
Full Answer
What is PIE in social work?
What is the mission of PIE?
Who created the classification system?
About this website

What does pie stand for in social work?
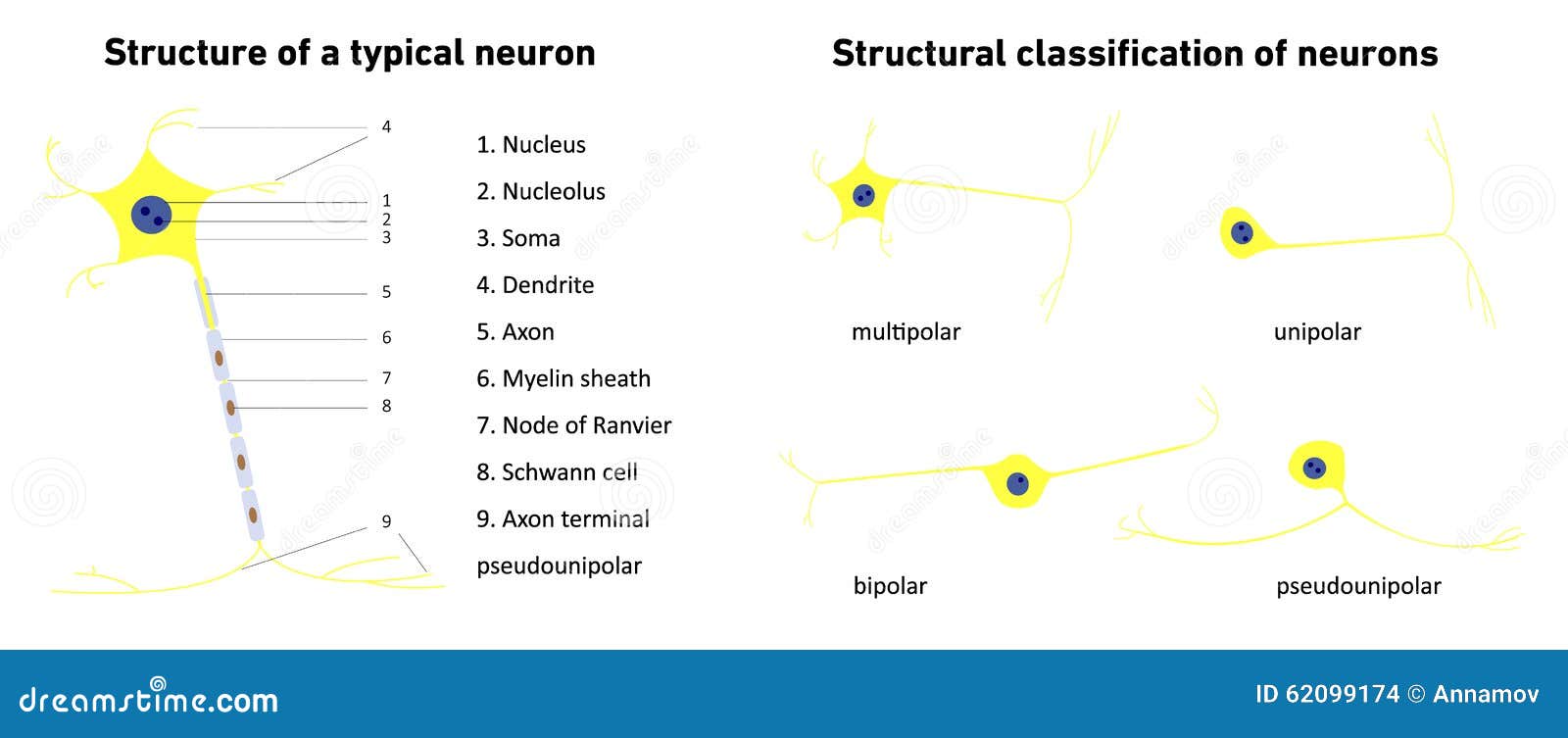
Person-in-Environmentof the Person-in-Environment (PIE) system (Karls & Wandrei, 1994) for. social work education and practice.
What is pie theory?
The most basic systems theory of generalist social work practice is Person-In-Environment or “PIE.” By considering the various relationships and communities that a person has (e.g., school, family, church, etc.), social workers gain an understanding of how the person and his or her environments affect each other ...
How does the pie perspective will be helpful to your future career as a social worker?
