What is the difference between a pericarp and a fruit?
A pericarp is a fraction of the fruit that constitutes the outer layer in the fruit anatomy, which encloses the seed. It develops from the flower’s ovary and surrounds the seed that develops from an ovule after the flower’s fertilization. Pericarp can be squishy or sapless. The pericarp constitutes the edible tissue of fruit.
What is pericarp in biology?
Feb 12, 2020 · What is the pericarp of a fruit? Fruits are the mature ovary or ovaries of one or more flowers. In fleshy fruits , the outer layer (typically edible) is the pericarp , which is the tissue that develops from the ovary wall of the flower and surrounds the seed to protect it in environments apart from the parent plant.
What is the function of the pericarp in berries?
The pericarp of a fruit is theoutermost part of most of fruit formed from the wall of the ripened ovarywhich may edible, in case of false fruit or accessory fruits it is highly reduced and present inside the fruit that surrounding the small seeds and may not be edible like in apple.
What is the pericarp of a seed?
The fruit wall, or pericarp, is divided into three regions: the inner layer, or endocarp; the middle layer, or mesocarp; and the outer layer, or exocarp. These regions may be fleshy or dry (sclerified) or any combination of the two, but they are classified as …

What is the pericarp of an apple?
What is called pericarp?
: the ripened and variously modified walls of a plant ovary composed of an outer exocarp, middle mesocarp, and inner endocarp layer — see endocarp illustration.
Where is the pericarp of a fruit?
What is the pericarp and what is its function?
What does pericarp mean in plants?
Do all fruits have pericarp?
What composes the pericarp?
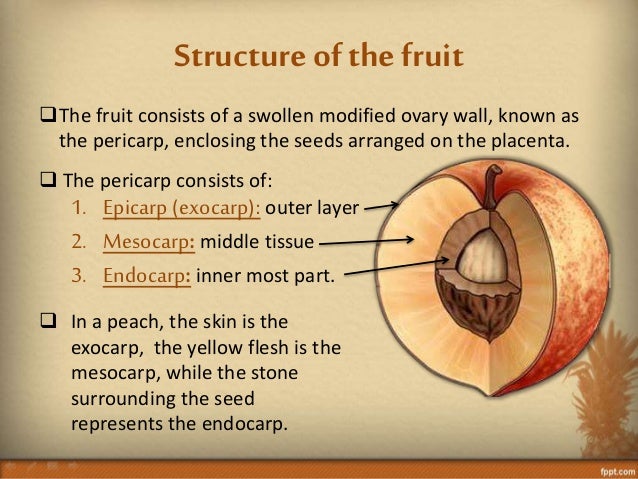
It possesses three distinct layers: Epicarp: It is the outermost layer that forms the skin or peel of the fruit. Mesocarp: It is generally a fleshy or dry mid-portion of the fruit. Endocarp: It is the inmost part surrounding the seed.
What is the pericarp composed of?
What is pericarp in bio?
What do you mean by cotyledons?
A cotyledon is part of the embryo within the seed of a plant. Often when the seed germinates, or begins to grow, the cotyledon may become the first leaves of the seedling. Botanists use the number of cotyledons present in the seed of a plant as a means of classification.
What is the meat of fruit called?
The mesocarp (from Greek: meso-, "middle" + -carp, "fruit") is the fleshy middle layer of the pericarp of a fruit; it is found between the epicarp and the endocarp. It is usually the part of the fruit that is eaten.
Is Grass a fruit?
Is grass a fruit or a Vegetable? – Concluding, Grass is a vegetative plant so it cannot be considered as a fruit. Though the most variety of grass bears some type of fruit that we can consume. Technically, we can say a Grass is a Vegetable and we can eat it whenever we want.
What part of an apple do we eat?
Pulp. The pulp, also called the flesh, is just beneath the skin of the apple. This part of the apple contains a great deal of nutrition including pectin, vitamin C, calcium and other minerals. This part of the apple is also the sweetest.
Are oranges ovaries?
The Whole Bushel In a botanical sense, a fruit is usually restricted to sweet, fleshy foods like bananas, oranges, and peaches. But in a biological sense, cereal grains, nuts, and tomatoes are mature ovaries, and thus, fruits. The fruit encases and protects the seed while it grows.
Are fruits alive?
As weird as it may sound, the fruits and vegetables in the produce aisle at the grocery store are still alive. So alive, in fact, that they still have “internal clocks” that respond to the environment, according to a new study in the journal Current Biology.
Whats is a seed?
Seed. A seed is a small embryonic plant enclosed in a covering called the seed coat, usually with some stored food. It is the product of the ripened ovule of gymnosperm and angiosperm plants which occurs after fertilization and some growth with in the motherplant.
What is the pericarp?
fruit development. …the ripened ovary wall, or pericarp, which may develop entirely or in part into fleshy, fibrous, or stony tissue, are important. Often three distinct pericarp layers can be identified: the outer (exocarp), the middle (mesocarp), and the inner (endocarp).
