Medication
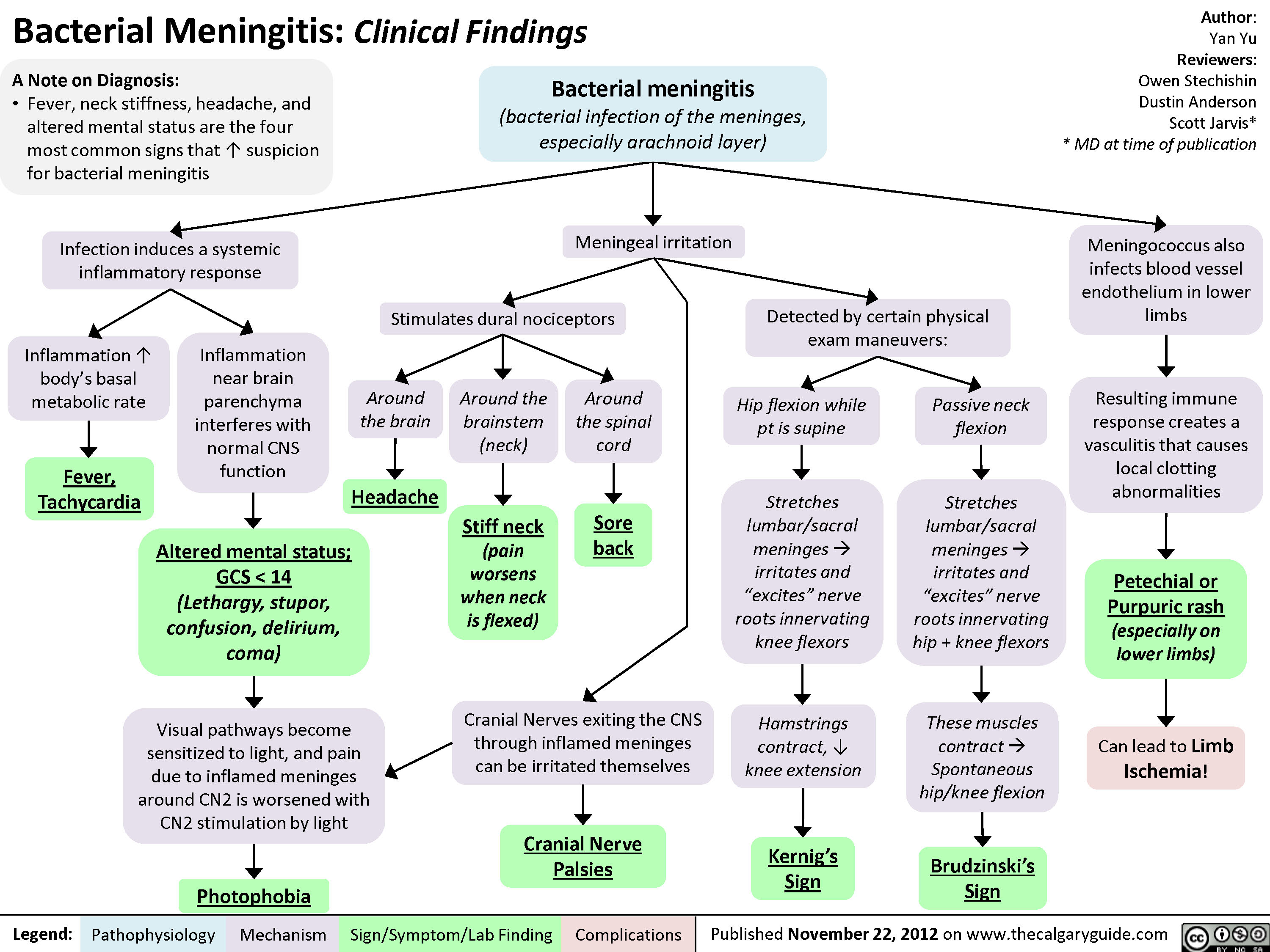
The hallmark symptoms of bacterial meningitis are:
- high fever
- stiff neck
- severe headache
Self-care
Viral meningitis is contagious after three days once the infection starts and ten days after the symptoms develop. Bacterial meningitis is contagious depending on the type of bacteria causing the infection. It may be contagious during the incubation period and for about an additional fourteen days.
