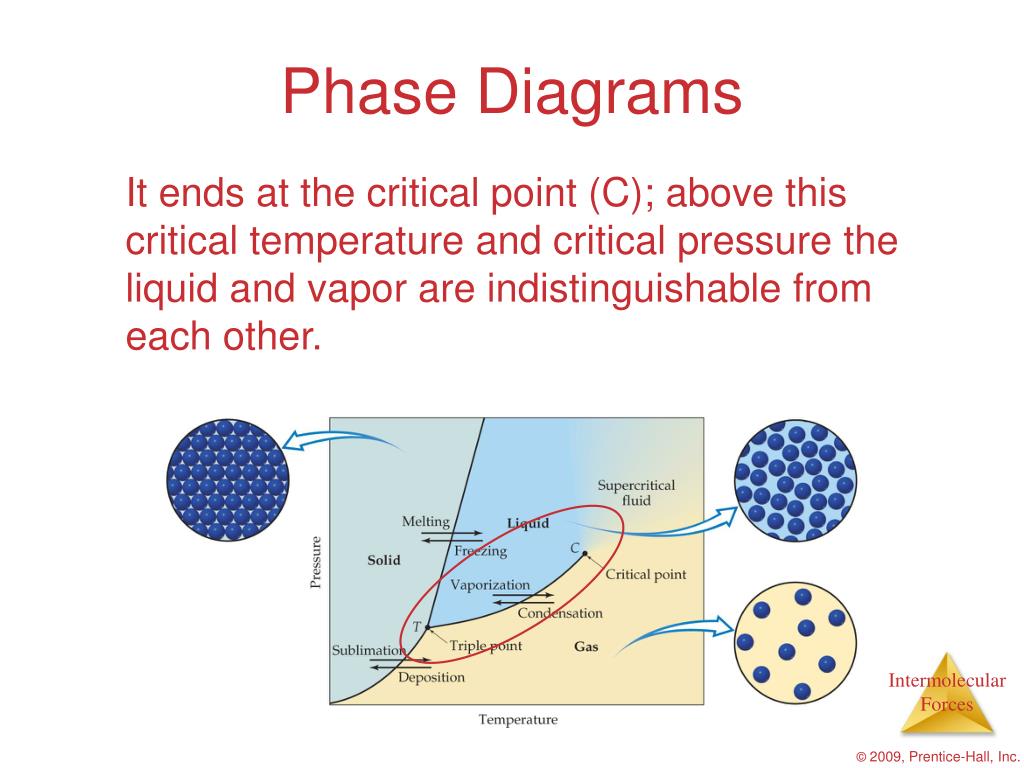
Which phase change corresponds to evaporation?
- Examine the situation to determine that there is a change in the temperature or phase. ...
- Identify and list all objects that change temperature or phase.
- Identify exactly what needs to be determined in the problem (identify the unknowns). ...
- Make a list of what is given or what can be inferred from the problem as stated (identify the knowns). ...
What are the six processes of a phase change?
What Are the Six Processes of a Phase Change?
- Fusion. Fusion occurs when a substance changes from a solid to a liquid. ...
- Solidification. Solidification occurs when a substance changes from a liquid to a solid. ...
- Vaporization. Vaporization occurs when a substance changes from a liquid to a gas. ...
- Condensation. ...
- Sublimation. ...
- Physical Vapor Deposition. ...
How do you calculate phase change?
You can calculate changes in enthalpy using the simple formula: ∆H = H products − H reactants. Definition of Enthalpy. ... Finally, calculate the final heating phase (from 273 to 300 K) in the same way as the first: ∆H = nC∆T = 5 mol × 75.4 J/K mol × 27 K = 10.179 kJ. Sum these parts to find the total change in enthalpy for the reaction:
What happens to heat energy during a phase change?
- Movement of the entire atomic structure creates changes in the state of matter (in relation to the environment)
- Movement of the bonding electrons causes chemical reactions
- Move
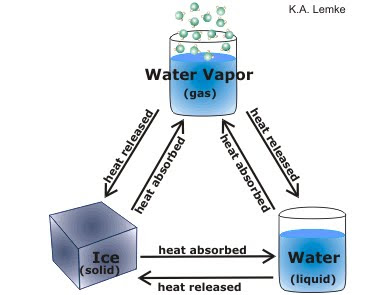
Is evaporation an example of phase change?
1 Answer. Phase changes include vaporization, condensation, melting, freezing, sublimation, and deposition. Evaporation, a type of vaporization, occurs when particles of a liquid reach a high enough energy to leave the surface of the liquid and change into the gas state.
What is the phase change of condensation?
During condensation, a substance is changed from the gaseous to the liquid state of matter. Vaporization, which is more often referred to as "boiling," is the complementary process in which a chemical is converted from the liquid state of matter to a gaseous physical form.
What are the 5 phase changes?
Sublimation, deposition, condensation, evaporation, freezing, and melting represent phase changes of matter.
What are examples of phase changes?
Examples of Phase Change Freezing is when liquid water freezes into ice cubes. Melting is when those ice cubes melt. Condensation is when dew forms on grass in the morning. Vaporization is when water boils and turns into steam.
What phase change is precipitation?
When the water vapor in clouds cools, it can condense into a liquid and fall as rain or freeze into a solid and fall as snow or ice crystals.
What is the phase change of melting?
Melting, or fusion, is a physical process that results in the phase transition of a substance from a solid to a liquid. This occurs when the internal energy of the solid increases, typically by the application of heat or pressure, which increases the substance's temperature to the melting point.
What is evaporation example?
Drying clothes in the sun is one of the most common examples of evaporation. The water present in the clothes when they are washed (and hung on the line) is removed by the evaporation process. Crystallization is the process of obtaining crystals from the “mother” liquid. It takes place due to evaporation.
