The phenotypic ratio is the relationship between the number of offspring who will inherit a certain characteristic or a set of traits. This ratio is often obtained by executing a test cross and then analysing the data from that cross to determine how frequently a trait or trait combination will be shown based on the genotype of the offspring.
What is the phenotypic ratio?
The phenotypic ratio is the number of times a specific combination of alleles appears in the predicted phenotypes of any offspring. Genetic information relating to the studied trait must be known.
What is the difference between monohybrid cross and phenotype ratio?
Phenotype ratio for the offspring refers to the characters which are observable and determined by functional genes or traits. Monohybrid cross deals with only one character. Gregor J Mendel was the first who studied the inheritance of a single character. Using monohybrid cross we can determine the phenotypic ratio of an individual.
How do you calculate phenotypic outcomes?
However, due to dominant and recessive alleles, there are only four possible phenotypic outcomes: The phenotypic ratio calculation result requires us to count the colored squares that relate to phenotype and add them up. We then list them as ratios, starting with the largest number. This gives us the following result: 9:3:3:1.
What is the phenotypic ratio acquired from a test cross used for?
The phenotypic ratio acquired from a test cross is used by researchers to get gene expression for generations of an organism. A test cross is a genetics technique for investigating and obtaining the phenotypes and genotypes of organisms’ progeny.
What is Phenotypic Ratio?
How does phenotypic ratio help us?
What is the E allele of guinea pigs?
Where are the mother's alleles in a Punnett square?
What is it called when a gene is homozygous?
What is a trait that is observable or measurable in an organism at any point during that organism's?
How is hair length determined?
See 4 more
About this website

What does a 1 2 1 phenotypic ratio mean?
incomplete dominanceA cross of two F1 hybrids, heterozygous for a single trait that displays incomplete dominance is predicted to give a 1:2:1 ratio among both the genotypes and phenotypes of the offspring.
What is the phenotype of the offspring?
Within an individual organism, the specific combination of alleles for a gene is known as the genotype of the organism, and (as mentioned above) the physical trait associated with that genotype is called the phenotype of the organism.
What type of cross produces a 1 1 1 1 phenotypic ratio?
In the monohybrid cross, a testcross of a heterozygous individual resulted in a 1:1 ratio. With the dihybrid cross, you should expect a 1:1:1:1 ratio!
How do you find phenotype ratio?
Write the amount of homozygous dominant (AA) and heterozygous (Aa) squares as one phenotypic group. Count the amount of homozygous recessive (aa) squares as another group. Write the result as a ratio of the two groups. A count of 3 from one group and 1 from the other would give a ratio of 3:1.
What is the phenotype of YY and YY?
Yy is the heterozygous genotype (one dominant allele, one recessive allele). The phenotype of this genotype is yellow seed color. yy is the homozygous dominant genotype (2 y alleles). The phenotype of this genotype is green seed color.
What is phenotype and example?
Phenotype Phenotype refers to an individual's observable traits, such as height, eye color and blood type. A person's phenotype is determined by both their genomic makeup (genotype) and environmental factors.
What does the 9 3 3 1 ratio mean?
The 9:3:3:1 ratio simply means that nine are wild-type meaning they are normal; six exhibit one mutant and one normal character, three are normal for one trait the other three are normal for the opposite trait; one has both mutant phenotypes.
What does a 3 1 ratio mean in genetics?
The F2 generation always produced a 3:1 ratio where the dominant trait is present three times as often as the recessive trait. Mendel coined two terms to describe the relationship of the two phenotypes based on the F1 and F2 phenotypes.
Which of the following crosses will lead to a 9 3 3 1 ratio of phenotypes?
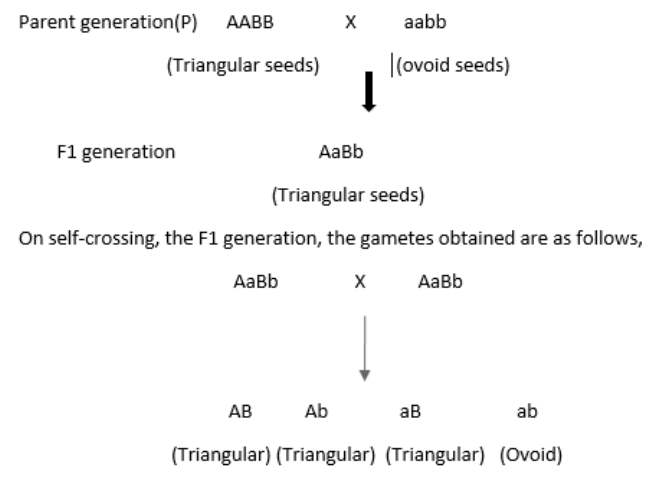
dihybrid crossA phenotypic ratio of 9:3:3:1 is predicted for the offspring of a SsYy x SsYy dihybrid cross.
