Can the PDSA model be used for Change Management?
Use the PDSA model for effective change management Use the PDSA model for effective change management Educ Prim Care. 2015 Jul;26(4):279-81.doi: 10.1080/14739879.2015.11494356. Authors
What is the PDSA process used for?
The PDSA process is widely used and familiar to many involved in clinical care. As such, it offered familiarity and our training provided more in-depth exposure to how it could be used. Simple exposure to this process could improve other aspects of clinics’ care. More important, it allows clinic staff to own the study process [24, 29].
Are PDSA cycles quick and dirty tests of change?
This has led to the impression that PDSA cycles involve ‘quick and dirty’ tests of change. In the rush to empower healthcare staff, there is a danger that the scientific rigour of the PDSA method is frequently compromised.
What is the value of PDSA in Healthcare Improvement?
The value of PDSA in healthcare improvement. The purpose of the PDSA method lies in learning as quickly as possible whether an intervention works in a particular setting and to making adjustments accordingly to increase the chances of delivering and sustaining the desired improvement.

What is PDSA model in healthcare?
The Plan-Do-Study-Act (PDSA) method is a way to test a change that is implemented. Going through the prescribed four steps guides the thinking process into breaking down the task into steps and then evaluating the outcome, improving on it, and testing again.
Why is the PDSA model good?
The PDSA model is efficient and provides clear focus for a project. Moreover, beginning with a thorough planning stage leads to effective action and relevant meaningful data. Good ideas are adequately tested before being implemented.
What is PDSA cycle NHS?
Plan, Do, Study, Act (PDSA) cycles and the model for improvement. What is it? The model for improvement provides a framework for developing, testing and implementing changes leading to improvement. It is based in scientific method and moderates the impulse to take immediate action with the wisdom of careful study.
What are the phases of the PDSA model for performance improvement?
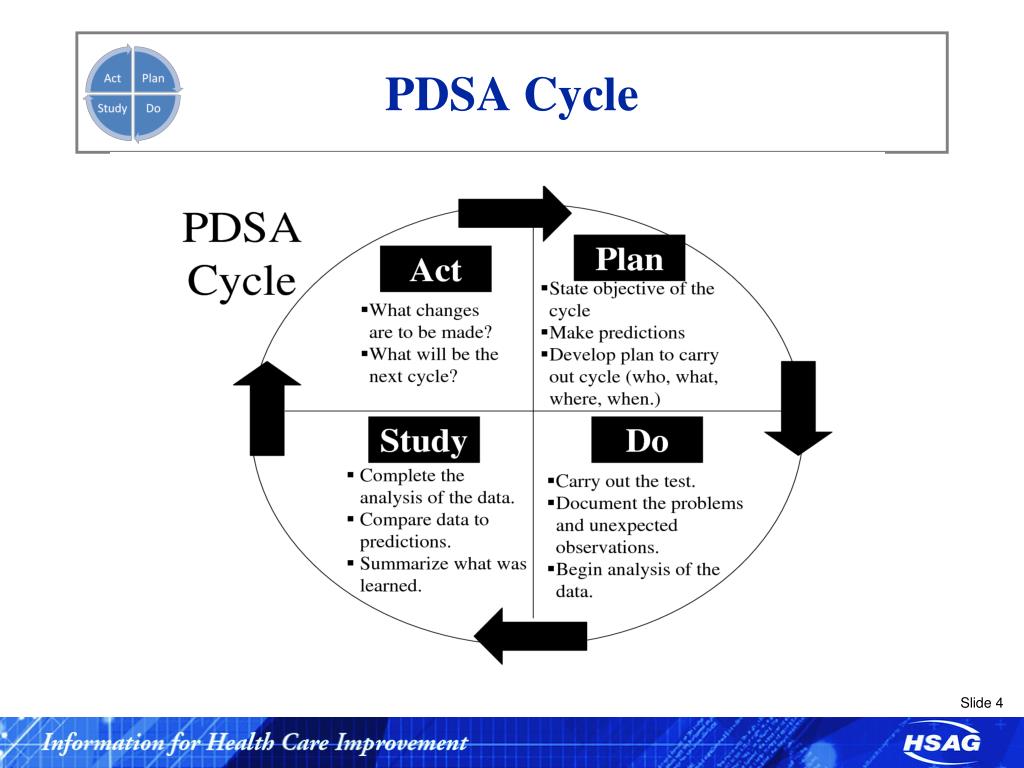
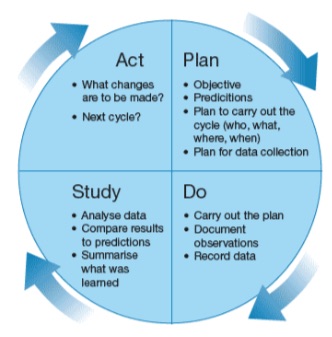
Plan: Develop the initiative. Do: Implement your plan. Study: Analyze the results. Act: Adjust the process based on the results found in the Study phase.
