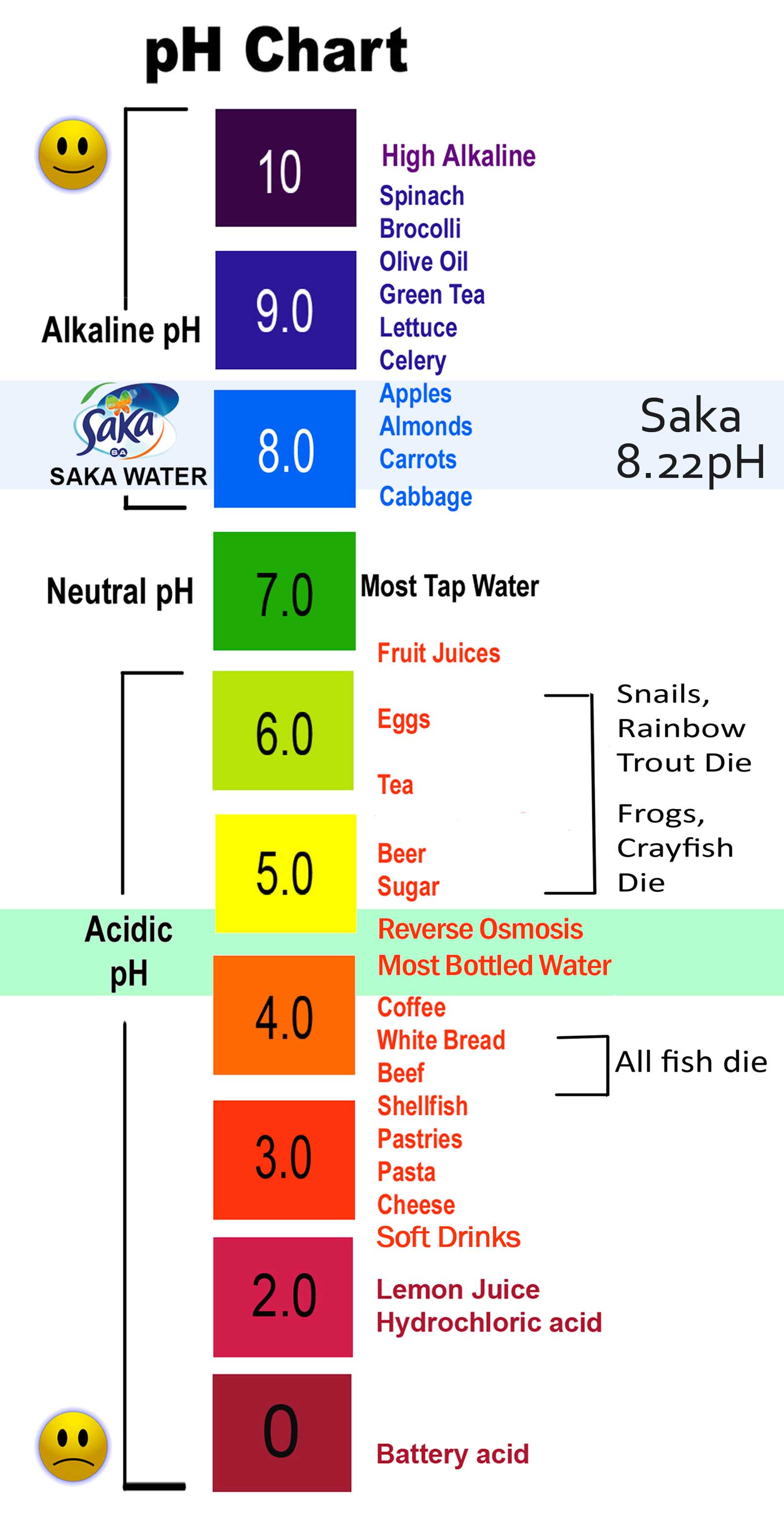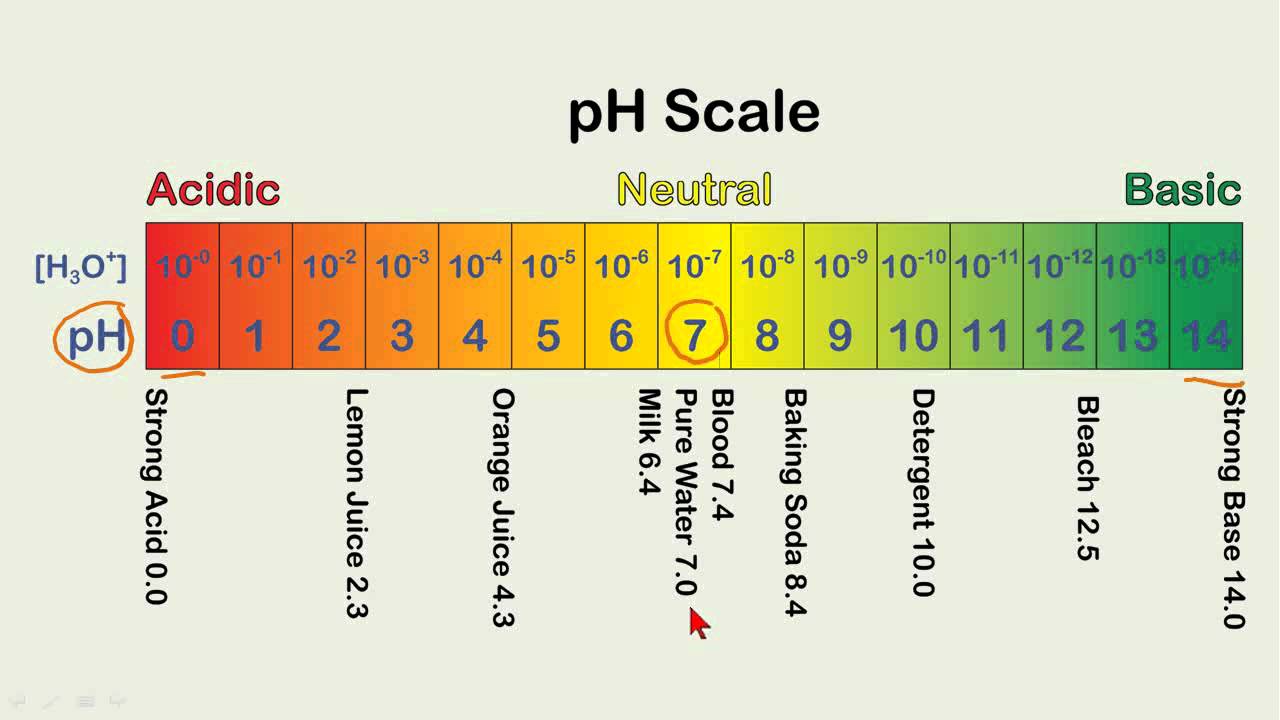
pH scale examples:
- pH 0: Battery acid
- pH 1: Gastric acid
- pH 2: Vinegar
- pH 3: Soda, orange juice
- pH 4: Acid rain, tomato juice
- pH 5: Banana, black coffee
- pH 6: Milk, urine
- pH 7: Pure water
What does pH scale stand for?
pH stands for potential hydrogen with the “p” meaning potential and the “H” standing for hydrogen. The pH scale is a scale that is used to rank the relative basicity or acidity of substances to other substances, based on the amount of hydrogen ion activity in a substance.
What number is highest on the pH scale?
The pH scale measures how acidic or basic a substance is. The pH scale ranges from 0 to 14. A pH of 7 is neutral. A pH less than 7 is acidic. A pH greater than 7 is basic. The pH scale is logarithmic and as a result, each whole pH value below 7 is ten times more acidic than the next higher value.
What does the pH scale tell you?
Points to Remember on pH Scale
- pH of strong acid or base does not depend upon temperature.
- pH of weak acid decreases with increase in temperature due to increase in ionization.
- pH of weak base increases with increase in temperature due to increase in ionization or [OH-] ion concentration.
What does each number represent on a pH scale?
