
What percent of your daily calories should come from protein?
Protein is the main building block of most of our cells. Our bodies use about 210 grams of the stuff daily. While the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and nutritional agencies recommend that 10 percent to 35 percent of your calories come from protein, that message offers more confusion than clarity.
How much protein should I consume daily?
The average adult needs a minimum of 0.8 grams of protein per kilogram of body weight per day. 2 One kilogram equals 2.2 pounds, so a person who weighs 165 pounds, or 75 kg, would need about 60 grams of protein per day. However, your protein needs may increase if you are very active.
What are the disadvantages of too much protein?
What Are the Disadvantages of Too Much Protein?
- Protein Requirements. Protein foods are your only source of essential amino acids, which are the building blocks of your body's muscles and other tissues.
- Kidney Function. The kidneys make up one of your body's most important filtration and detoxification systems. ...
- Excessive Protein
How much protein does the body need daily?
The daily protein requirement for the average person is 0.8g per kilo of body weight or 0.36gms per pound of body weight. To build muscles, the recommended daily protein intake is 2.2gms per kg of lean body mass. It doesn’t harm healthy kidneys if you take more protein, but it also doesn’t speed up muscle gain.
How much protein should I eat a day?
How much protein is in a pound of protein?
How to calculate protein intake?
Why is protein important for muscle building?
How much protein does an older person need?
Why is protein important for weight loss?
What are the molecules that make up proteins?
See 4 more
About this website
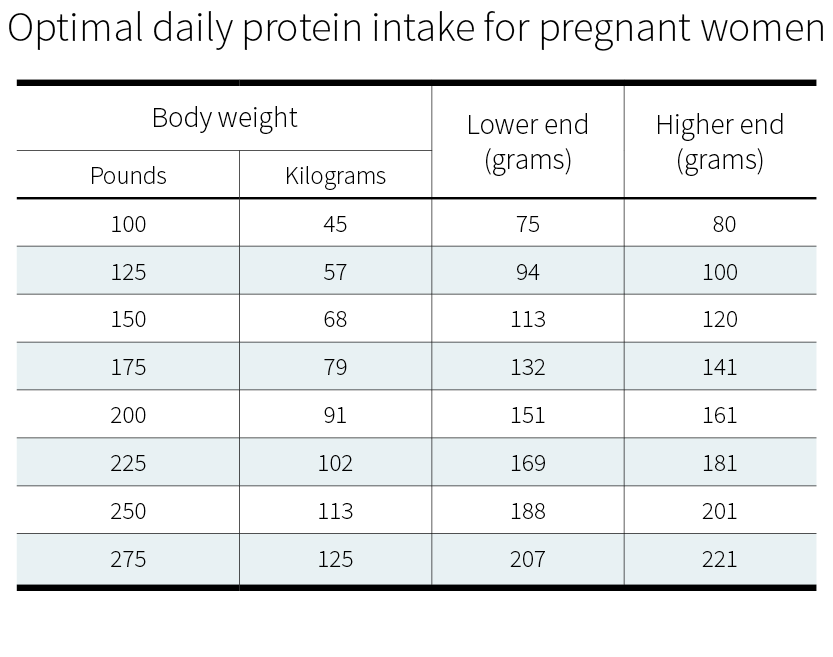
What is percentage daily value?
The % Daily Value (%DV) is the percentage of the Daily Value for each nutrient in a serving of the food. The Daily Values are reference amounts (expressed in grams, milligrams, or micrograms) of nutrients to consume or not to exceed each day.
Why is there no percent daily value for proteins?
Trans fat, sugar and protein rarely have a daily value percentage listed on the nutrition label. This is because it hasn't established any specific guidelines about how much a person can consume for optimal health.
How much protein is too much?
It's hard to provide a specific answer since so much is still uncertain and the experts themselves don't agree. However, for the average person (who is not an elite athlete or heavily involved in body building) it's probably best to aim for no more than 2 gm/kg; that would be about 125 grams/day for a 140-pound person.
What happens if you eat too much protein?
