What is the prognosis for an uti?
Oct 01, 2019 · Physiology of the Urinary System. Urine is formed by nephrons present inside the kidneys. The production of urine is the body’s way of eliminating excess water, waste products, and salt. After its formation in the nephrons, the urine flows through several structures in the kidney. From the kidney, the urine flows into the ureters downward into the bladder via …
What are the risk factors of an uti?
Sep 01, 2019 · URINARY TRACT INFECTION PATHOPHYSIOLOGY DEFINITION: It is an inflammation of the urinary epithelium usually caused by bacteria from gut flora. It can occur anywhere along the urinary tract (urethra, bladder, ureter, kidney). UTI may occur alone or with pyelonephritis, prostatitis, or kidney stones.
Can an uti go away on its own?
What is the pathophysiology of a UTI? Urinary tract infections are caused by bacterium that invade the urinary epithelium cells causing irritation and inflammation of these cells. The infection can start in the urethra and can progress its way up to the bladder, ureters, or kidney. Click to see full answer. In respect to this, what causes a UTI?
What are some common causes of an uti?
Apr 12, 2022 · Uropathogenic bacteria, derived from a subset of fecal flora, have traits that enable adherence, growth, and resistance of host defenses. These traits facilitate colonization and infection of the...

What is urinary tract infection pathophysiology?
urinary tract infection (UTI), in humans, inflammation of the renal system characterized by frequent and painful urination and caused by the invasion of microorganisms, usually bacteria, into the urethra and bladder. Infection of the urinary tract can result in either minor or major illness.Mar 3, 2022
What is the main cause of a UTI?
A UTI develops when microbes enter the urinary tract and cause infection. Bacteria are the most common cause of UTIs, although fungi rarely can also infect the urinary tract. E. coli bacteria, which live in the bowel, cause most UTIs.Feb 4, 2022
What are 3 symptoms of a UTI?
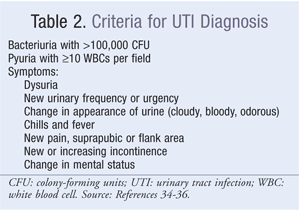
SymptomsA strong, persistent urge to urinate.A burning sensation when urinating.Passing frequent, small amounts of urine.Urine that appears cloudy.Urine that appears red, bright pink or cola-colored — a sign of blood in the urine.Strong-smelling urine.More items...•Apr 23, 2021
Why does my girlfriend keep getting UTIs?
Women are more prone to UTIs mostly because of their anatomy. A woman's urethra is shorter than a man's. Plus it is located near the openings of the vagina and anus, meaning there's more opportunity for bacteria from both those areas to spread—or be wiped—into the urethra.
What is a UTI?
DEFINITION: It is an inflammation of the urinary epithelium usually caused by bacteria from gut flora. It can occur anywhere along the urinary tract (urethra, bladder, ureter, kidney). UTI may occur alone or with pyelonephritis, prostatitis, or kidney stones.
What is the upper UTI?
Upper UTI include pyelonephritis (infection of upper urinary tracts – ureter, renal pelvis, and kidneys). Up to 50% of women may have a UTI at some point in their lives. Cystitis is more common in women because they have a shorter urethra than men, and that urethra is close to the anus.
Why do men have longer urethras than women?
Men have a longer urethra compared to women, making it harder for bacteria to enter the bladder. Men also produce mucous secretions from the prostate to protect them against infection. The body’s immune response plays a key role in ...
How does the bladder and urethra maintain a sterile environment?
The bladder and urethra maintain a sterile environment by preventing bacteria from clinging to its structures. Bacteria are expelled out of the body during urination. The normal composition of urine provides a bactericidal ...
What is the most common UTI?
The most common type of UTI is acute cystitis. Acute cystitis is an inflammation to the bladder and is the most common site of UTI. Cystitis is a part of lower UTI, along with urethritis ( inflammation of urethra). Upper UTI include pyelonephritis (infection of upper urinary tracts – ureter, renal pelvis, and kidneys).
What is the purpose of cystoscopy?
