Simply stated, the penumbra is the part of the brain that is sandwiched between brain regions committed to die and those that receive enough blood to communicate. Therefore, it is ischemic brain tissue that has just enough energy to survive for a short time but not enough to communicate and function. The life expectancy of the penumbra is short.
What is the penumbra in anatomy?
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia In pathology and anatomy the penumbra is the area surrounding an ischemic event such as thrombotic or embolic stroke. Immediately following the event, blood flow and therefore oxygen transport is reduced locally, leading to hypoxia of the cells near the location of the original insult.
What is the ischemic penumbra?
The ischemic penumbra has been defined in a variety of ways, but the most clinically relevant definition is that portion of the ischemic territory … The concept of the ischemic penumbra is an important one for both basic investigators of cerebral ischemia and for clinicians who treat stroke patients.
How is the penumbral area of the brain detected?
The penumbral area can also be detected based upon an integration of three factors. These factors include: the site of vessel occlusion, the extent of oligaemia (hypoperfused area surrounding the penumbra, but not at risk of infarction) at that moment, and the mismatch between this perfusion defect and the area of the brain already infarcted.
What is the life expectancy of the penumbra?
Therefore, it is ischemic brain tissue that has just enough energy to survive for a short time but not enough to communicate and function. The life expectancy of the penumbra is short. Although the penumbra is an elegant concept, in practice it has been a difficult one to exploit.
How long does the penumbra area last?
Is the penumbra a brain tissue?
About this website
Where is the penumbra located in the brain?
Ischemic penumbra denotes the part of an acute ischemic stroke that is at risk of progressing to infarction but is still salvageable if reperfused. It is usually located around an infarct core which represents the tissue which has already infarcted or is going to infarct regardless of reperfusion.
What does the penumbra do?
The penumbra causes partial solar eclipses, penumbral lunar eclipses, and partial lunar eclipses. The antumbra is responsible for only one type of eclipse, the annular solar eclipse. The partial lunar eclipse happens when the Earth's penumbra veils a part of the Moon's visible surface, which isn't covered by the umbra.
What is the penumbra region in a stroke?
In a stroke event, the penumbra is the area surrounding the ischemic core and it is defined as perfused brain tissue at a level within the thresholds of functional impairment and morphologic integrity, which has the capacity to recover and be salvaged if perfusion is improved rapidly.
What is a penumbra in biology?
The penumbra was classically defined as the hypoperfused tissue surrounding the ischemic core in which blood flow is too low to maintain electric activity but sufficient to preserve ion channels.
What is a penumbra in simple terms?
Definition of penumbra 1a : a space of partial illumination (as in an eclipse) between the perfect shadow on all sides and the full light. b : a shaded region surrounding the dark central portion of a sunspot.
What is an example of penumbra?
The definition of a penumbra is the lighted area around the shadow of a planet or moon during an eclipse. An example of the penumbra is the outer lighted area surrounding the shadow of the moon which is created during an eclipse.
What is the ischemic penumbra and why is it important?
The ischemic penumbra refers to tissue at risk of infarction where perfusion is inadequate to support neuronal function, but just adequate to maintain cell viability (1).
How long can penumbra last?
It is believed that without reperfusion, penumbra will progress to infarction, irrespective of the timing of its assessment relative to stroke onset. Studies have demonstrated that penumbra can persist for long time periods of up to 48 hours.
Which part of the brain is affected by a stroke?
The cerebrum is divided into the right and left sides, or hemispheres. Depending on the area and side of the cerebrum affected by the stroke, any, or all, of these functions may be impaired: Movement and sensation. Speech and language.
What causes the penumbra stroke?
In pathology and anatomy the penumbra is the area surrounding an ischemic event such as thrombotic or embolic stroke. Immediately following the event, blood flow and therefore oxygen transport is reduced locally, leading to hypoxia of the cells near the location of the original insult.
What is a synonym for penumbra?
shadow, dark, gloom, obscurity, shade, concealment, darkening, decline, diminution, dimming, extinction, obliteration, occultation, shroud, veil, adumbration, blackness, coolness, cover, darkness.