Excess protein consumed is usually stored as fat, while the surplus of amino acids is excreted. This can lead to weight gain over time, especially if you consume too many calories while trying to increase your protein intake.
Which nutrients do not have a daily value?
Trans fat and total sugars have no percent Daily Value (%DV), so use the number of grams (g) to compare and choose foods.
Why is there no daily value for sugar?
Total Sugars include sugars naturally present in many nutritious foods and beverages, such as sugar in milk and fruits as well as any added sugars that may be present in the product. There is no Daily Value* for total sugars because no recommendation has been made for the total amount to eat in a day.
What percent of daily value is 20g of protein?
In the example, 20 grams of protein in the protein bar, divided by 50 grams of recommended protein ingestion, results in a decimal value of 0.40. Multiply that by 100 to get the percent daily value of 40 percent.
What does it mean daily value not established?
The good news is, just because some nutrients may not have a listed %DV, doesn't mean that they are bad or unnecessary for a healthy diet. It simply means that the U.S. FDA has not made an official recommendation for how much of these nutrients you should have in your diet.
Daily Protein Requirements: Are You Getting Enough? - WebMD
You need protein for your muscles, bones, and the rest of your body. Exactly how much you need changes with age: Babies need about 10 grams a day.
How Much Protein Should I Eat? - Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics
This website uses cookies. We use cookies to optimize and personalize your experience, provide relevant content and analyze online traffic. We also share information with our analytics and website partners, who may use it to inform decisions about current or future services.
How Much Protein Do I Need? How to Calculate Ideal Intake - Verywell Fit
Between 10% and 35% of your total calories should come from protein sources. This number varies depending on your body composition, health, activity level and type, and your goals.
What are the nutritional facts?
The Nutrition Facts label must list total fat, saturated fat, trans fat, cholesterol, sodium, total carbohydrate, dietary fiber, total sugars, added sugars, protein, and certain vitamins and minerals. While the actual amount and %DV of vitamin D, calcium, iron, and potassium must be listed, other vitamins and minerals may be listed voluntarily by ...
What is %DV in nutrition?
The %DV is how much a nutrient in a single serving of an individual packaged food or dietary supplement contributes to your daily diet. For example, if the DV for a certain nutrient is 300 micrograms (mcg) and a packaged food or supplement has 30 mcg in one serving, the %DV for that nutrient in a serving of the product would be 10%.
What are the nutrients in a TV?
Higher in dietary fiber, vitamin D, calcium, iron, and potassium. Lower in saturated fat, sodium, and added sugars. If playback doesn't begin shortly, try restarting your device. Videos you watch may be added to the TV's watch history and influence TV recommendations.
Why is the nutrition label updated?
The Nutrition Facts label on packaged foods and drinks has been updated to make it easier for you to make informed choices.
Do you have to list vitamins and minerals in food?
However, they are required to list any vitamins and minerals that are added to the food or if a statement is made on the package labeling about their health effects or the amount contained in the food (for example, "high" or "low").
Is %DV the same as %DV?
The DVs for many nutrients have been updated based on new nutrition research. So, the %DV may be different on some of your favorite products or supplements. As a result, you may need to consume more or less of a certain food, beverage or dietary supplement in order to meet the DVs or the recommended amounts.
How much protein does the average American consume?
In comparison, the average American consumes around 16% of his or her daily calories in the form of protein, from both plant and animal sources. The Protein Summit reports in AJCN argue that 16% is anything but excessive. In fact, the reports suggest that Americans may eat too little protein, not too much.
Why is protein important?
Protein is essential to good health. The very origin of the word — from the Greek protos, meaning "first" — reflects protein’s top-shelf status in human nutrition. You need it to put meat on your bones and to make hair, blood, connective tissue, antibodies, enzymes, and more. It’s common for athletes and bodybuilders to wolf down extra protein ...
What is the RDA for protein?