Why is PDSA important in healthcare?
Using PDSA cycles can help clinicians deliver improvements in patient care through a structured experimental approach to learning and tests of change. The PDSA approach facilitates individual, team and organisational learning, making it an essential tool for the future hospital.
What are the important parts of the plan step of the PDSA cycle?
Stages in PDSA CycleIdentify the problem.Analyze the problem.Clarify goals and objectives.Define success.Identify key team players.Plan strategies putting a plan into action.
How do you use the PDSA model?
Steps in the PDSA CycleStep 1: Plan. Plan the test or observation, including a plan for collecting data. ... Step 2: Do. Try out the test on a small scale. ... Step 3: Study. Set aside time to analyze the data and study the results. ... Step 4: Act. Refine the change, based on what was learned from the test.
Who developed the PDSA model?
Edward Deming'sThe PDSA method originates from industry and Walter Shewhart and Edward Deming's articulation of iterative processes which eventually became known as the four stages of PDSA.
Is PDSA a conceptual framework?
In healthcare, PDSA training often overemphasises the conceptual simplicity of the framework and underemphasises the different ways in which the method can be adapted to solve increasingly complex problems.
What is PDSA cycle explain in detail?
The Plan, Do, Study, Act (PDSA) cycle is a method for rapidly testing a change - by planning it, trying it, observing the results, and acting on what is learned. This is a scientific method used for action-oriented learning.
When was the PDSA model introduced?
1993Deming introduced his Shewhart cycle for learning and improvement in the USA in 1986. Dr. Deming introduced a more abbreviated PDSA cycle in 1993.
When was PDSA model created?
1993In 1993 he introduced his new revision of the Shewhart cycle; Plan, Do Study, Adjust (Act) (PDSA).
What is PDSA cycle?
The PDSA Cycle (Plan-Do-Study-Act) is a systematic process for gaining valuable learning and knowledge for the continual improvement of a product, process, or service. Also known as the Deming Wheel, or Deming Cycle, this integrated learning - improvement model was first introduced to Dr. Deming by his mentor, Walter Shewhart ...
What is the act step?
The Act step closes the cycle, integrating the learning generated by the entire process, which can be used to adjust the goal, change methods, reformulate a theory altogether, or broaden the learning – improvement cycle from a small-scale experiment to a larger implementation Plan. These four steps can be repeated over and over as part ...
Why is it important to use PDSA?
When using the PDSA cycle, it's important to include internal and external customers; they can provide feedback about what works and what doesn't. The customer defines quality, so it would make sense to also involve them in the process when appropriate or feasible, to increase acceptance of the end result.
How to summarize a cause analysis?
The end of the cause analysis should summarize the cause analysis by describing and justifying the root causes.
Is PDSA a cycle?
The PDSA cycle is ongoing, and organizations become more efficient as they intuitively adopt PDSA into their planning.
What is PDSA cycle?
As a standard quality-improvement process , the PDSA cycle helps introduce a new program into a complex environment, such as primary care. An improvement process, for example, may identify the need for a workflow that can improve efficiency (e.g., calling patients with invalid addresses) or training (e.g., best practices for recording historical colonoscopies). This process can also identify additional intervention components to improve effectiveness or reach (e.g., clinic posters that show how to do the test). While PDSA activities are often conducted as multiple small cycles to implement a change, we asked intervention clinic staff to conduct and report on only a single PDSA cycle as part of the pragmatic trial. Because of the heterogeneity of our sites, we assessed each clinic’s quality improvement infrastructure and experiences with the PDSA process before we asked those sites to conduct an activity.