How do you find the genotypic and phenotypic ratios?
0:284:46Genotypic Ratios and Phenotypic Ratios for Punnett Squares - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipCode you will write the homozygous dominant then the heterozygous then the homozygous recessive. SoMoreCode you will write the homozygous dominant then the heterozygous then the homozygous recessive. So let's go ahead and write this out. First let's look for homozygous dominant we have one of those
How do you write genotype and phenotype ratios?
6:147:36Genotype and Phenotype Ratios and Percents ( Punnett Square Basics)YouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipAnd phenotype. First. Thing I need to do which is dominant white or black remember anytime you haveMoreAnd phenotype. First. Thing I need to do which is dominant white or black remember anytime you have heterozygous that is the dominant trait. So I have the heterozygous white rabbit here and then a
How do you find the phenotypic ratio in a Punnett square?
Your Punnett square contains one YY, two Yy and one yy, so your genotypic ratio is 1 : 2 : 1. If Y is dominant and y is recessive, there are only two phenotypes because YY and Yy have the same phenotype, so your phenotypic ratio is 3 : 1 (the two Yys plus the one YY make 3 of that phenotype).
What are 3 examples of phenotypes?
In humans, phenotype examples include earwax type, height, blood type, eye color, freckles, and hair color. And phenotypes aren't just physical traits. Behavior is also considered a phenotype.
What are the 3 types of phenotypes?
With one locus and additive effects we have three phenotypic classes: AA, Aa and aa.
What would be the phenotypic ratio of offspring made from two heterozygous individuals both are RrYy )?
Both the product rule and the Punnett Square approaches showed that a 9:3:3:1 phenotypic ratio is expected among the progeny of a dihybrid cross such as Mendel's RrYy × RrYy. In making these calculations, we assumed that: both loci assort independently; one allele at each locus is completely dominant; and.
How do you write a phenotype?
1:204:46Genotypic Ratios and Phenotypic Ratios for Punnett Squares - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipIt is the dominant trait. So it will be 1 2. 3 because anytime you have a capital letter you get theMoreIt is the dominant trait. So it will be 1 2. 3 because anytime you have a capital letter you get the dominant trait and then 1 for short which is the recessive trait.
What is a phenotypic ratio example?
A phenotypic ratio example is 1:3. This means for every one organism that has the dominant phenotype in the offspring there will be three that have...
What does a phenotypic ratio of 1 1 mean?
A phenotypic ratio of 1:1 means that there are equal numbers of two phenotypes expected in the progeny of a cross.
What is phenotypic and genotypic ratio?
A phenotypic ratio is a numerical comparison of how many offspring will have one phenotype versus another. A genotypic ratio is a numerical compari...
How do you find the phenotypic ratio?
To find a phenotypic ratio you first carry out a Punnett square to find the potential phenotypes of the offspring. You then use the numbers to crea...
Phenotypic Ratio: Definition, Calculation, and Examples - Research Tweet
Before learning how to calculate a phenotypic ratio, you need to be familiar with the following genetic terms: • Gene: A gene is anything that is inherited from a parent and handed on to their children. • Allele: A gene variant that is passed down from one of two parents. • The thread-like structure made up of nucleic acids and proteins that carries the gene is called a chromosome.
What is phenotypic ratio?
A phenotypic ratio is a quantifiable relationship between phenotypes that shows how often the frequency of one phenotype corresponds with the frequency of another. The phenotypic ratio acquired from a test cross is used by researchers to get gene expression for generations of an organism.
What is the most common phenotype?
The most common phenotype will be a dark, long, straight-haired human child with a combination of all the dominant genes. This is due to the fact that once the alleles are joined, the dominant allele always takes precedence. The following phenotypes will be observed:
What happens when two heterozygous parents each pass on one allele to their children?
This happens when two heterozygous parents each pass on one allele to their children, resulting in two potential phenotypes despite the presence of multiple genotypes. It’s crucial to keep in mind that genotypic and phenotypic ratios aren’t usually equal.
How many phenotypes can a dihybrid cross produce?
Because the two genes now give way to numerous phenotypic outputs, this dihybrid cross will produce more than two phenotypic results. The phenotypic ratio now stands at 9:3:3:1, with the options being long, black hair, long brown hair, short black hair, and short brown hair. We can observe that when additional genes are introduced into the breeding process, the phenotypes get more complicated.
