
What is the surface of the eye called?
The surface of the eye and the inner surface of the eyelids are covered with a clear membrane called the conjunctiva. The layers of the tear film keep the front of the eye lubricated. Tears lubricate the eye and are made up of three layers. These three layers together are called the tear film.
What is the membrane that covers the eyelid called?
The surface of the eye and the inner surface of the eyelids are covered with a clear membrane called the conjunctiva. Tears lubricate the eye and are made up of three layers. These three layers together are called the tear film.
What is the mucous layer of the eye called?
The surface of the eye and the inner surface of the eyelids are covered with a clear membrane called the conjunctiva. The layers of the tear film keep the front of the eye lubricated. Tears lubricate the eye and are made up of three layers. These three layers together are called the tear film. The mucous layer is made by the conjunctiva.
What is the function of the outer layer of the eye?
Cornea The cornea is the clear outer layer of the eye that protects the eye from harmful particles and ultraviolet rays. This part of the eye is also responsible for bending the light that enters the eye. The cornea’s shape or curvature determines the eye’s focusing abilities for both near and distant objects.
What is the outer part of the eye called?
Cornea: The cornea is the clear, outer part of the eye's focusing system located at the front of the eye. Iris: The iris is the colored part of the eye that surrounds the pupil. It regulates the amount of light that enters the eye.
What is the surface of the eye called?
Cornea. The clear, dome-shaped surface that covers the front of the eye. Iris. The colored part of the eye.
What is the outer surface of cornea?
Cornea and sclera constitute the outer covering or coat of the eyeball. The main purpose of this coat is to protect structures inside the eye. The cornea is a transparent avascular tissue that acts as a structural barrier and protects the eye against infections.
Where is the eye surface?
The ocular surface includes the outer layer of the cornea, the tears, the conjunctiva, and the margin of the eye lids. This part of the eye has the most frequent injuries and ocular disease manifestations due to direct exposure to the environment.
What is the skin in the corner of your eye called?
An epicanthal fold is skin of the upper eyelid that covers the inner corner of the eye. The fold runs from nose to the inner side of the eyebrow. An epicanthal fold is a skin fold of the upper eyelid covering the inner corner of the eye.
What are the 3 layers of the eye?
Eye Anatomy and FunctionThe outer layer of the eyeball is a tough, white, opaque membrane called the sclera (the white of the eye). ... The middle layer is the choroid. ... The inner layer is the retina, which lines the back two-thirds of the eyeball.
What's a sclera?
The sclera is the white outer coating of the eye. It is tough, fibrous tissue that extends from the cornea (the clear front section of the eye) to the optic nerve at the back of the eye. The sclera gives the eyeball its white color. The cornea and sclera are made of the same type of collagen fibers.
Is cornea and lens the same thing?
The cornea is the outer clear, round structure that covers the iris and the pupil. The cornea directs light rays into the eye and helps focus them on the light-sensitive retina at the back of the eye, providing sharp, clear vision. The lens is located behind the iris and is normally clear.
What are parts of eye called?
Articles On Eye Basics Iris: the colored part. Cornea: a clear dome over the iris. Pupil: the black circular opening in the iris that lets light in. Sclera: the white of your eye.
What are the 7 parts of the eyes?
Parts of the human eye are:Sclera.Cornea.Iris.Pupil.Lens.Retina.Optic nerves.
What are the 4 layers of the eye?
IntroductionThe sclera and cornea make up the exterior layers.The uvea is the vascular layer in the middle, subdivided into the iris, ciliary body, and choroid.The retina constitutes the innermost layer and is made up of nervous tissue.
What are the 3 layers of eye?
The wall of the eyeouter layer – made up of the sclera and cornea (called the fibrous tunic)middle layer – made up of the uvea (called the vascular tunic)inner layer – made up of the retina (called the neural tunic)
How do the eyelids remove tears from the eye?
The eyelids also remove the tears from the eye’s surface by pushing the tears through the lacrimal puncta into the tear duct, this is called the ‘watermelon seed’ effect. The edges of the upper and lower lids are lubricated by an oily secretion ...
What glands are responsible for lubricating the edges of the eyelids?
The edges of the upper and lower lids are lubricated by an oily secretion produced by the meibomian glands , which are located inside the eyelids. This oily secretion contributes to the makeup of the tear film, and serves to decrease the rate at which the tears evaporate.
Why do tears come out of the eye?
When the eyelids open and close, they push the tears out of the eye through the tear duct, to be drained down the back of the nose. When the tear duct becomes clogged or blocked, the tears are unable to drain out of ...
Why is my eye watery?
When the tear duct becomes clogged or blocked, the tears are unable to drain out of the eye properly— usually resulting in an irritated, watery eye. A blocked tear duct is common among newborns, but can also occur in adults as following an eye injury, infection, or as a result of an ocular tumor.