To allow the social worker to identify aspects of the environment that may be contributing to client problems. The social worker can then choose to intervene with the problematic environmental systems as much as their role will allow. To initiate social change on a macro-level.
What is an example of person-in-environment?
Some examples include home, school, or work. A microsystem typically includes family, peers, or caregivers. Relationships in a microsystem are bi-directional, meaning, how you respond and react to the people will affect their response and reaction to you. This is the most influential level within the theory.
How do you use pie theory?
The P.I.E. Theory of Success – Performance, Image, Exposure10% - You must perform exceptionally well.30% - Cultivate the proper image.60% - Manage your exposure so the right people will know you.Again, you need more than great performance to get ahead!More items...•
Who invented the pie model?
The earliest known pie chart is generally credited to William Playfair's Statistical Breviary of 1801, in which two such graphs are used. Playfair presented an illustration, which contained a series of pie charts.
What are theoretical perspectives in social work?
Social work theories attempt to describe, explain and predict social events based on scientific evidence, studies and research. Social work perspectives draw from psychology, philosophy, economics, education and other fields to attempt to explain what drives and motivates people at various stages of life.
What is an example of systems theory in social work?
SYSTEMS THEORY A person's parents, friends, school, economic class, home environment and other factors all influence how a person thinks and acts. Seeking to help correct missing or ineffective parts of that system can have a positive impact on behavior.
Is person-in-environment a theoretical framework?
A person-in-environment perspective is said to provide a more adequate framework for assessing an individual and his or her presenting problem and strengths than an approach that focuses solely on changing an individual's behavior or psyche, or one that focuses solely on environmental conditions.
Why is social environment important in social work?
A well-designed social environment helps foster positive peer relationships, creates positive interactions between adults and children, and provides opportunities for adults to support children to achieve their social goals.
How does social environment affect human behavior?
The environment can facilitate or discourage interactions among people (and the subsequent benefits of social support). For example, an inviting space with comfortable chairs and privacy can encourage a family to stay and visit with a patient. The environment can influence peoples' behavior and motivation to act.
What is the difference between family social work and family therapy?
Social work is a behavioral health profession that focuses on services for individuals, families, groups, and communities. Marriage and family therapy is a clinical mental health profession centered on the well-being of individuals and families within the context of relationships.
What are the 3 elements of the pie theory?
Three of these elements (client, target and action) contribute directly to the effective use of the PIE System. This element identifies the decision to work directly with people who request or are willing to be in a client role to address a social functioning problem.
What does pie mean in leadership?
She said leadership is really a PIE, where P = Performance, I = Image, and E = Exposure. When you focus on those three elements, you will succeed.
What is pie an acronym for?
Persuade, Inform, Entertain (writing)
What is the pie model of capital structure?
A model of the debt-equity ratio of the firms, graphically depicted in slices of a pie that represent the value of the firm in the capital markets.
THE PERSON-IN-ENVIRONMENT SYSTEM (PIE) Flashcards | Quizlet
Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like The person-In-Environment System was developed by, PIE was developed for, PIE and more.
Person In-Environment Framework - 1672 Words - Internet Public Library
Undocumented Family 1670 Words | 7 Pages. The effects of growing up in a family where family members are at risk for the deportation can also be understood from the perspective of toxic stress, that is, the notion that adverse experiences that upset child, parent and household, can result in biological, neurological and psychological changes.
The Person-in-Environment (PIE) System for Describing Problems of ...
Not a subscriber? Subscribe Now / Learn More. PsychiatryOnline subscription options offer access to the DSM-5 library, books, journals, CME, and patient resources.
PIE: Person-In-Environment - University of Calgary in Alberta
Domain of Practitioner. This component is used to acknowledge that social workers, like the people they work with, have their own person-in-environment systems, personally and professionally.
What is PIE in social work?
The Social Work profession struggled for many years to establish its unique identity among the human services profession. An important step in this struggle was the embracing of the “person in environment” (PIE) perspective. This perspective highlights the importance of understanding individuals and families in light of their environment contexts and has become the philosophy undergirding the social work profession thus addressing a long standing debate over how much attention should be given to individual or environmental change.
What is the mission of PIE?
Importantly, regardless of the changes over the years, the mission of PIE has remained the same -- to provide a tool with which the problems, strengths and coping capacities presented by clients can be systematically and comprehensively assessed, described, and addressed within an eclectic framework that highlights social work’s unique contribution to the human service field.
Who created the classification system?
