Routes of Medication Administration
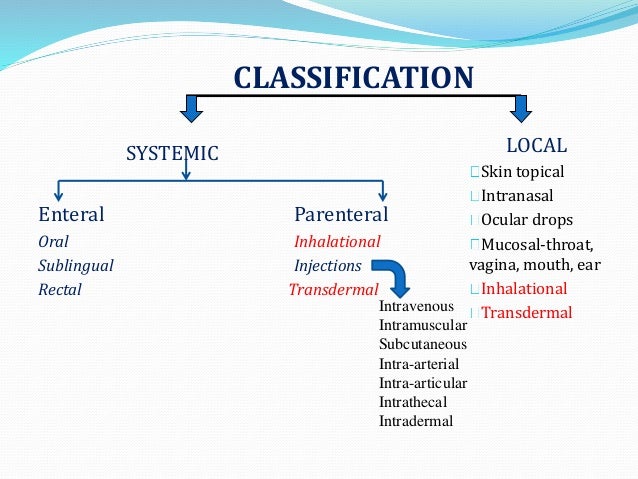
- Routes of Medication Administration. In general, two categories of medication administration exist: parenteral and nonparenteral. ...
- Parenteral. This administration route involves medication that is injected in the body anywhere other than the mouth or alimentary canal (the entire passage along which food passes through the body ...
- Nonparenteral. ...
What are the 10 routes of medication administration?
This route includes:
- Oral (medications are taken by mouth and absorbed into the system through the digestive system. ...
- Sublingual (medication is placed under the tongue for absorption by the body)
- Topical (applied directly to a part of the body)
- Transdermal (active ingredients are delivered via the skin for systemic distribution. ...
What are the different routes of medication administration?
What are the 8 routes of drug administration?
- Oral route. Many drugs can be administered orally as liquids, capsules, tablets, or chewable tablets.
- Injection routes. Administration by injection (parenteral administration) includes the following routes:
- Sublingual and buccal routes.
- Rectal route.
- Vaginal route.
- Ocular route.
- Otic route.
- Nasal route.
What are the 6 routes of Drug Administration?
intramuscular route; nasal route; oral route; parenteral route; pharmaceutical products; pulmonary route; rectal rou te; routes of administration; subcutaneous route; systemic medications ...
What are the different routes of Drug Administration?
The choice of route of administration may be influenced by many factors among which include:
- convenience
- state of the patient
- desired onset of action
- patient’s co-operation
- the nature of the drug as some drugs may be effective by one route only e.g., insulin
- age of the patient
- effect of gastric pH, digestive enzymes and first-pass metabolism
What are the 5 parenteral routes?
There are five commonly used routes of parenteral (route other than digestive tract) administration: subcutaneous (SC/SQ), intraperitoneal (IP), intravenous (IV), intrader- mal (ID), and intramuscular (IM). Not all techniques are appropriate for each species.
What is parenteral drug with example?
Thus, topical drugs, although not taken by mouth involving the digestive tract, are not considered parenteral as their actions are typically only local. Some examples of parenteral drugs include epinephrine, insulin, and IV infusions.
What is the most common parenteral route of administration?
Parenteral Route of Medication Intravenous injection is the most common parental route of medication administration and has the benefit of bypassing the first-pass metabolism by the liver.
What is does parenteral mean?
Medical Definition of parenteral (Entry 1 of 2) : situated or occurring outside the intestine parenteral drug administration by intravenous, intramuscular, or subcutaneous injection especially : introduced otherwise than by way of the intestines enteric versus parenteral feeding.
Why are parenteral medications used?
Parenteral medications enter the body by injection through the tissue and circulatory system. Injection medications are absorbed more quickly and are used with patients who are nauseated, vomiting, restricted from taking oral fluids, or unable to swallow.
What is parenteral give their types?
Types of Parenteral Routes. The most common parenteral routes of drug administration are intravenous, intraosseous, intramuscular, subcutaneous, epidural, and intradermal. Let's take a closer look at each. Medicines or fluids that go directly into the patient's vein are being given by the intravenous (IV) route.
What are parenteral devices?
The term "Parenteral Devices" is used for the equipments needed for the administration of parenteral drugs. These devices include syringes and cannulas. These devices must be sterile, pyrogen-free and free from particulate matter1.
What is parenteral drug?
Parenteral drug products are the dosage forms intended for administration by a route that does not involve the gastrointestinal (GI) tract (thu s, parenteral). Most of the parenteral drug products are injectable dosage forms that are intended for administration by injection using a syringe and a needle. Parenteral dosage forms are preferred for one or more of the following reasons:
Where are injections given?
Nevertheless, drugs may be administered into almost any organs or area in the body, including the joints (intraarticular), joint fluid area (intrasynovial), spinal column (intraspinal), spinal fluid (intrathecal), arteries (intraarterial), and in the heart (intracardiac). In addition, parenteral routes of administration include dosage forms such as sublingual tablets, transdermal patches, and inhalers.