Why is the PDSA cycle important?
Therefore, the PDSA cycle may prove useful in adapting and implementing research-based interventions, particularly where its incorporation into every-day care is a central question.
What is PDSA in health care?
The Plan-Do-Study-Act (PDSA) cycle is a commonly used improvement process in health care settings that might have untapped potential for pragmatic research. A PDSA activity uses small tests of change to optimize a process. A pragmatic clinical trial called the Strategies and Opportunities to STOP Colon Cancer in Priority Populations (STOP CRC) recently used this process to optimize the implementation of a cancer screening outreach program. Unlike traditional trials, pragmatic clinical trials, occur in real-world settings where everyday care happens; as such, they require extensive collaboration between researchers and the staff of a health care system [1–6]. This paper describes how our study used PDSA in pragmatic research to assist in improving implementation of the planned intervention (a mailed outreach program); however, this technique could have broader applications in a wide range of quality improvement activities and other types of pragmatic trials.
How is PDSA used in clinical practice?
While PDSA cycles are commonly used in clinical care, few clinical research trials have documented its use for implementation. Standard clinical trials emphasize internal rather than external validity, using highly controlled environments and selected populations. In contrast, pragmatic studies are generally embedded in care delivery environments. Few research-based interventions can be used ‘off the shelf’; adaptations are often needed to accommodate unique aspects of a setting or population. Since the PDSA cycle is a clinical improvement process, it is often familiar to clinical staff. Therefore, the PDSA cycle may prove useful in adapting and implementing research-based interventions, particularly where its incorporation into every-day care is a central question.
What are the benefits of PDSA?
Clinic-selected PDSA activities included refining the intervention staffing model, improving outreach materials, and changing workflow steps. Common benefits of using PDSA cycles in pragmatic research were that it provided a structure for staff to focus on improving the program and it allowed staff to test the change they wanted to see. A commonly reported challenge was measuring the success of the PDSA process with the available electronic medical record tools.
A. Recruit Team
B. Draft An Aim Statement
- Describe what you want to accomplish in an aim statement. Try to answer those three fundamental questions: 1. What are we trying to accomplish? 2. How will we know that a change is an improvement? 3. What change can we make that will result in improvement?
C. Describe Current Context and Process
- Brainstorm
Examine your current process. Start by asking the team these basic questions: 1. What are we doing now? 2. How do we do it? 3. What are the major steps in the process? 4. Who is involved? 5. What do they do? 6. What is done well? 7. What could be done better? You might have already a… - Try a Swim Lane Map
You may find it helpful to construct a swim lane mapto visually describe your process. Creating a process flow or at least depicting the current process can be very useful. If your team runs into road blocks, you might have found where the problem is occurring—or maybe the right person fo…
D. Describe The Problem
- Using the aim statement created in Step B, state your desired accomplishments, and use data and information to measure how your organization meets/does not meet those accomplishments. For example: If your objective is to maximize your staff's quality of work life, you might find evidence by surveying employees on workplace stressors.
E. Identify Causes and Alternatives
- Analyze Causes
For the problem in your problem statement, work to identify causes of the problem using tools such as control charts, fishbones, and work flow process maps (e.g., flowcharts, swim lane maps). The end of the cause analysis should summarize the cause analysis by describing and ju… - Develop Alternatives
Try to mitigate your root causes by completing the statement, "If we do __________, then __________ will happen." Choose an alternative (or a few alternatives) that you believe will best help you reach your objective and maximize your resources. Develop an action plan, including necessary staff/r…
Reflect on Plan and Outcomes
- If your team determined the plan resulted in success, standardize the improvement and begin to use it regularly. After some time, return to Stage 1: Planand re-examine the process to learn where it...
- If your team believes a different approach would be more successful, return to Stage 1: Plan, and developa new and different plan that might result in success.
Celebrate Improvements and Lessons Learned
- Communicate accomplishments to internal and external customers
- Take steps to preserve your gains and sustain your accomplishments
- Make long-term plans for additional improvements
- Conduct iterative PDSA cycles when needed