What is penumbra in imaging?
CT perfusion A fairly common definition for penumbra is the area of brain with 1,2: prolonged (increased) T-max, typically >6 seconds (or other measures of delayed arrival of contrast such as mean transit time (MTT) or time to peak (TTP)), and... normal or increased cerebral blood volume (CBV) due to autoregulation.
What is the penumbra effect radiography?
The penumbra effect happens when the X-ray source cannot be regarded as a point source and is enhanced as the distance between the object and the detector increases.
Which penumbra is the best?
This all being said, Black Plague was indeed the best of Penumbra series and in overall gameplay, but SOMA trumps overall story. I would have said Amnesia is better, but later in the game enemies would spawn out of mid-air if you ran around a corner too fast.
What is the ischemic penumbra and why is it important?
The ischemic penumbra refers to tissue at risk of infarction where perfusion is inadequate to support neuronal function, but just adequate to maintain cell viability (1).
What is Earth's umbra and penumbra?
During an eclipse, two shadows are cast. The first is called the umbra (UM bruh). This shadow gets smaller as it goes away from the sun. It is the dark center of the eclipse shadow. The second shadow is called the penumbra (pe NUM bruh).
What happens to the penumbra region?
The penumbra region typically occurs when blood flow drops below 20 mL/100 g/min. At this point electrical communication between neurons fails to exist. Cells in this region are alive but metabolic pumps are inhibited, oxidative metabolism is reduced but neurons may begin to depolarize again. Areas of the brain generally do not become infarcted until blood flow to the region drops below 10 to 12 mL/100 g/min. At this point, glutamate release becomes unregulated, ion pumps are inhibited and adenosine triphosphate (ATP) synthesis also stops which ultimately leads to the disruption of intracellular processes and neuronal death.
How to estimate the size of a penumbra?
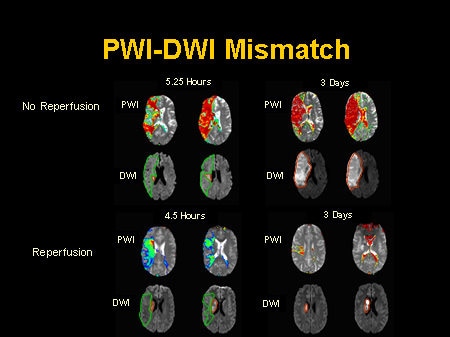
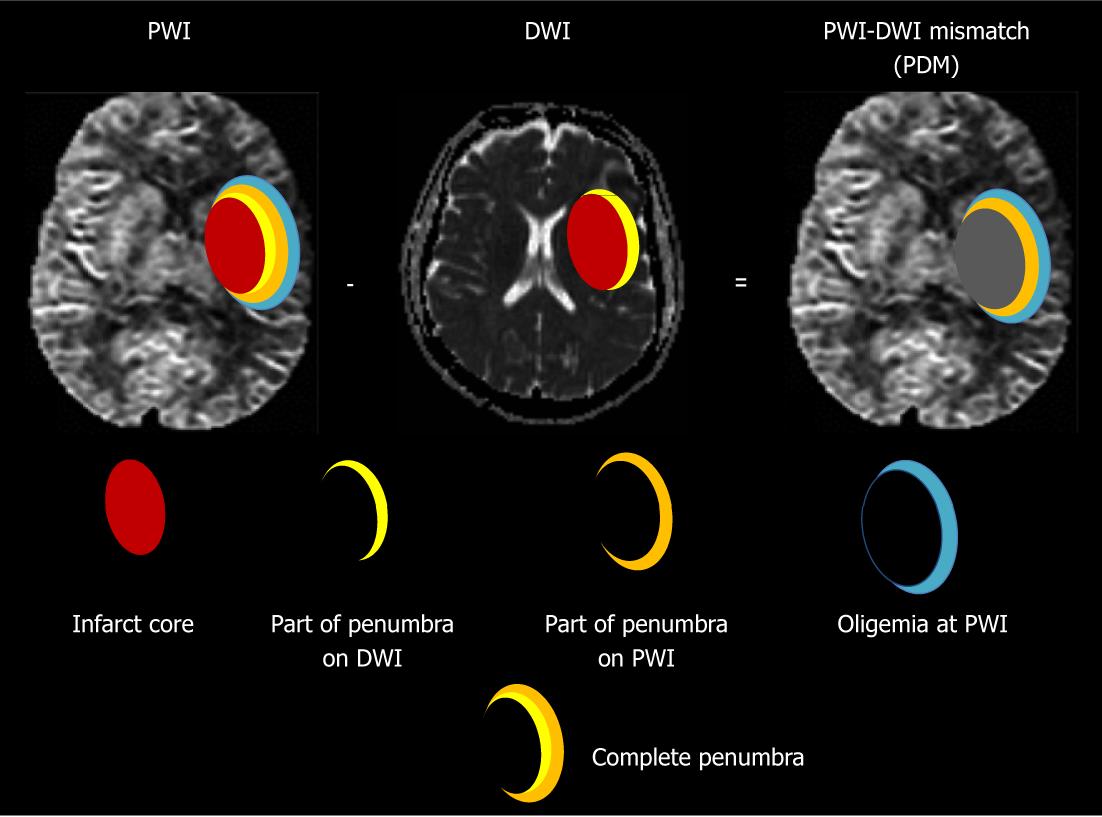
Both of these sequences somewhat overestimates their volumes of interest, but the size of the penumbra can roughly be estimated by subtracting abnormal volume by DWI from abnormal volume by PWI.
What is the term for the area surrounding an ischemic event such as thrombotic or embolic stroke?
Ischemia-related medical term. In pathology and anatomy the penumbra is the area surrounding an ischemic event such as thrombotic or embolic stroke. Immediately following the event, blood flow and therefore oxygen transport is reduced locally, leading to hypoxia of the cells near the location of the original insult.
Why is saving the penumbra important?
