| Compound | Formula | Ka value | pKa value |
| Acetic acid | CH 3 COOH | 1.7 x 10 -5 | 4.75 |
| Benzoic acid | C 6 H 5 COOH | 6.3 x 10 -5 | 4.20 |
| Boric acid | H 3 BO 3 | 5.9 x 10 -10 | 9.15 |
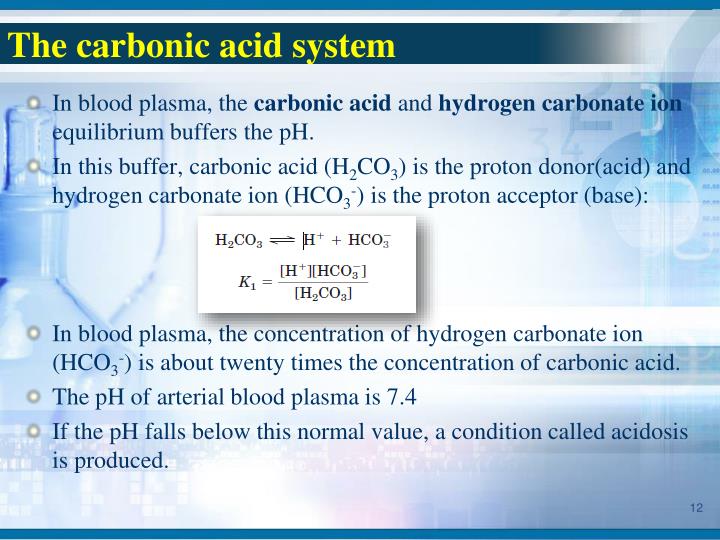
| Carbonic acid | H 2 CO 3 HCO 3– | 4.3 x 10 -7 4.8 x 10 -11 | 6.35 10.33 |
How to calculate pKa values?
pKa value can be determined by the titration curve. To calculate the pKa of the solution, firstly, we will determine the equivalence point and then find the pH of the solution. pKa of the solution is equivalent to the pH of the solution at its equivalence point. Hence we can quickly determine the value of pKa by using a titration curve.
How do you calculate pKa?
pKa = - log Ka. at half the equivalence point, pH = pKa = -log Ka. A large Ka value indicates a strong acid because it means the acid is largely dissociated into its ions. A large Ka value also means the formation of products in the reaction is favored.
What is the equation for carbonic acid?
What does the formula for carbonic acid? carbonic acid, (H2CO3), a compound of the elements hydrogen, carbon, and oxygen. It is formed in small amounts when its anhydride, carbon dioxide (CO2), dissolves in water. HCO3− + OH− ⇌ CO32− + H2O (fast) Between pH values of 8 and 10, all the above equilibrium reactions are significant.
What are the uses of carbonic acid?
Carbonic acid is used topically to treat dermatitides, such as ringworm, and can be used as a mouthwash or vaginal douche. It can also be given orally to induce vomiting in cases of poisoning or a drug overdose.
What is the pH of carbonic acid?
pH of Common Acids and BasesAcidName10 mMH2CO3carbonic acid4.18H2CrO4chromic acid2.33H2MoO4molybdic acid2.94H2Shydrogen sulfide4.4722 more rows•Jan 17, 2021
What is pKa value of acid?
Definition of pKa pKa is a number that describes the acidity of a particular molecule. It measures the strength of an acid by how tightly a proton is held by a Bronsted acid. The lower the value of pKa, the stronger the acid and the greater its ability to donate its protons.
How many Ka does carbonic acid have?
Chapter 27 Appendix C: Dissociation Constants and pK a Values for Acids at 25°CNameFormulaK a1Carbonic acidH 2CO 34.5 × 10 −7Chloroacetic acidCH 2ClCO 2H1.3 × 10 −3Chlorous acidHClO 21.1 × 10 −2Chromic acidH 2CrO 41.8 × 10 −140 more rows
How do you find the pKa value?
0:291:45Calculating pKa - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipSo first of all we have to find the KA. And then we find the pKa. So the pKa is going to come fromMoreSo first of all we have to find the KA. And then we find the pKa. So the pKa is going to come from the concentration multiplying the concentration of hydronium. Times. The fluoride ion concentration
Is carbonic acid a strong acid?
Is carbonic acid a strong acid? No, carbonic acid is not a strong acid. H2CO3 is a weak acid that dissociates into a proton (H+ cation) and a bicarbonate ion (HCO3- anion). This compound only partly dissociates in aqueous solutions.
Which acid has highest pKa value?
HF (pKa = 3.1) , HCl (pKa = -6.0) , HBr (pKa = -9.0) , HI (pKa = -9.5). Hence HF has the highest pKa value.