How long does it take for eyelashes to grow back?
The eyelashes fall out on their own and take around six to eight weeks to grow back.
Why do my eyelashes get sore?
It is caused by an inflammation of the eyelids, usually as a result of a blockage in the meibomian glands at the base of the eyelashes. When meibomian glands do not produce enough oil, or produce oil of poor quality, bacterial growth may occur— resulting in a bacterial infection.
Where are the meibomian glands located?
Meibomian glands. Meibomian glands are the oil glands located inside the eyelids. Their opening pores line the edges of the eyelids, near the eyelashes. Around 25 to 40 meibomian glands line the upper eyelid and 20 to 30 line the lower eyelid. These glands secrete the oil that coats the eye and tear film, to prevent the tears from evaporating too ...
What is the ring on the periphery of the cornea called?
Appearance of arcus senilis (corneal arcus). Arcus senilis. As people get older, a white ring often develops in the periphery of the cornea. This is called arcus senilis (also called corneal arcus ), and it's the most common aging change in the cornea.
Why is the cornea wider than the iris?
It lies directly in front of the iris and pupil, and it allows light to enter the eye. Viewed from the front of the eye, the cornea appears slightly wider than it is tall. This is because the sclera (the "white" of the eye) slightly overlaps the top and bottom of the anterior cornea. The horizontal diameter of the cornea typically measures about 12 ...
How thick is the Descemet membrane?
Descemet's (pronounced "DESS-eh-mays") membrane gradually thickens throughout life — it's about 5 microns thick in children and 15 microns thick in older adults. The corneal endothelium.
What is the middle layer of the cornea?
The corneal stroma. This middle layer of the cornea is approximately 500 microns thick, or about 90 percent of the thickness of the overall cornea. It is composed of strands of connective tissue called collagen fibrils. These fibrils are uniform in size and are arranged parallel to the cornea surface in 200 to 300 flat bundles called lamellae that extend across the entire cornea. The regular arrangement and uniform spacing of these lamellae is what enables the cornea to be perfectly clear.
How thick is the cornea?
The center thickness of the average cornea is about 550 microns, or slightly more than half a millimeter. The cornea has five layers. From front to back, these layers are: The corneal epithelium. This outer layer of the cornea is five to seven cells thick and measures about 50 microns — making it slightly less than 10 percent of the thickness ...
What is the innermost layer of the cornea?
The corneal endothelium. This is the innermost layer of the cornea. The back of the endothelium is bathed in the clear aqueous humor that fills the space between the cornea and the iris and pupil. The corneal endothelium is only a single layer of cells thick and measures about 5 microns.
What is the condition called when you have a severe abscess on your cornea?
Corneal ulcer. A corneal ulcer is a serious abscess-like infection of the cornea that can lead to significant pain, scarring and vision loss.
What is the white part of the eyeball?
The white visible portion of the eyeball. The muscles that move the eyeball are attached to the sclera. Suspensory ligament of lens. A series of fibers that connects the ciliary body of the eye with the lens, holding it in place.
What is the optic nerve?
Optic nerve. A bundle of nerve fibers that connect the retina with the brain. The optic nerve carries signals of light, dark, and colors to a part of the brain called the visual cortex, which assembles the signals into images and produces vision. Posterior chamber. The back part of the eye's interior. Pupil.
Which layer of the eye senses light?
The opening in the middle of the iris through which light passes to the back of the eye. Retina. The light-sensitive nerve layer that lines the inside of the back of the eye. The retina senses light and creates impulses that are sent through the optic nerve to the brain. Sclera.
What is the anterior chamber of the eye?
Anterior chamber. The front section of the eye's interior where aqueous humor flows in and out, providing nourishment to the eye.
What part of the eye is covered by the skin?
Upper eyelid. Skin that covers the upper part of the eyeball, including the cornea, when closed.
What is the clear dome-shaped surface that covers the front of the eye?
Cornea. The clear, dome-shaped surface that covers the front of the eye.
Which membrane is responsible for supplying blood to the outer portion of the retina?
Choroid. The thin, blood-rich membrane that lies between the retina and the sclera and is responsible for supplying blood to the outer portion of the retina.
How does the visual system work?
The eyes receive light from many different directions and distances. To be seen, all this light must focus on the comparatively tiny area of the retina. This means the eyes have to bend light from different angles and directions.
What muscle is used to control the upper eyelid?
The upper and lower eyelids help to protect the eye, and keep its surface moist. The upper eyelid is more mobile and is attached to a special muscle, called the levator palpebrae superioris. This muscle allows you to control the upper eyelid. Eyelids help to spread the tear film across the eye by blinking. They also produce a special oil which slows down the evaporation of the tear film.
How do lenses work?