As time elapses after the onset of stroke, the extent of the penumbra tends to decrease; therefore, in the emergency department a major concern is to protect the penumbra by increasing oxygen transport and delivery to cells in the danger zone, thereby limiting cell death. The existence of a penumbra implies that salvage of the cells is possible. There is a high correlation between the extent of spontaneous neurological recovery and the volume of penumbra that escapes infarction; therefore, saving the penumbra should improve the clinical outcome.
What is the term for the area of the brain that is damaged but not yet dead?
One widely accepted definition for penumbra describes the area as "ischemic tissue potentially destined for infarction but it isn't irreversibly injured and the target of any acute therapies." The original definition of the penumbra referred to areas of the brain that were damaged but not yet dead, and offered promise to rescue the brain tissue with the appropriate therapies.
What is the use of PET scans in the penumbral?
The third decade of penumbral research found a transitional leap as using positron emission tomography (PET) scanning can identify brain tissue with decreased blood flow and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) has the ability to detect portions of the ischemic tissue that has not yet died.
Is a penumbra salvageable?
The existence of a penumbra implies that salvage of the cells is possible. There is a high correlation between the extent of spontaneous neurological recovery and the volume of penumbra that escapes infarction; therefore, saving the penumbra should improve the clinical outcome.
What is the penumbra of the brain?
Simply stated, the penumbra is the part of the brain that is sandwiched between brain regions committed to die and those that receive enough blood to communicate. Therefore, it is ischemic brain tissue that ...
What is the ischemic penumbra?
Simply stated, the penumbra is the part of the brain that is sandwiched between brain regions committed to die and those that receive enough blood to communicate. Therefore, it is ischemic brain tissue that has just enough energy to survive for a short time but not enough to communicate and function. The life expectancy of the penumbra is short. Although the penumbra is an elegant concept, in practice it has been a difficult one to exploit. For one thing, it is unstable in both time and space. Depending on the severity and the duration of the focal ischemia, it may be anywhere in the ischemic brain. We believe that nimodipine binding experiments have taught us a great deal about the ischemic penumbra. Second, cells in the penumbra may die not by necrosis but by apoptosis. If that is true, then our concepts about the benign transient ischemic attack may need revision. Third, the penumbra may regain its ability to survive not only through reperfusion but also by interrupting the process of commitment to apoptosis.