What is intraarticular injection?
An intraarticular injection is made into the synovial cavity of a joint, usually to obtain a local therapeutic effect. For example, an intraarticular injection of a corticosteroid provides an anti- inflammatory action in an arthritic joint.
What is intrathecal route?
Intrathecal route involves drug administration into the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). This route is needed if CSF is the desired site of drug action because most drugs do not reach the CSF from the systemic circulation. Drugs administered intrathecally include antineoplastics, antibiotics, anti-inflammatory, and diagnostic agents.
What is an IV push?
A bolus means the drug is injected into the vein over a short period of time. A bolus is used to administer a relatively small volume and is often written as IV push (IVP).
Where is intradermal injection?
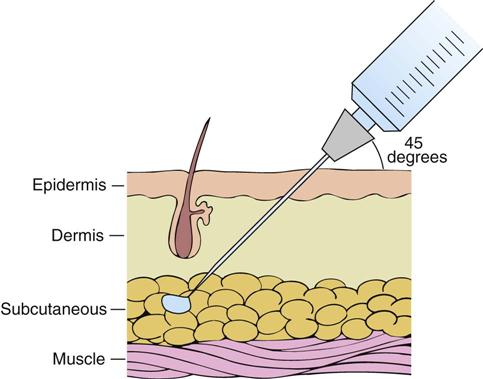
Intradermal administration involves injection just beneath the epidermis, within the dermal or skin layers. The usual site for intradermal injection is the anterior forearm. The volume of solution that can be administered intradermally is limited to 0.1 mL. The onset of action and the rate of absorption of medication from this route are slow. This route is used for diagnostic agents, desensitization, testing for potential allergies, or immunization.
Where to administer IV infusion?
IV infusion can be administered through peripheral veins, typically in the forearm or the peripherally inserted central catheter. The commonly administered IV infusion products include Lactated Ringers Injection USP; Sodium Chloride Injection USP (0.9%), which replenish fluids and electrolytes; and Dextrose Injection USP (5%), which provides fluid plus nutrition; and various combinations of dextrose and saline. Other solutions of essential amino acids or lipid emulsions are also used as infusions.
What are the different routes of medication administration?
Oral: A majority of the drugs are administered orally as it is a convenient, safe and affordable route of administration. …
What is difference between enteral and parenteral routes of administration?
What do Enteral and Parenteral Nutrition Refer To? Enteral nutrition generally refers to any method of feeding that uses the gastrointestinal (GI) tract to deliver part or all of a person’s caloric requirements. … Parenteral nutrition refers to the delivery of calories and nutrients into a vein.
What are the 10 routes of drug administration?
Oral administration. This is the most frequently used route of drug administration and is the most convenient and economic. …
What are the common injectable routes of administration?
Administration by injection (parenteral administration) includes the following routes:
What are the 7 Medication rights?
To ensure safe medication preparation and administration, nurses are trained to practice the “7 rights” of medication administration: right patient, right drug, right dose, right time, right route, right reason and right documentation [12, 13].
What is the fastest route of absorption for a drug?
The fastest route of absorption is inhalation, and not as mistakenly considered the intravenous administration. Absorption is a primary focus in drug development and medicinal chemistry, since a drug must be absorbed before any medicinal effects can take place.
Can IV drugs be taken orally?
IV administration can also be a controlled way to give drugs over time. Certain drugs may be given by IV administration because if you took them orally (by mouth), enzymes in your stomach or liver would break them down.
What is difference between enteral and parenteral routes of administration?
What do Enteral and Parenteral Nutrition Refer To? Enteral nutrition generally refers to any method of feeding that uses the gastrointestinal (GI) tract to deliver part or all of a person’s caloric requirements. … Parenteral nutrition refers to the delivery of calories and nutrients into a vein.
What are the 10 routes of drug administration?
Oral administration. This is the most frequently used route of drug administration and is the most convenient and economic. …
What is the slowest route of medication administration?
Swallowing a drug is a relatively slow method of taking a drug. After the drug is swallowed, it is dissolved in the stomach and then absorbed into the bloodstream from the linings of the stomach and later, the small intestine.
What are the common injectable routes of administration?
Administration by injection (parenteral administration) includes the following routes:
What are the 7 Medication rights?
To ensure safe medication preparation and administration, nurses are trained to practice the “7 rights” of medication administration: right patient, right drug, right dose, right time, right route, right reason and right documentation [12, 13].
What is the fastest route of absorption for a drug?
The fastest route of absorption is inhalation, and not as mistakenly considered the intravenous administration. Absorption is a primary focus in drug development and medicinal chemistry, since a drug must be absorbed before any medicinal effects can take place.
Can IV drugs be taken orally?
IV administration can also be a controlled way to give drugs over time. Certain drugs may be given by IV administration because if you took them orally (by mouth), enzymes in your stomach or liver would break them down.