Each number represents a 10-fold change in the acidity/basicness of the water. Water with a pH of five is ten times more acidic than water having a pH of six. As this diagram shows, pH ranges from 0 to 14, with 7 being neutral. pHs less than 7 are acidic while pHs greater than 7 are alkaline (basic).

What has a pH of 11 examples?
Ammonia: pH 11-13.
What is pH give two examples?
pH is a numeric scale in chemistry that is used to determine whether the substance is acidic, basic or neutral in nature. Substances that have a pH level of less than 7 are acidic in nature. For e.g Acidic substances such as vinegar, tamarind, lemon, etc. Substances that have a level of more than 7 are basic in nature.
What is a real life example of pH?
pH is very important in everyday life and has wide applications as the pH of the soil can lead to increased agricultural yield and the pH of oceans affects aquatic life. pH is important in the digestion of food, stopping tooth decay, and acts as a remedy for the acidic effect of honeybee bite.
What is pH in our daily life?
pH plays a very important role in the digestion of food in our stomach. In the stomach, the secretion of hydrochloric acid happens which changes the stomach pH between one to three and this pH range is responsible for the activation of the pepsin enzyme which will digest the food.
What is the pH scale?
The pH scale is a precise way of classifying the acidity, basicity or neutrality of a solution. As a logarithmic scale, 1 pH unit is ten times stronger, or ten times weaker, than the one below or above it, depending on its position: a pH of 4 is ten times more acidic than a pH of 5, but ten times weaker than a pH of 3.
What is the difference between acid and base?
An acid always yields hydrogen positive ions (H +) while a base always yields hydroxide negative ions (OH – ). Hydrogen ion concentration is calculated in an aqueous solution based on the molarity of the hydronium ions, which is measured in moles per litre. You need to know the molarity to calculate the pH.
Why is it easier to calculate pH in strong acids?
It’s easier to calculate in strong acids because the ions completely dissociate in water. For instance, hydrochloric acid is a strong acid that’s 100% ionised into cations and anions when dissolved in water. If you want to calculate the pH of a hydrochloric acid solution with 0.0025 M concentration, you simply need to add the number to the formula, ...
What does the pH scale measure?
The pH scale measures the relative acidity and alkalinity of solutions. It’s a negative logarithmic scale of base ten that measures the potential of a solution to accept protons in the form of hydrogen ions. For example, a solution with pH level 8 is ten times more alkaline than pure water, which has a pH level of 7. This implies that the particular solute has ten times more potential to accept protons compared to water.
Why is the pH scale important?
It can also be used to predict chemical reactions, as well as to help determine the chemical composition of analytes in a titration experiment. Many chemical manufacturing processes require the use of the pH scale.
How to use pH scale?
How to Use the pH Scale. The pH scale is an analytical tool that you can use both theoretically and experimentally. For instance, if the hydronium concentration of an acid is known, you can theoretically calculate the pH of the solution. Conversely, if the pH is precisely measured, you can calculate the concentration of the solution.
How to compare different types of solutions?
You can compare various types of solutions using the pH scale. It’s a visual and numerical sale that can be represented by numbers, graphics, pictures, and colours. In fact, many pH indicators change colours to indicate pH range. The sample chart below compares the acidity and basicity of various common solutions in the home:
What is an acid or a base?
Whether a liquid is an acid or a base has to do with hydrogen ions (abbreviated with the chemical symbol H + ). In water (H 2 O), a small number of the molecules dissociate (split up). Some of the water molecules lose a hydrogen and become hydroxide ions (OH − ). The "lost" hydrogen ions join up with water molecules to form hydronium ions (H 3 O + ). For simplicity, hydronium ions are referred to as hydrogen ions H +. In pure water, there are an equal number of hydrogen ions and hydroxide ions. The solution is neither acidic or basic.
What is pH?
Acidity and alkalinity are measured with a logarithmic scale called pH. Here is why: a strongly acidic solution can have one hundred million million, or one hundred trillion (100,000,000,000,000) times more hydrogen ions than a strongly basic solution! The flip side, of course, is that a strongly basic solution can have 100,000,000,000,000 times more hydroxide ions than a strongly acidic solution. Moreover, the hydrogen ion and hydroxide ion concentrations in everyday solutions can vary over that entire range.
