) per MWh of electricity generated, see: Emission factor.
In Thomson scattering a charged particle emits radiation under incident light. The particle may b…
See also
• Absorption spectroscopy
• Absorption spectrum
• Atomic spectral line
• Electromagnetic spectroscopy