Is the penumbra ischemic?
Therefore, it is ischemic brain tissue that has just enough energy to survive for a short time but not enough to communicate and function. The life expectancy of the penumbra is short. Although the penumbra is an elegant concept, in practice it has been a difficult one to exploit.
What is the meaning of penumbra?
penumbra. 1. Region of very low illumination on a dark background. 2. Zone in which the brightness varies from some illumination to zero ( umbra) in the shadow cast by an opaque object intercepting light from an extensive light source. See shadow.
What is the term for the region of partial illumination or radiation caused by light or x-rays not originating?
The region of partial illumination or radiation caused by light or x-rays not originating from a point source; also called geometric unsharpness.
What is the penumbra of an ischemic stroke?
Ischemic penumbra denotes the part of an acute ischemic stroke that is at risk of progressing to infarction but is still salvageable if reperfused. It is usually located around an infarct core which represents the tissue which has already infarcted or is going to infarct regardless of reperfusion.
What is the ischemic penumbra on MRI?
MRI. On MRI, the ischemic penumbra is also determined by the area of the brain with reduced perfusion 1: penumbra: shows perfusion changes same as that with CT. infarcted core: shows restricted diffusion (established infarct) apart from decreased cerebral blood volume and cerebral blood flow.
What is the area of the brain with reduced perfusion minus the infarct core?
In practice, which parameters are used to define each component has varied. A fairly common definition for penumbra is the area of brain with 1,2 :
Does the infarct core have a CBF?
This region will have only a moderate decreased cerebral blood flow (CBF). This is in contrast to the infarct core which will have a marked decrease in cerebral blood flow and also a decrease in cerebral blood volume.
What is the penumbra?
The penumbra was classically defined as the hypoperfused tissue surrounding the ischemic core in which blood flow is too low to maintain electric activity but sufficient to preserve ion channels. However, this area is subjected to a wave of deleterious metabolic processes propagated from the core to the neighboring tissue, including excitotoxicity, spreading depression, oxidative stress, and inflammatory response, which lead to the expansion of the ischemic core and the subsequent worsening clinical outcome.
What is the ischemic penumbra?
Thus, the ischemic penumbra is a diagnostic target, allowing the extension of therapeutic windows; it is also a biochemical target, in which an intermittent bioenergetic compromise takes place, and it is a target for brain plasticity, neuroprotection, and neurorepair.
What growth factors are overexpressed in the penumbra?
Growth factors such as transforming growth factor-β or fibroblast growth factor-2 and the chemokine stromal cell-derived factor-1 are overexpressed in the penumbra, being involved in the recruitment of bone marrow-derived cells and neural stem cells to sites of ischemic injury. 21 Stromal cell-derived factor-1 is expressed up to 30 days after stroke in the penumbra, and even later in the ischemic core, when new blood vessels appear. Indeed, stromal cell-derived factor-1 expression in the penumbra was associated with reactive perivascular astrocytes, suggesting that stromal cell-derived factor-1 may play a role in enhancing plasticity after ischemia. 22 The administration of vascular endothelial growth factor has also been related to the promotion of neurogenesis in the subventricular zone and angiogenesis in the ischemic penumbra after stroke. 23 – 25
Is the ischemic penumbra a target for brain plasticity?
The Ischemic Penumbra as a Target for Brain Plasticity. In the acute phase, stroke treatment focuses on saving as much penumbral tissue as possible. However, many patients with still viable penumbra are not treated by reperfusion therapies.
Is the ischemic penumbra a diagnostic target?
Thirty years later, the ischemic penumbra is an evolved concept that presents more applications. Thus, the ischemic penumbra is a diagnostic target, allowing the extension of therapeutic windows; it is also a biochemical target, in which an intermittent bioenergetic compromise takes place, and it is a target for brain plasticity, neuroprotection, and neurorepair.
Where does neurogenesis occur?