Nutrition
Meningitis is usually caused by a viral or bacterial infection. Viral meningitis is the most common and least serious type. Bacterial meningitis is rare, but can be very serious if not treated. Several different viruses and bacteria can cause meningitis, including: meningococcal bacteria – there are several different types, called A, B, C, W, X, Y and Z; pneumococcal bacteria
What are the first signs of bacterial meningitis?
meningitis, bacteremia and miscarriages. The pathogen that causes this infection is the Listeria bacteria. Juan José Quereda, researcher with a Ramón y Cajal contract and professor at the CEU Cardenal Herrera University (CEU UCH), where he leads the ...
What is bacterial meningitis and is it contagious?
Is meningitis caused by bacteria or a virus?
What is the bacteria that causes meningitis?

What is the mechanism of meningitis?
The bacteria or infective organism spreads through the blood. They reach the meninges by one of two main routes: through the bloodstream or through direct contact between the meninges and either the nasal cavity or the skin. The infection begins in one part of the body – e.g. throat or lungs and spreads to the brain.
What is the pathophysiology of viral meningitis?
The pathogenesis of viral meningitis begins when the causative agent enters the host through respiratory secretions or by the fecal-oral route to cause primary infection in the respiratory or gastrointestinal (GI) tract.
What are the physiological effects of meningitis?
Some of the most common complications associated with meningitis are: hearing loss, which may be partial or total – people who have had meningitis will usually have a hearing test after a few weeks to check for any problems. recurrent seizures (epilepsy) problems with memory and concentration.
What is the first stage of meningitis pathogenesis?
The first symptom of meningitis is usually vomiting. A severe bursting headache develops when the meninges have become inflamed and the pressure of the cerebrospinal fluid has increased. Stiffness of the neck then develops, owing to irritation of the spinal nerves supplying those muscles.
What is bacterial meningitis?
What is bacterial meningitis? Meningitis is an infection of the membranes (meninges) that protect the spinal cord and brain. When the membranes become infected, they swell and press on the spinal cord or brain. This can cause life-threatening problems. Meningitis symptoms strike suddenly and worsen quickly.
What's the difference between viral and bacterial meningitis?
Meningitis caused by bacteria can be deadly and requires immediate medical attention. Vaccines are available to help protect against some kinds of bacterial meningitis. Meningitis caused by viruses is serious but often is less severe than bacterial meningitis.
How does meningitis cross the blood brain barrier?
In order to cause meningitis, bacterial pathogens must survive in the bloodstream and penetrate or transmigrate across the blood–brain barrier (BBB), which is primarily comprised of a single layer of specialized endothelial cells.
What are the complications of bacterial meningitis?
There are many complications that are associated with bacterial meningitis. These include short-term complications such as seizures, focal neurological deficits and subdural effusions, and long-term complications such as hearing loss, cognitive impairment, hydrocephalus, learning disability, and epilepsy [8,36,37,38].
What part of the brain is affected by meningitis?
Bacterial meningitis is a serious and life threatening form of meningitis that occurs due to a bacterial infection. Meningitis affects the meninges, which are membranes that surround the brain and spinal cord. The meninges work with the cerebrospinal fluid to protect the central nervous system (CNS).
What is the anatomy and physiology of meningitis?
Meningitis is inflammation of the layers of tissue that cover the brain and spinal cord (meninges) and of the fluid-filled space between the meninges (subarachnoid space). Meningitis can be caused by bacteria, viruses, or fungi, by disorders that are not infections, or by drugs.
What are the 5 causes of meningitis?
And while meningitis is most often caused by bacteria or a virus, did you know that physical injury, illness, and certain medications can also lead to the condition? There are actually five types of meningitis — bacterial, viral, parasitic, fungal, and non-infectious — each classified by the cause of the disease.
What are 5 symptoms of meningitis?
Symptoms of meningitis, septicaemia and meningococcal disease include:a high temperature.cold hands and feet.vomiting.confusion.breathing quickly.muscle and joint pain.pale, mottled or blotchy skin.spots or a rash.More items...
How is viral meningitis contracted?
You can get viral meningitis by breathing in viral particles that have been sneezed or coughed into the air by another infected person. You can also become infected by touching surfaces contaminated with the virus, or through contact with faeces (for example, by changing nappies).
How does meningitis cross the blood brain barrier?
In order to cause meningitis, bacterial pathogens must survive in the bloodstream and penetrate or transmigrate across the blood–brain barrier (BBB), which is primarily comprised of a single layer of specialized endothelial cells.