What is monohybrid cross?
A monohybrid cross occurs when two homozygous parents cross, resulting in just one trait in their offspring. It can also happen when both parents’ genotypes are entirely dominant or completely recessive, resulting in the opposite phenotype for some genetic characteristics. Using a Punnett Square, this may be easily established.
What is the definition of phenotype?
The phenotype is defined as the expression of genes and alleles in observable characteristics. Eye colour, height, and even hair texture are all phenotypes. Through a test cross, genotypes may be used to determine the phenotypes of an organism’s progeny and, as a result, the phenotypic ratio.
Why do breeders use only one phenotype?
When two phenotypes are involved , dihybrid crossings come into play. However, there is a reason why breeders seldom use only one phenotype. If they do, they will never have the opportunity to investigate other options or build even more distinctive and interesting features. Why raise bigger pigs for more meat if they only get brain defects from both parents? As a result, geneticists continue to seek and promote beneficial breeds while avoiding breeding fewer desirable ones. They can calculate the phenotypic ratio using a dihybrid cross calculator.
What is the ratio of a phenotype?
Ratios are comparisons between numbers. Phenotypes are physical characteristics. When ratios are used to describe phenotypes it's called a phenotypic ratio. Phenotypic ratio is the number of one phenotype compared to another phenotype. In this picture the phenotypic ratio of white mice to brown mice is 2:1.
Why use Punnett squares?
It's often associated with Punnett squares. Punnett squares are diagrams used to assist people in determining the phenotypes of a genetic cross. For example, suppose you allow two black chickens to breed. A Punnett square could help predict the likelihood of producing offspring with a specific phenotype.
What is phenotypic variation in chickens?
Phenotypic Variation in Chickens. Notice how all three chickens have different phenotypes . A phenotype represents one of the physical characteristics of an organism. In this example, each chicken displays a different phenotype for feather color.
What is the ratio of white mice to brown mice?
In this picture the phenotypic ratio of white mice to brown mice is 2:1.
How many chances do black chickens have of producing white offspring?
So in genetic terms you'd say these two black chickens have a 75% chance of producing black offspring, or a 25% chance of producing white offspring. That is the function of a Punnett square. Predictions made by the example Punnett square (feather color) were given in percentages.
What is ratio in math?
Ratios (comparisons between two numbers) are everywhere. Consider baking a turkey in the oven for example. The time a turkey is cooked depends on the weight of the bird. Time and weight are both numerical values that are being compared. Hence, we're looking at a ratio. Or consider the number of servings a box of macaroni contains. The number of servings compared to the one box is another ratio.
What is Dominic Corsini's education background?
in Secondary Biology and General Science with a Minor in Environmental Education, an M.Ed. in Educational Leadership, an M.S. in Biology, and a K-12 Principal Certification Program. Corsini has experience as a high school Life, Earth, Biology, Ecology, and Physical Science teacher.
What is Phenotypic Ratio?
Phenotypic ratio is a term that describes probability of finding the patterns and frequency of genetic trait outcomes in the offspring of organisms. A phenotype is an observable or measurable characteristic and is the result of expressed genes. For example, by noting the traits in a long-haired, pink-nosed and a short-haired, black-nosed guinea pig breeding pair, we can calculate the probability of their offspring having pink or black noses and short or long hair. The number of times each phenotype is expected to occur according to strict calculation determines the phenotypic ratio.
How does phenotypic ratio help us?
Phenotypic ratio helps us to predict gene expression in the future generations of organisms. In phenotypic ratio calculations, we map out specific parental alleles and predict the probability of how they will be expressed in their offspring. Knowledge of allele dominance is required, although it is possible to figure out very simple parental ...
What is the E allele of guinea pigs?
Here, the small ear gene is recessive and both parents have the Ee allele, where E represents the phenotype for big ears and e small ears.
Where are the mother's alleles in a Punnett square?
In a Punnett square, the mother’s alleles are noted at the top and the father’s at the side. The dominant allele is always listed first.
What is it called when a gene is homozygous?
Allele: a version of a gene that comes from one of the two parents. When an allele from either parent is the same, it is called a homozygous gene. If two alleles inherited from the parents are different, the alleles of that organism ’s offspring can also be heterozygous. (See below image).
What is a trait that is observable or measurable in an organism at any point during that organism's?
Phenotype: a trait that is observable or measurable in an organism at any point during that organism’s lifetime. A phenotype is an expressed gene.
How is hair length determined?
The hair length is, for this example’s purposes, determined by a single allele. Both parents carry a complete set of DNA that includes instructions for both hair lengths and both come from very long lines that only include their particular hair length.