The RDA is the amount of a nutrient you need to meet your basic nutritional requirements. In a sense, it’s the minimum amount you need to keep from getting sick — not the specific amount you are supposed to eat every day. To determine your daily protein intake, you can multiply your weight in pounds by 0.36, or use this online protein calculator.
What are some good sources of protein?
Beef, poultry, and pork (as well as milk, cheese, and eggs) can certainly provide high-quality protein, but so can many plant foods — including whole grains, beans and other legumes, nuts, and vegetables. The table below provides some healthier sources of protein.
Is protein more effective than food?
Some studies described in the summit reports suggest that protein is more effective if you space it out over the day’s meals and snacks, rather than loading up at dinner like many Americans do.
Who was the scientist who organized the Protein Summit?
Rodriguez was among more than 40 nutrition scientists who gathered in Washington, D.C., for a "Protein Summit" to discuss research on protein and human health. The summit was organized and sponsored by beef, egg, and other animal-based food industry groups, but it also generated a set of scientific reports that were independently published a special supplement to the June issue of the American Journal of Clinical Nutrition (AJCN).
Is it important to consume the right amount of protein?
A very informative post on consuming the right amount and the right sources of protein to stay healthy! It is important to consume the optimal amount of protein as over-consumption or under-consumption may lead to serious health problems. Choosing the right source of protein will have a significant effect on your health.
What is %DV in nutrition?
The %DV can help you determine if a serving of food is high or low in a nutrient. The Daily Values are reference amounts (in grams, milligrams, or micrograms) of nutrients to consume or not to exceed each day. The Daily Values have been updated, which may make the percent Daily Value higher or lower on the new Nutrition Facts label.
What About Trans Fat, Protein, and Total Sugars?
Protein generally has no percent Daily Value (%DV) listed on the label, so use the number of grams (g) as a guide.
Why is the nutrition label updated?
The Nutrition Facts label on packaged foods and drinks has been updated to make it easier for you to make informed choices.
What is the percentage of a nutrient?
The 100% DV is regarded as the amount of a nutrient that will satisfy the requirement for the nutrient in 97% – 98% of all adults. Calcium serves as a good example. The 100% DV is 1000mg. A serving of milk has 300mg, which is 30% DV. What is simple for calcium is not at all simple for protein. Please notice the grams of protein and the %DV protein in the three Nutrition Facts panels above: For Milk – 8g protein which supplies 16% of the Daily Value. For Peanuts – 7g protein which supplies 7% of the Daily Value. For Kidney Beans – 8g protein which supplies an unstated % of the Daily Value. A testing procedure with the abbreviation PDCAAS is responsible for the various %DVs. The initials stand for Protein Digestibility Corrected Amino Acid Score. Proteins differ in how useful they are in the body and the Score is a measure of that usefulness. This test method was accepted in the early 1990s by the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations, and by the federal Food and Drug Administration (FDA) a short time later. The test to determine the PDCAA Score is complicated. It requires knowing both the digestibility of the protein (as determined in animal feeding studies) and the amounts of each essential amino acid in the protein. The amino acids that the body cannot make, and that must come from food intake, are the essential amino acids. Due to the testing difficulty, the Score has been determined for protein from only about fifteen sources. Several types of beans have been tested, but not kidney beans. In general, proteins from animal sources have a Score between 0.9 and 1.0. A huge exception is gelatin. Because it almost completely lacks one of the essential amino acids, it has a Score of 0. Proteins from plant sources vary in their Score. Soy protein has a 1.0. Wheat protein has a 0.4. And peanut protein has a 0.5. Milk protein is of very high quality and its PDCAA Score is 1.0, which is the highest Score value allowed. Peanut protein, with a Score of 0.5, is of lesser quality. Peanut protein provides half of the %DV as the same amount of milk protein. Two of the Nutrition Facts panels above show that 50g protein is recommended in a two thousand calories per day diet. The third − for kidney beans − does not have the information. The FDA requires that the PDCAA Score be used when determining the %DV for protein. For example, the %DV protein for a serving of peanuts is calculated as: 100 x PDCAAS x (g protein per serving/50g). %DV peanut protein which has a Score of 0.5: = 100 x 0.5 x 7g/50g = 7%DV. For milk protein which has Score of 1.0: %DV = 100 x 1.0 x 8g/50g = 16%DV It is optional to include the %DV for protein in the Nutrition Facts panel, even when the PDCAA Score is known. An exception to this is that the %DV must be stated if there is a front-of-package nutrition claim for protein. “Good source of protein” is an example of such a claim. There are also specific regulations when a food is intended for children less than 4 years of age, infants, pregnant women, and lactating women. This was a guest post by Richard Perlmutter, MS. He is the owner of Abington Nutrition Services LLC which prepares nutrition labeling for products manufactured by food and beverage companies. He also takes an interest in seeing that government nutrition policy is in line with nutritional science.