In the early 1980’s, a task force of practitioners and academicians, led by Dr. James Karls and Dr. Karin Wandrei, was formed to develop a classification system useable in all fields of social work practice and one that would be both user and client friendly.
Definitions
A π-system is a non-empty collection of sets P {\displaystyle P} that is closed under non-empty finite intersections, which is equivalent to P {\displaystyle P} containing the intersection of any two of its elements. If every set in this π -system is a subset of Ω {\displaystyle \Omega } then it is called a π-system on Ω . {\displaystyle \Omega .}
Examples
For a , b ∈ R , {\displaystyle a,b\in \mathbb {R} ,} the intervals ( − ∞ , a ] {\displaystyle (-\infty ,a]} form a π -system, and the intervals ( a , b ] {\displaystyle (a,b]} form a π -system if the empty set is also included.
π-Systems in probability
π -systems are more commonly used in the study of probability theory than in the general field of measure theory. This is primarily due to probabilistic notions such as independence, though it may also be a consequence of the fact that the π -𝜆 theorem was proven by the probabilist Eugene Dynkin.
What Is PIE Theory?
Dustin is currently providing counseling to Charles, a 40-year-old man who beat his wife until she was unconscious. It is not easy for many people to have empathy for a criminal like Charles, but social workers like Dustin garner empathy for their clients by using the person-in-environment (PIE) theory.
Who is the pioneer of PIE theory?
Mary Richmond was the pioneer of PIE theory in her 1917 book Social Diagnosis. The PIE theory is a way for social workers to: Assess for all aspects of a client's environment. Intervene in certain aspects of their client's environment. Advocate for social change and social program creation.
What does Sarah use Pie theory for?
Sarah uses PIE theory to look at Annie's multiple environmental influences. Assessment and Evaluation. Sarah asks Annie about her home life, her parents, the neighborhood she lives in, and if her family attends a religious organization.
Why is Annie not able to adhere to the structured school environment?
The lack of structure can explain why Annie is not able to adhere to the structured school environment. Lack of sleep or nutrition could be causing anger and attention issues. Exposure to violence each day may be why she chooses violence on the playground. Sarah has evaluated Annie's problem based on the PIE theory.
What is PIE in social work?
The Social Work profession struggled for many years to establish its unique identity among the human services profession. An important step in this struggle was the embracing of the “person in environment” (PIE) perspective. This perspective highlights the importance of understanding individuals and families in light of their environment contexts and has become the philosophy undergirding the social work profession thus addressing a long standing debate over how much attention should be given to individual or environmental change.
What is the mission of PIE?
Importantly, regardless of the changes over the years, the mission of PIE has remained the same -- to provide a tool with which the problems, strengths and coping capacities presented by clients can be systematically and comprehensively assessed, described, and addressed within an eclectic framework that highlights social work’s unique contribution to the human service field.
Who created the classification system?
In the early 1980’s, a task force of practitioners and academicians, led by Dr. James Karls and Dr. Karin Wandrei, was formed to develop a classification system useable in all fields of social work practice and one that would be both user and client friendly.
Overview
In mathematics, a π-system (or pi-system) on a set is a collection of certain subsets of such that
• is non-empty.
• If then
That is, is a non-empty family of subsets of that is closed under non-empty finite intersections. The importance of π-systems arises from the fact that if two probability measures agree on a π-syste…
Relationship to 𝜆-systems
A 𝜆-system on is a set of subsets of satisfying
• if then (where ),
• if is a sequence of (pairwise) disjoint subsets in then
Whilst it is true that any 𝜎-algebra satisfies the properties of being both a π-system and a 𝜆-system, it is not true that any π-system is a 𝜆-system, and moreover it is not true that any π-system is a 𝜎-al…
π-Systems in probability
π-systems are more commonly used in the study of probability theory than in the general field of measure theory. This is primarily due to probabilistic notions such as independence, though it may also be a consequence of the fact that the π-𝜆 theorem was proven by the probabilist Eugene Dynkin. Standard measure theory texts typically prove the same results via monotone classes, rather than π-systems.
See also
• δ-ring – Ring closed under countable intersections
• Field of sets – Algebraic concept in measure theory, also referred to as an algebra of sets
• Ideal (set theory) – Non-empty family of sets that is closed under finite unions and subsets
Citations
1. ^ Kallenberg, Foundations Of Modern Probability, p. 2
2. ^ Durrett, Probability Theory and Examples, p. 404
3. ^ Kallenberg, Foundations Of Modern probability, p. 48