In order for an object to be seen, the light coming from the object must hit the retina. Structures in the eye bend the light rays entering the eye so that when they reach the retina they are focused. The cornea and lens both help to do this. The cornea gives the initial bend to the light but the lens is the fine tuner. The lens can change shape with the help of the ciliary body which contains fine muscle fibres that pull on it. Depending on the angle of the light coming into it, the lens becomes more or less curved (convex). This alters its strength and allows it to focus the light correctly on to the back of the eye. This is very similar to the action of a lens in a camera which focuses the light on to the film.
What part of the eye produces sharpest images?
Near the centre of the retina is the macula. The macula is a small highly sensitive part of the retina. It is responsible for detailed central vision, the part you use when you look directly at something. It contains the fovea, the area of your eye which produces the sharpest images of all.
How does the lens shape change?
The lens can change shape with the help of the ciliary body which contains fine muscle fibres that pull on it. Depending on the angle of the light coming into it, the lens becomes more or less curved (convex). This alters its strength and allows it to focus the light correctly on to the back of the eye.
How many muscles are involved in the movement of the eye?
The movement of each eye is controlled by six muscles that pull the globe of the eye in various directions. They work together in a synchronised way. For example, to look left, the lateral rectus muscle of the left eye pulls the left eye outward and the medial rectus of the right eye pulls the right eye towards the nose. At the same time levator palpebrae superioris lifts the upper eyelid.
Why do pupils get bigger in darkness?
In darkness your pupils will get bigger to allow in more light. The retina is a layer on the inside of the back of the eyeball.
Did you know that the eye is made up of over 2 million parts, each contributing a distinct vital role in your ability to see?
The eye is a complicated organ (second in its complexity to the brain), and all of its parts need to work in perfect harmony to en able you to see the world around you.
How does aqueous humor flow out of the anterior chamber?
The aqueous humor flows out of the anterior chamber through the trabecular meshwork. As new fluid is produced, the “old” fluid drains out. If there is a problem within the trabecular meshwork and the fluid cannot drain properly, or the fluid is being produced faster than it can drain out, the pressure within the eye can increase.
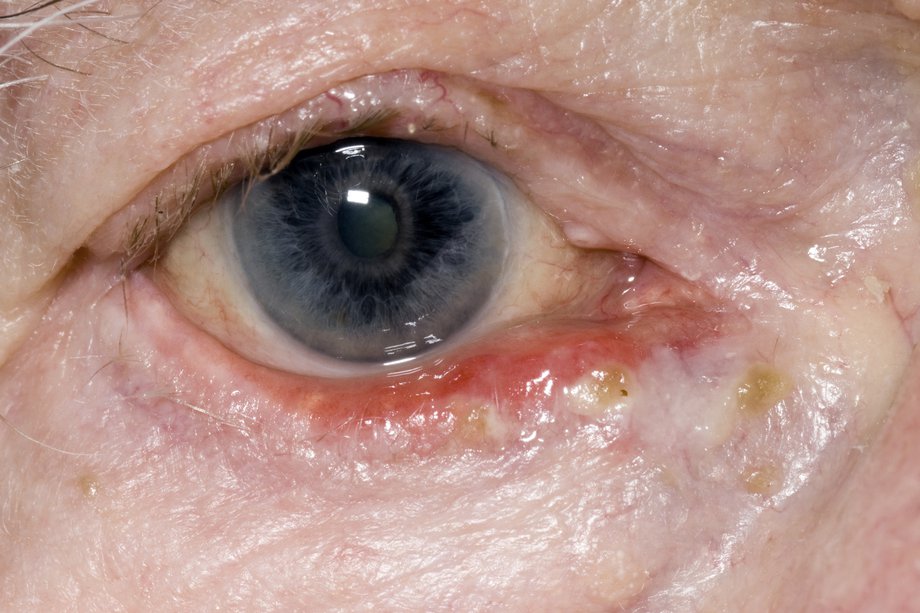
Why is my conjunctiva red?
Often, the conjunctiva can become red from other conditions as well, such as dry eyes and eye allergies. If you suspect you have an eye condition, contact an eye doctor near you, who can diagnose and treat the condition. SEE RELATED: Eye Anatomy: External Parts of the Eye.
Why is my eye red?
When the conjunctival vessels become swollen, the eye appears red or pink— this is generally caused by an infection called conjunctivitis, also known as “pink eye”.
Why do you have to dilate your pupils during an eye exam?
During an eye exam, the pupils are dilated with the use of special eye drops in order to allow the eye doctor to examine the inner structures and the retina in the back of the eye.
What is the tissue that covers the sclera?
The sclera at the front of the eye is covered with a protective tissue called the conjunctiva.
What is the outermost layer of the eye?
Sclera. The outermost layer of the eye consists of the sclera, also known as the white part of the eye. The sclera is made up of tough fibrous tissue and is responsible for giving the eye it’s round shape and protecting the inner structures of the eye. The sclera is thickest in the back of the eye as it provides extra protection to ...