What does the initials mean in protein digestibility?
The initials stand for Protein Digestibility Corrected Amino Acid Score. Proteins differ in how useful they are in the body and the Score is a measure of that usefulness.
What are essential amino acids?
The amino acids that the body cannot make, and that must come from food intake, are the essential amino acids. Due to the testing difficulty, the Score has been determined for protein from only about fifteen sources. Several types of beans have been tested, but not kidney beans.
Which protein has the highest PDCAA score?
Milk protein is of very high quality and its PDCAA Score is 1.0, which is the highest Score value allowed. Peanut protein, with a Score of 0.5, is of lesser quality. Peanut protein provides half of the %DV as the same amount of milk protein.
How much calcium is in milk?
A serving of milk has 300mg, which is 30% DV. What is simple for calcium is not at all simple for protein. Please notice the grams of protein and the %DV protein in the three Nutrition Facts panels above: For Milk – 8g protein which supplies 16% of the Daily Value.
What is the recommended intake of nutrients?
Recommended intakes of nutrients vary by age and sex and are known as Recommended Dietary Allowances (RDAs) and Adequate Intakes (AIs). However, one value for each nutrient, known as the Daily Value (DV), is selected for the labels of dietary supplements and foods. A DV is often, but not always, similar to one’s RDA or AI for that nutrient.
What is a DV in nutrition?
A DV is often, but not always, similar to one’s RDA or AI for that nutrient. DVs were developed by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) to help consumers determine the level of various nutrients in a standard serving of food in relation to their approximate requirement for it.
How much protein should I eat a day?
Most official nutritional organizations recommend a fairly modest protein intake. The DRI (Dietary Reference Intake) is 0.36 grams of protein per pound (0.8 grams per kg) of body weight.
How much protein is in a pound of protein?
The DRI (Dietary Reference Intake) is 0.36 grams of protein per pound (0.8 grams per kg) of body weight. This may be enough to prevent deficiency, but the amount you need depends on many factors, including your activity level, age, muscle mass, physique goals, and overall health.
How to calculate protein intake?
You can calculate it by multiplying your calorie intake by 0.075. Summary. A protein intake at around 30% of calories seems to be optimal for weight loss. It boosts your metabolic rate and causes a spontaneous reduction in calorie intake.
Why is protein important for muscle building?
A higher protein intake can help build muscle and strength ( 10. Trusted Source. ). Meanwhile, those who want to maintain the muscle they’ve built may need to increase their protein intake when losing body fat, as a high protein intake can help prevent the muscle loss that usually occurs when dieting ( 11.
How much protein does an older person need?
Older adults have significantly increased protein needs as well — up to 50% higher than the DRI, or about 0.45–0.6 grams per pound (1–1.3 grams per kg) of body weight ( 23, 24 ).
Why is protein important for weight loss?
Protein is important when it comes to losing weight. As you may know, you need to consume fewer calories than you burn to lose weight. Evidence suggests that eating protein can increase the number of calories you burn by boosting your metabolic rate (calories out) and reducing your appetite (calories in) ( 1.
What are the molecules that make up proteins?
Proteins consist of smaller molecules called amino acids, which link together like beads on a string. These linked amino acids form long protein chains, which then fold into complex shapes.