Altman demonstrated in 1962 that new neurons are produced during adulthood, so neurogenesis continues postnatally for some mammals, 16 specifically in the subgranular zone of the hippocampus and the forebrain subventricular zone of the lateral ventricle (subventricular zone). 17 – 19 Since then, neurogenesis is considered a new target for the treatment of stroke. 20
Can MRI be used for human brain?
Most of these MRI methods are unfortunately restricted to experimental models and state-of-the-art brain imaging and must be fully validated for the human brain before translation into clinical practice. Nonetheless, these methods might provide the neuroscientist new opportunities to better map and understand the gradients of injury versus repair zones in the penumbra. 4
What is the definition of a penumbra?
Definition of penumbra. 1 a : a space of partial illumination (as in an eclipse) between the perfect shadow on all sides and the full light. b : a shaded region surrounding the dark central portion of a sunspot. 2 : a surrounding or adjoining region in which something exists in a lesser degree : fringe the seventeenth century lay in the penumbra ...
When was the term "penumbra" first used?
The first known use of penumbra was in 1665. See more words from the same year. From the Editors at Merriam-Webster. 'Stygian,' 'Umbra,' and Other Darkness...
What are some examples of penumbras?
Examples of penumbra in a Sentence. the lunar eclipse began with a subtle darkening of the lunar surface as it passed within the Earth's penumbra a penumbra of despair fell over the doomed city.
How long does the penumbra area last?
Introduction: Habitually, when one speaks about penumbra area it refers to an ischemic region with the risk of permanent affection but potentially recoverable, that extend during a period of 4 to 6 hours. Nevertheless, with the reperfusion we cannot always get a neurofunctional recovery, or hinder the extension of the infarct. In this work, the author checked the mechanisms that participate in the lesion of penumbra area, as far as extension, duration as well as their relation with the therapeutic windows.
Is the penumbra a brain tissue?
Development: Penumbra is a brain tissue at risk of infarct but is potentially recoverable and receives a variable level of cerebral blood flow (diminished, normal or augmented) which presents a functional alteration principally of its metabolism that is produced by various mechanisms like phenomenon of no reflow, reperfusion injury, hemodynamics disorders, spreading depolarization, delayed neural death, deafferentation (diaschisis), postischemic exofocal neural death, slowly progressive neural damage, among other alteration different a simple lesion by energy failure, these disorders may act during several months.

Overview
History
The first decade of research focused on physiologic profile of the penumbra tissue after stroke, mapping the cerebral blood flow, and quantifying oxygen and glucose consumption to define these areas. The second decade revealed the mechanism of the neuronal cell death. As the Biochemical pathways were dissected penumbral science became a rapidly evolving area of molecular biology. The third decade of penumbral research found a transitional leap as using po…
Definition
One widely accepted definition for penumbra describes the area as "ischemic tissue potentially destined for infarction but it isn't irreversibly injured and the target of any acute therapies." The original definition of the penumbra referred to areas of the brain that were damaged but not yet dead, and offered promise to rescue the brain tissue with the appropriate therapies.
Blood flow
The penumbra region typically occurs when blood flow drops below 20 mL/100 g/min. At this point electrical communication between neurons fails to exist. Cells in this region are alive but metabolic pumps are inhibited, oxidative metabolism is reduced but neurons may begin to depolarize again. Areas of the brain generally do not become infarcted until blood flow to the region drops below 10 to 12 mL/100 g/min. At this point, glutamate release becomes unregulated, ion pumps are inhibite…
Identification by imaging
Positron emission tomography (PET) can quantify the size of the penumbra, but is neither widely available nor rapidly accessible. Magnetic resonance imaging can estimate the size of the penumbra with a combination of two MRI sequences:
• Perfusion weighted imaging (PWI) shows decreased blood perfusion in the infarcted core and the penumbra
Clinical relevance
A higher volume of penumbra around a cerebral infarction means a greater volume of potentially salvageable brain matter by thrombolysis and thrombectomy. Such therapies have a greater effect on regaining functions such as movement after a cerebral infarction. In the penumbra, microglia are thought to exert neuroprotective effects via specialized contacts with neuronal somata, termed somatic junctions. Understanding and supporting these microglial actions could broade…