How does meningitis cause increased intracranial pressure?
Meningitis causes an imbalance between the water content of the brain parenchyma, CSF volume, and cerebral blood flow (CBF), resulting in an increase of ICP.
What part of the brain is affected by meningitis?
Bacterial meningitis is a serious and life threatening form of meningitis that occurs due to a bacterial infection. Meningitis affects the meninges, which are membranes that surround the brain and spinal cord. The meninges work with the cerebrospinal fluid to protect the central nervous system (CNS).
What Is Bacterial Meningitis?
Acute bacterial meningitis is the most common form of meningitis. Approximately 80% of all cases are acute bacterial meningitis. Bacterial meningit...
Who Gets Bacterial Meningitis?
Children between the ages of 1 month and 2 years are the most susceptible to bacterial meningitis.Adults with certain risk factors are also suscept...
What Causes Bacterial Meningitis?
The bacteria most often responsible for bacterial meningitis are common in the environment and can also be found in your nose and respiratory syste...
What Are The Symptoms of Bacterial Meningitis?
You want to watch for high fever, headaches, and an inability to lower your chin to your chest due to stiffness in the neck.In older children and a...
What is the best treatment for bacterial meningitis?
Prophylaxis. When someone has bacterial meningitis, a doctor may recommend antibiotics to help prevent people around the patient from getting sick. Doctors call this prophylaxis. CDC recommends prophylaxis for: Close contacts of someone with meningitis caused by N. meningitidis.
What happens when you have sepsis?
It is a life-threatening medical emergency. Sepsis happens when an infection triggers a chain reaction throughout your body. Without timely treatment, sepsis can quickly lead to tissue damage, organ failure, and death. Some causes of bacterial meningitis are more likely to affect certain age groups:
How long does it take for TB to show up in a baby?
If you think your baby or child has any of these symptoms, call the doctor right away. Typically, symptoms of bacterial meningitis develop within 3 to 7 days after exposure; note, this is not true for TB meningitis, which can develop much later after exposure to the bacteria.
How does meningitis spread?
How It Spreads. Certain germs that cause bacterial meningitis, such as L. monocytogenes, can spread through food. But most of these germs spread from one person to another. How people spread the germs often depends on the type of bacteria.
What are the risks of meningitis?
Certain medical conditions: Certain medical conditions, medications, and surgical procedures put people at increased risk for meningitis. For example, having an HIV infection or a cerebrospinal fluid leak, or not having a spleen can increase a person’s risk for several types of bacterial meningitis. Working with meningitis-causing pathogens: ...
How do you spread N. meningitidis?
N. meningitidis: People spread these bacteria by sharing respiratory or throat secretions (saliva or spit). This typically occurs during close (coughing or kissing) or lengthy (living together) contact.
What to do when you cough and sneeze?
Cover your mouth and nose with a tissue when you cough or sneeze (use your upper sleeve or elbow if a tissue isn’t available)
What is the most common form of meningitis?
Acute bacterial meningitis is the most common form of meningitis. Approximately 80 percent of all cases are acute bacterial meningitis. Bacterial mening itis can be life threatening. The infection can cause the tissues around the brain to swell. This in turn interferes with blood flow and can result in paralysis or even stroke.
How long does it take for bacterial meningitis to show symptoms?
The onset of symptoms is fast, within 24 hours. If allowed to progress, you can die from bacterial meningitis.
What is meningitis caused by?
Meningitis can be caused by a bacterial, fungal or viral infection. Meningitis can be acute, with a quick onset of symptoms, it can be chronic, lasting a month or more, or it can be mild or aseptic.
How to treat meningitis?
Bacterial meningitis is treated with antibiotics. A general intravenous antibiotic with a corticosteroid to bring down the inflammation may be prescribed even before all the test results are in. When the specific bacteria are identified, your doctor may decide to change antibiotics. In addition to antibiotics, it will be important to replenish fluids lost from loss of appetite, sweating, vomiting and diarrhea.
How old are you when you get bacterial meningitis?
Who gets bacterial meningitis? Children between the ages of 1 month and 2 years are the most susceptible to bacterial meningitis. Adults with certain risk factors are also susceptible. You are at higher risk if you abuse alcohol, have chronic nose and ear infections, sustain a head injury or get pneumococcal pneumonia.
What are the symptoms of a stroke in older children?