What do you mean by evaporation?
Evaporation happens when a liquid substance becomes a gas. When water is heated, it evaporates. The molecules move and vibrate so quickly that they escape into the atmosphere as molecules of water vapor. Evaporation is a very important part of the water cycle.
What are the 6 phase changes of water?
When water changes state in the water cycle, the total number of water particles remains the same. The changes of state include melting, sublimation, evaporation, freezing, condensation, and deposition. All changes of state involve the transfer of energy.
Where does evaporation take place?
surfaceEvaporation is a type of vaporization that occurs on the surface of a liquid as it changes into the gas phase. The surrounding gas must not be saturated with the evaporating substance.
What is the phase change from a gas to a liquid?
Condensation (Gas → Liquid) Condensation, the opposite of evaporation, is the change in the state of matter from the gas phase to the liquid phase.
What are 7 examples of phase changes?
Learning ObjectivesSolid → LiquidMelting or fusionLiquid → GasVaporizationLiquid → SolidFreezingGas → LiquidCondensationSolid → GasSublimationJul 30, 2020
What are the causes of evaporation?
When a liquid material becomes a gas, evaporation occurs. It evaporates as water is hot. The molecules move and vibrate so rapidly that they disper...
What are the steps of evaporation?
In the water cycle, there are four key phases. Evaporation, condensation, precipitation and collection are as they are. Let’s look at the steps of...
How does evaporation become condensation?
At higher layers of the atmosphere, water molecules that have travelled upward by evaporation finally reach the colder air. Water vapour condenses...
How can evaporation be prevented?
Cool the water down by holding it in the shade, adding ice or freezing with refrigerated pipes or restricting its exposure to sunlight. This reduce...
What is evaporation examples?
Evaporation is described as the phase in which the water state takes place from the liquid to the gaseous or vapour state. An example of evaporatio...
What is evaporation?
Evaporation is a form of vaporisation in which a liquid or solid is transformed into vapour. It involves a change in the state of matter.
What are the various factors that affect the rate of evaporation?
Evaporation is the process in which a liquid or solid is converted into vapour. Various factors that alter evaporation rate are surface area, tempe...
Does temperature alter the evaporation rate?
Yes, the temperature does affect the rate of evaporation. On increasing the temperature, the rate of evaporation increases.
How does humidity alter the rate of evaporation?
Humidity does affect the rate of evaporation. The larger the moisture, the more is air close to saturation. Hence lesser would be the rate of evapo...
What is the process of water vapor turning into steam?
Vaporization is when water boils and turns into steam. Deposition is one you may not know, but this happens when water vapor goes directly to freezing, like when there is frost on a cold winter morning. An example of sublimation happens when dry ice turns directly into gas. Gas can also change into a plasma.
What is the term for the change of a substance from solid to liquid?
Melting: the substance changes back from the solid to the liquid.
What happens when a substance hits its melting point?
Once a substance hits its melting point, it is a combination of solid and liquid for a while, as you can see by the flat line on the graph at stage II. At a certain point, all of the solid has turned into liquid. Now, the liquid can absorb energy in the form of heat for quite a while until it gets to its boiling point.
Why does water boil at a lower temperature?
If you try to boil water at a high altitude, you know that water boils at a lower temperature due to the lower pressure at that altitude. Substances on Earth can exist in one of six phases, but mostly they exist in one of three: solid, liquid or gas. There are six changes of phase that substances go through:
What is the term for the process of a substance changing from a gas to a solid without going through the?
Deposition: the substance changes directly from a gas to a solid without going through the liquid phase.
What happens when a substance is in a solid state?
When a substance is in a solid state, it can absorb a lot of energy in the form of heat until it hits its melting point. Think about snow outside. Once snow hits the ground, it stays there, whether it is -50 degrees F outside or all the way up to 32 degrees F.
What are the six phases of a substance?
There are six distinct changes of phase which happens to different substances at different temperatures. The six changes are: Freezing: the substance changes from a liquid to a solid. Melting: the substance changes back from the solid to the liquid. Condensation: the substance changes from a gas to a liquid. Vaporization: the substance changes ...
What is the process of evaporation?
Evaporation is a form of vaporisation that usually happens on the surface of liquids and it involves the transition of the liquid particles into the gaseous phase. Therefore, this process is said to involve a change in the state of matter of liquids. The surrounding gas must not be saturated with the substance which is evaporating.
How does Evaporation Cause Cooling?
Evaporation causes cooling naturally. The underlying principle behind this is, in order to change its state, the matter must either gain or lose energy. In the case of change of phase from liquid to gas, molecules of matter require energy to overcome their potential energy by their kinetic energy. So, the liquid takes this energy from its surroundings.
What happens to water molecules in the atmosphere?
At higher layers of the atmosphere, water molecules that have travelled upward by evaporation finally reach the colder air. Water vapour condenses in the humid, damp air, creating bigger droplets of water that will be visible as clouds gradually.
How does evaporation affect the temperature of a liquid?
The energy extracted from the vaporised liquid as evaporation occurs will decrease the temperature of the liquid, resulting in a process known as evaporative cooling.
How does an air cooler work?
The basic principle behind the working of an air cooler is evaporative cooling. As on a hot, dry day, the temperature is high and humidity is low, the evaporation rate is higher. The water takes energy from the air and gets converted to vapour. This makes the air cooler. Schematic Representation of Working of an Air Cooler.
What happens when water evaporates?
When water vapour formed from evaporation comes in contact with the cold tumbler, it loses energy and gets converted to water.
When a liquid material becomes a gas, evaporation occurs?
When a liquid material becomes a gas, evaporation occurs. It evaporates as water is hot. The molecules move and vibrate so rapidly that they disperse as water vapour molecules into the atmosphere.