A cystoscopy can be used to look at the bladder’s appearance in individuals with acute cystitis. In mild infections, the bladder’s mucosa will appear red. In more advanced infections, the mucosa will have hemorrhagic areas along with pus and exudates. If left untreated the infection can cause bladder wall necrosis.
What is the immune response to bacteria?
Immune response to bacteria begins once the bacteria passes the distal urethra and goes into the bladder. Toll-like receptors on the uroepithelium recognize bacterial patterns and initiate an immune response. This recruits neutrophils and macrophages which leads to phagocytosis and inflammation.
What are the symptoms of a UTI?
Part of urinary tract affected. Signs and symptoms. Kidneys (acute pyelonephritis) Back pain or side (flank) pain. High fever.
What is the cause of UTI?
This type of UTI is usually caused by Escherichia coli (E. coli), a type of bacteria commonly found in the gastrointestinal (GI) tract. However, sometimes other bacteria are responsible.
Why does my bladder get infected?
Causes. Urinary tract infections typically occur when bacteria enter the urinary tract through the urethra and begin to multiply in the bladder. Although the urinary system is designed to keep out such microscopic invaders, these defenses sometimes fail.
What are the complications of a UTI?
Complications of a UTI may include: Recurrent infections, especially in women who experience two or more UTIs in a six-month period or four or more within a year. Permanent kidney damage from an acute or chronic kidney infection (pyelonephritis) due to an untreated UTI.
How to reduce the risk of urinary tract infection?
You can take these steps to reduce your risk of urinary tract infections: Drink plenty of liquids, especially water. Drinking water helps dilute your urine and ensures that you'll urinate more frequently — allowing bacteria to be flushed from your urinary tract before an infection can begin. Drink cranberry juice.
Which organs remove waste from the body?
Your urinary system — which includes your kidneys, ureters, bladder and urethra — removes waste from your body through urine. Your kidneys, located in the rear portion of your upper abdomen, produce urine by filtering waste and fluid from your blood.
What is the urinary system?
Male urinary system. Your urinary system — which includes your kidneys, ureters, bladder and urethra — removes waste from your body through urine. Your kidneys, located in the rear portion of your upper abdomen, produce urine by filtering waste and fluid from your blood. A urinary tract infection (UTI) is an infection in any part ...
What is UTI in medical terms?
Urinary tract infection (UTI) refers to a symptomatic bacterial infection within the urinary tract. This includes a lower urinary tract infection – cystitis (symptomatic infection of the bladder), or an upper urinary tract infection – acute pyelonephritis (symptomatic infection of the kidney). These definitions are based upon a grouping of symptoms.
Why is the urinary tract sterile?
Except for the distal urethra, the urinary tract is normally sterile due to host defenses against bacterial colonization.
Is UTI a complicated condition?
This is only treated in certain cases, such as prior to a urological operation, in pregnant women, or in immunocompromised patients. UTIs may be considered complicated if symptoms of pye lonephritis emerge, or if a UTI is found in certain patient populations, including the immunosuppressed, men, pregnant women, diabetics, ...
Why are females at higher risk for UTI?
Now, females are a higher risk for UTI’s because the urethra is shorter – so the bladder is physically closer to the outside than in a male whose urethra is much longer. However, as males age and their prostates enlarge, they experience urinary stasis, which can cause an increased risk of UTI’s.
Can a UTI be a sepsis?
So let’s recap. A UTI is an infection that occurs anywhere in the urinary tract. It can progress to sepsis if left untreated – in fact we call that urosepsis.
What causes urinary tract infections?
A urinary tract infection is caused by micro-organisms in the urinary tract. Most of these bacterial organisms are from the gastrointestinal tract. Common causes of UTIs are E.Coli (about 85% or more), Klebsiella species and Staphylococcus saprophyticus (1). Lower UTIs affect the bladder (cystitis) and urethra.
What is the VUR in UTI?