What is fruit development?
fruit development. …the ripened ovary wall, or pericarp, which may develop entirely or in part into fleshy, fibrous, or stony tissue, are important.
What are the three layers of the pericarp?
…the ripened ovary wall, or pericarp, which may develop entirely or in part into fleshy, fibrous, or stony tissue, are important. Often three distinct pericarp layers can be identified: the outer (exocarp), the middle (mesocarp), and the inner (endocarp).
What are the three regions of angiosperm?
In angiosperm: Fruits. The fruit wall, or pericarp, is divided into three regions: the inner layer, or endocarp; the middle layer, or mesocarp; and the outer layer, or exocarp. These regions may be fleshy or dry (sclerified) or any combination of the two, but they are classified as either one or the…. Read More.
What are the three parts of the fruit wall?
The fruit wall, or pericarp, is divided into three regions: the inner layer, or endocarp; the middle layer, or mesocarp; and the outer layer, or exocarp.
Where does the word "fruit" come from?
Fruit. The word fruit matured in Middle English and grew from the seeds of Anglo-French frut and fruit, which are rooted in the Latin verb frui, meaning " to enjoy" or "to have the use of.".
What does "fruit" mean in Latin?
Fruit. The word fruit matured in Middle English and grew from the seeds of Anglo-French frut and fruit, which are rooted in the Latin verb frui, meaning "to enjoy" or "to have the use of.". Scientifically, it is the name for the fleshy or dry ripened ovary of a flowering plant enclosing a seed or seeds.
Is apricot a fruit?
So, apricots, bananas, grapes, as well as bean pods, corn grains, tomatoes, cucumbers, and (when in their shell) acorns and almonds are all fruits—fruits are not necessarily sweet, succulent, or pulpy foods. The botanical use of ovary has similarities in meaning to the one found in human anatomy textbooks.
What is the ovary of a flower?
In botany, ovary applies to the part of a flower where seeds are formed. The ovary bears ovules, which enclose the seeds, and consists of one or more carpels. Ovary derives from Latin ovum, meaning "egg," and ovule is the Latin diminutive. Carpel also is seeded in Latin.
What does the name Carpel mean?
Carpel. Carpel derives from New Latin carpellum, and, in turn, Greek karpos, meaning "fruit.". A homograph of karpos means "wrist," which gives English carpal, as in carpal tunnel syndrome, as well as carpus, which is used in medical writing as a name for the joint.
What is the meaning of the word "carpel"?
Carpel derives from New Latin carpellum, and, in turn, Greek karpos, meaning "fruit." A homograph of karpos means "wrist," which gives English carpal, as in carpal tunnel syndrome, as well as carpus, which is used in medical writing as a name for the joint. The fruity homograph refers to the ovule-bearing structures in an angiosperm that comprises the innermost whorl of a flower that matures into a fruit. From the Greek root the science terms exocarp, mesocarp, and endocarp sprouted. Together, they designate the regions of what comprises the fruit's pericarp.
What is a homograph of karpos?
A homograph of karpos means "wrist," which gives English carpal, as in carpal tunnel syndrome, as well as carpus, which is used in medical writing as a name for the joint. The fruity homograph refers to the ovule-bearing structures in an angiosperm that comprises the innermost whorl of a flower that matures into a fruit.
What is the anatomy of a fruit?
Fruit anatomy is the plant anatomy of the internal structure of fruit. Fruits are the mature ovary or ovaries of one or more flowers. They are found in three main anatomical categories: aggregate fruits, multiple fruits, and simple fruits. Aggregate fruits are formed from a single compound flower and contain many ovaries or fruitlets.
Where does the edible portion of a fruit come from?
In some fruits, the edible portion is not derived from the ovary, but rather from the aril , such as the mangosteen or pomegranate, and the pineapple from which tissues of the flower and stem provide food.
What fruit has fleshy mesocarp?
Lastly, drupes are known for being one-seeded with a fleshy mesocarp; an example of this would be the peach. However, there are fruits where the fleshy portion is developed from tissues that are not the ovary, such as in the strawberry. The edible part of the strawberry is formed from the receptacle of the flower.
Is strawberry a fruit?
The edible part of the strawberry is formed from the receptacle of the flower. Due, to this difference the strawberry is known as a false fruit or an accessory fruit.
What is dry fruit?
Dry dehiscent fruits are described as a fruit where the pod has an increase in internal tension to allow seeds to be released. These include the sweet pea, soybean, alfalfa, milkweed, mustard, cabbage and poppy.
What is dry dehiscent fruit?
Dry dehiscent fruits are described as a fruit where the pod has an increase in internal tension to allow seeds to be released. These include the sweet pea, soybean, alfalfa, milkweed, mustard, cabbage and poppy. Dry indehiscent fruit differ in that they do not have this mechanism and simply depend on physical forces.
What are some examples of dry indehiscent fruit?
Examples of species indehiscent fruit are sunflower seeds, nuts, and dandelions.