In older children and adults, you may see confusion, irritability, increasing drowsiness. Seizures and stroke may occur.
How old do you have to be to get a booster shot?
All children aged 11-12 years old, with a booster dose at 16 years old.
What is bacterial meningitis?
Meningitis is an infection of the membranes (meninges) that protect the spinal cord and brain. When the membranes become infected, they swell and press on the spinal cord or brain. This can cause life-threatening problems. Meningitis symptoms strike suddenly and worsen quickly.
How is bacterial meningitis diagnosed?
To diagnose this condition, a healthcare provider will do a spinal tap (also called a lumbar puncture) to take a sample of fluid from around the spinal cord. The fluid is then tested for bacteria. The healthcare provider will also ask about your symptoms and do a physical exam.
How long does it take for meningitis to come on?
Lack of appetite. Seizures (sometimes also seen in adults if the meningitis is advanced) Symptoms typically come on quickly, in as little as a couple of hours or up to a day or two. If you think you or your child may have meningitis, go to an emergency room right away.
Why do people get meningitis?
Experts don't always know why meningitis happens. Some people get it when their immune system is weak or they've recently been sick. A head injury may also increase risk. Bacterial meningitis is more common in infants under 1 year of age and people ages 16 to 21.
What does it mean when your neck is stiff?
If you feel like you've got the flu with unusual stiffness in your neck, it could be meningitis.
Can meningitis cause stroke?
It can lead to brain damage, paralysis, or stroke. In some cases, it can be fatal. Many different types of bacteria can cause meningitis. Vaccines are available that target many of these bacteria. For this reason, it's important to know what's causing meningitis.
How to manage meningitis?
To improve patient outcomes, it is best managed by an interprofessional team that includes an infectious disease expert, emergency department physician, laboratory professional, internist, nurse practitioner, and a pediatrician. The key is to start prompt treatment without delay. One should not wait for cultures if suspicion is high of meningitis. The infectious disease specialist should consult with a board-certified infectious disease pharmacist so optimal antimicrobial therapy based on the latest antibiogram data can be initiate empirically, enhancing the chance for successful treatment. These patients need inpatient treatment until all symptoms have disappeared, therefore the nursing staff will be responsible for administration as well as monitoring for therapeutic effectiveness and adverse drug events, reporting any concerns to the team. The outlook for patients with delayed diagnosis or treatment is poor. More important, delays also lead to litigation. [16][17]
What is the CSF for meningitis?
The CSF should be sent for Gram stain, culture, complete cell count (CBC), and glucose and protein levels. Bacterial meningitis typically results in low glucose and high protein levels in the cerebrospinal fluid. As CSF glucose levels are dependent on circulating serum glucose levels, the CSF to serum glucose ratio is considered more reliable parameter for the diagnosis of acute bacterial meningitis than absolute CSF glucose levels. A neutrophil predominance on cell count would be expected.
What is the rmpm gene?
rmpM gene as a genetic marker for human bacterial meningitis.
What to do before lumbar puncture?
The diagnosis would be confirmed with bacteria identified on gram stain or culture. A non-contrast CT scan of the head should be performed before lumbar puncture if the patient has a risk of herniation. Risk factors include papilledema on the exam, new onset seizures, focal neurologic deficits, or is immunocompromised. Consider delaying the lumbar puncture if the patient has unstable vital signs, coagulation abnormalities, or has had a recent seizure. Treat with antibiotics empirically if testing is going to be delayed. Blood cultures should be obtained as 53% of patients have concurrent bacteremia. Elevated C-reactive protein or procalcitonin levels would suggest a bacterial rather than viral etiology. [10][11][12]
What is the Creative Commons 4.0 license?
This book is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits use, duplication, adaptation, distribution, and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, a link is provided to the Creative Commons license, and any changes made are indicated.
Is meningitis a serious disease?
Bacterial meningitis is a bacterial infection of the meninges, which is the protective covering for the brain and spinal cord resulting in inflammation. It is a serious and life-threatening condition that requires prompt diagnosis and treatment.[1][2][3]
Is meningitis more common in children?