Previous UTI. Voiding dysfunction. Vesicoureteral reflex ( VUR) - this is the reflux of urine from the bladder into the ureter (can be unilateral or bilateral), Around 33% of infants and children who have a urinary tract infection have VUR. Sexual abuse – can cause urinary symptoms but infection is uncommon.
What is the best way to collect urine?
A clean catch urine sample is the recommended method for urine collection. If a clean catch urine sample is unobtainable, other non-invasive methods such as urine collection pads should be used. Cotton wool balls, gauze and sanitary towels should not be used to collect urine in infants and children.
Is it normal to have a urine dip and discharge?
Vulvovaginitis or vaginal foreign body – this would present with vaginal discharge and urine dip would be normal. There may be a history of sexual abuse, if this is the case or if it is suspected then social services must be informed and safeguarding measures put into place. The use of bubble baths may also cause this.
Can meningitis cause rash?
Meningitis – presentation will include photophobia, neck stiffness and rash (1). It is rare but healthcare professionals should be aware that urinary symptoms could be due to child abuse. Consider if a child has dysuria or ano-genital discomfort that is persistent or recurrent and has no medical explanation.
What is a UTI?
What is a urinary tract infection (UTI)? UTIs are common infections that happen when bacteria, often from the skin or rectum, enter the urethra, and infect the urinary tract. The infections can affect several parts of the urinary tract, but the most common type is a bladder infection (cystitis).
What are the factors that increase the risk of UTI?
Other factors that can increase the risk of UTIs: A previous UTI. Sexual activity, and especially a new sexual partner. Changes in the bacteria that live inside the vagina (vaginal flora), for example caused by menopause or use of spermicides. Pregnancy.
Why are UTIs more common in women?
UTIs are more common in women and girls because their urethras are shorter and closer to the rectum, which makes it easier for bacteria to enter the urinary tract.
Can a toddler have a UTI?
While fever is the most common sign of UTI in infants and toddlers, most children with fe ver do not have a UTI. Talk to a doctor if you are concerned. See a doctor right away if your child is younger than 3 months old and has a fever of 100.4 °F (38 °C) or higher.
Can antibiotics cause diarrhea?
However, any time you take antibiotics, they can cause side effects. Side effects can range from minor reactions, such as a rash, to very serious health problems, such as antibiotic-resistant infections or C. diff infection, which causes diarrhea that can lead to severe colon damage and death. Call your doctor if you develop any side effects ...
Overview
Symptoms
- Urinary tract infections don't always cause signs and symptoms, but when they do they may include: 1. A strong, persistent urge to urinate 2. A burning sensation when urinating 3. Passing frequent, small amounts of urine 4. Urine that appears cloudy 5. Urine that appears red, bright pink or cola-colored — a sign of blood in the urine 6. Strong-smelling urine 7. Pelvic pain, in wo…
Causes
- Urinary tract infections typically occur when bacteria enter the urinary tract through the urethra and begin to multiply in the bladder. Although the urinary system is designed to keep out such microscopic invaders, these defenses sometimes fail. When that happens, bacteria may take hold and grow into a full-blown infection in the urinary tract. The most common UTIsoccur mainly in w…
Risk Factors
- Urinary tract infections are common in women, and many women experience more than one infection during their lifetimes. Risk factors specific to women for UTIsinclude: 1. Female anatomy.A woman has a shorter urethra than a man does, which shortens the distance that bacteria must travel to reach the bladder. 2. Sexual activity. Sexually active women tend to hav…
Complications
- When treated promptly and properly, lower urinary tract infections rarely lead to complications. But left untreated, a urinary tract infection can have serious consequences. Complications of a UTImay include: 1. Recurrent infections, especially in women who experience two or more UTIsin a six-month period or four or more within a year. 2. Permanent kidney damage from an acute or …
Prevention
- You can take these steps to reduce your risk of urinary tract infections: 1. Drink plenty of liquids, especially water.Drinking water helps dilute your urine and ensures that you'll urinate more frequently — allowing bacteria to be flushed from your urinary tract before an infection can begin. 2. Drink cranberry juice. Although studies are not conclusive that cranberry juice prevents UTIs, …