What is the name of the ions that join up with water molecules to form hydronium ions?
The "lost" hydrogen ions join up with water molecules to form hydronium ions (H 3 O + ). For simplicity, hydronium ions are referred to as hydrogen ions H +. In pure water, there are an equal number of hydrogen ions and hydroxide ions. The solution is neither acidic or basic. An acid is a substance that donates hydrogen ions.
What scale do you use to measure hydrogen ion concentration?
In order to deal with these large numbers more easily, scientists use a logarithmic scale, the pH scale. Each one-unit change in the pH scale corresponds to a ten-fold change in hydrogen ion concentration.
How to measure pH in a solution?
pH test paper and indicator sticks are pieces of paper or stiffer sticks that contain pH indicators (chemicals that change color depending on how acidic or basic a solution is). To measure pH, a piece of pH test paper or an indicator stick is dipped into the liquid. The color of the dipped paper/stick is then matched to a color key that comes with the container of pH test paper or indicator sticks. Each color on the key represents a different pH. An example of a used pH indicator stick and the corresponding color key is shown below in Figure 1. pH meters are electronic devices that used to measure pH. They consist of a probe that is dipped in a solution, and a digital readout. pH meters are even more precise than pH test paper or indicator sticks. Table 2 below discusses what types of pH measuring devices are best for different science project applications, and offers a quick link to purchasing different pH test papers and indicator sticks.
How to measure pH?
To measure pH, a piece of pH test paper or an indicator stick is dipped into the liquid. The color of the dipped paper/stick is then matched to a color key that comes with the container of pH test paper or indicator sticks. Each color on the key represents a different pH.
What is the pH of pure water?
What the equation means is just what we said before: for each 1-unit change in pH, the hydrogen ion concentration changes ten-fold. Pure water has a neutral pH of 7. pH values lower than 7 are acidic, and pH values higher than 7 are alkaline (basic).
What Does pH Stand For?
The symbol is made up of two letters: a lowercase “p” which stands for “power” and an uppercase “H” for the element hydrogen. Together, it is an abbreviation for “power of hydrogen.” This terminology is used because the scale is logarithmic – it has to do with powers of ten.
Why is pH important?
Some chemical reactions only take place under certain pH conditions. Sometimes this is because H + or OH – acts as a reactant in the reaction. In other cases, acid or base can catalyze a reaction, meaning that they affect the rate of the reaction.
What is the difference between acidic and basic?
These numbers allow the classification of substances; the most acidic substances will be close to 0, while the most basic or alkaline substances will be close to 14. The lower the pH, the more H + ions and the stronger the acid would be, and the most basic or alkaline substances will have a classification between 7 and 14 and in this case the more OH- ions, hydroxide ions, the stronger the base.
What is the K-W constant?
K w is the dissociation constant or ionization constant of water.
What are the conditions that allow organisms to thrive?
As a result, ecosystems like lakes and rivers thrive under the pH conditions that are favorable to the biochemistry of the local flora and fauna.
Why do chemical reactions only occur under certain pH conditions?
Some chemical reactions only take place under certain pH conditions. Sometimes this is because H + or OH – acts as a reactant in the reaction. In other cases, acid or base can catalyze a reaction, meaning that they affect the rate of the reaction.
Is pOH the same as pH?
The term pOH is similar to pH, but refers to alkalinity or basicity, that is, the concentration of hydroxide ion (OH-) in a solution. The two scales function identically, except that the scale is reversed. A neutral substance has both pH and pOH of 7. The equation for pOH is the same as that shown earlier except using the concentration of hydroxide:
What is the pH?
The pH is a unit of measurement that serves to establish the level of acidity or alkalinity of a substance .
What does the acid level in the pH mean?
When it is obtained by a pH measurement that a product , substance or element is acidic, it means that it has a high or low amount of hydrogen ions (depending on the level).