Bacterial meningitis was previously more common in pediatric patients. However, as vaccines are developed and utilized, the prevalence of acute bacterial meningitis has decreased and the epidemiology of causative microorganisms has changed. Vaccinations have increased the median age of patients infected. In 2006 there were 72,000 meningitis-related hospitalizations in the United States. The majority of these cases were due to viral infection (54.6%). Bacterial infections accounted for 21.8% of cases, and 7.3% were due to fungi and parasite infections, while 17.2% were due to an unspecified cause. There was an 8% in-hospital mortality rate for patients with bacterial meningitis, and it rose substantially for patients older than 45. [7][8][9] The annual incidence of meningitis in the United States decreased from 2.00 cases per 100,000 population in 1998–1999 to 1.38 cases per 100,000 population in 2006–2007 while the median age of patients increased from 30.3 years in 1998–1999 to 41.9 years in 2006–2007.[4] As per CDC data, rates of meningococcal disease have been declining in the United States since the late 1990s. In 2017, there were about 350 total cases of meningococcal disease reported (incidence rate of 0.11 cases per 100,000 persons).
What is the inflammation of the membranes that outline your brain and spinal cord?
Overview. Meningitis is the inflammation of the membranes that outline your brain and spinal cord. These membranes are called meninges, giving the illness its name: “meningitis.”. Meningitis can be bacterial or viral, though there are also fungal forms of the disease. Viral meningitis is the most common form.
How long does it take for meningitis to show symptoms?
Symptoms can begin quickly, sometimes in just a couple hours, or they can progress over a day or two. Seek immediate medical attention if you show symptoms of bacterial meningitis. Your doctor will treat the condition as soon as possible, most likely with antibiotics.
What is the most common form of meningitis?
Viral meningitis is the most common form. Bacterial meningitis is the most serious form. Without treatment, bacterial meningitis can cause paralysis, stroke, seizures, sepsis, and even death. Read more: Meningitis ».
How to treat meningitis?
But the best way to combat meningitis is to prevent it through vaccination and sound health practices.
How long does it take for a baby to get a purple rash?
a rash of purple discoloration. Parents of babies and toddlers under the age of 2 should closely monitor any lingering irritability or lack of interest in eating, as these can also be symptoms of meningitis. Symptoms can begin quickly, sometimes in just a couple hours, or they can progress over a day or two.
What are the best ways to prevent meningitis?
There are vaccines that protect against pneumococcus, meningococcus, and Hib, all of which cause meningitis. Vaccinations are key to the prevention of meningitis. See your doctor to make sure your vaccinations, and those of your children, are up-to-date.
Is meningitis contagious?
But most of the germs that can lead to bacterial meningitis aren’t contagious. In fact, the bacteria that cause meningitis are less contagious than viruses that cause the cold or flu . Not all bacteria that cause meningitis are spread from one person to another.
What causes meningitis in animals?
Parasites can cause a rare type of meningitis called eosinophilic meningitis. Parasitic meningitis can also be caused by a tapeworm infection in the brain (cysticercosis) or cerebral malaria. Amoebic meningitis is a rare type that is sometimes contracted through swimming in fresh water and can quickly become life-threatening. The main parasites that cause meningitis typically infect animals. People are usually infected by eating foods contaminated with these parasites. Parasitic meningitis isn't spread between people.
What is the most common cause of meningitis in the US?
Viral meningitis is usually mild and often clears on its own. Most cases in the United States are caused by a group of viruses known as enteroviruses, which are most common in late summer and early fall. Viruses such as herpes simplex virus, HIV, mumps virus, West Nile virus and others also can cause viral meningitis.
How old is the most likely age to get meningitis?
Age. Most cases of viral meningitis occur in children younger than age 5. Bacterial meningitis is common in those under age 20.
What is the name of the membrane that protects the brain and spinal cord?
Close. Meningitis. Meningitis. Meningitis is an infection and inflammation of the fluid and three membranes (meninges) protecting your brain and spinal cord. The tough outer membrane is called the dura mater, and the delicate inner layer is the pia mater.
How long does it take for meningitis to kill?
Bacterial meningitis is serious and can be fatal within days without prompt antibiotic treatment. Delayed treatment increases the risk of permanent brain damage or death.
What to do if you suspect someone has meningitis?
Seek immediate medical care if you suspect that someone has meningitis. Early treatment of bacterial meningitis can prevent serious complications.
What is the term for inflammation of the membranes surrounding the brain and spinal cord?
Meningitis is an inflammation of the fluid and membranes (meninges) surrounding your brain and spinal cord.
Causes
Risk Factors
How It Spreads
Signs and Symptoms
Specialist to consult
Diagnosis
Treatment
Prevention