What is the Ka for H2CO3?
The acid dissociation constant, Ka, of carbonic acid (H2CO3) is 4.5 x 10-7.
What is Ka1 for carbonic acid?
For carbonic acid the Ka1 = 4.30 × 10^-7 and the Ka2 = 5.62 × 10^-11.
Is pKa the same as pH?
Difference Between pKa and pH pKa is the negative value of the logarithm of Ka. pH is the logarithmic value of the inverse of H+ concentration. pKa indicates whether an acid is a strong acid or a weak acid. pH indicates whether a system is acidic or alkaline.
What is the pKa of HCl?
1 Answer. Since HCl is a strong acid, the value of Ka turns out to be very large, that is, Ka=1071=107 (approx.)
How do you find pKa from pH?
When the moles of base added equals half the total moles of acid, the weak acid and its conjugate base are in equal amounts. The ratio of CB / WA = 1 and according to the HH equation, pH = pKa + log(1) or pH = pKa.
What is pKa of weak acid?
pKa of a weak acid (HA) and pKb of a weak base (BOH) are 3.2 and 3.4 , respectively.
What does pKa stand for?
Difference Between pKa and pKbpKa vs pKbThe negative logarithm of Ka is pKa.The negative logarithm of Kb is pKb.Relationship With Dissociation ConstantThe acid dissociation constant is related to pKa.The base dissociation constant is related to pKb.Indications3 more rows
Does high pKa mean strong acid?
In addition, the smaller the pKa value, the stronger the acid. For example, the pKa value of lactic acid is about 3.8, so that means lactic acid is a stronger acid than acetic acid.
What is pKa and pH?
pKa is the negative value of the logarithm of Ka. pH is the logarithmic value of the inverse of H+ concentration. Indication of Acidity. pKa indicates whether an acid is a strong acid or a weak acid.
Why pKa value is important?
Acid dissociation constants, or pKa values, are essential for understanding many fundamental reactions in chemistry. These values reveal the deprotonation state of a molecule in a particular solvent. There is great interest in using theoretical methods to calculate the pKa values for many different types of molecules.
What is the pH of carbonic acid?
Since pK a1 has a value of ca. 6.8 , at equilibrium carbonic acid will be almost 50% dissociated in the extracellular fluid ( cytosol) which has a pH of ca.7.2. Note that dissolved carbon dioxide in extracellular fluid is often called as "carbonic acid" in biochemistry literature, for historical reasons. The reaction in which it is produced.
Where is carbonic acid found?
The fact that the carbonic acid may form by irradiating a solid H 2 O + CO 2 mixture or even by proton-implantation of dry ice alone has given rise to suggestions that H 2 CO 3 might be found in outer space or on Mars, where frozen ices of H 2 O and CO 2 are found, as well as cosmic rays.
What temperature does carbonic acid decompose?
The pure compound decomposes at temperatures greater than ca. −80 °C. In biochemistry, the name "carbonic acid" is often applied to aqueous solutions of carbon dioxide, which play an important role in the bicarbonate buffer system, used to maintain acid–base homeostasis.
Is carbon dioxide converted to carbonic acid?
Hence, the majority of the carbon dioxide is not converted into carbonic acid, remaining as CO 2 molecules. In the absence of a catalyst, the equilibrium is reached quite slowly. The rate constants are 0.039 s −1 for the forward reaction and 23 s −1 for the reverse reaction. In nature, limestone may react with rainwater, ...
Is carbonic acid a dibasic acid?
In aqueous solution carbonic acid behaves as a dibasic acid. The Bjerrum plot shows typical equilibrium concentrations,in solution, in seawater, of carbon dioxide and the various species derived from it, as a function of pH. The acidification of natural waters is caused by the increasing concentration of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere, ...
Is carbonic acid anhydrous or anhydrous?
Pure carbonic acid. Carbonic acid, H 2 CO 3, is stable at ambient temperatures in strictly anhydrous conditions. It decomposes to form carbon dioxide in the presence of any water molecules. Carbonic acid forms as a by-product of CO 2 /H 2 O irradiation, in addition to carbon monoxide and radical species (HCO and CO 3 ).

Overview
Chemical equilibria
In aqueous solution carbonic acid behaves as a dibasic acid. The Bjerrum plot shows typical equilibrium concentrations, in solution, in seawater, of carbon dioxide and the various species derived from it, as a function of pH. The acidification of natural waters is caused by the increasing concentration of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere, which is caused by the burning of increasin…
Use of the term carbonic acid
Strictly speaking the term "carbonic acid" refers to the chemical compound with the formula , however, for historical reasons, dissolved carbon dioxide in extracellular fluid is often called as "carbonic acid" in biochemistry literature.
Since pKa1 has a value of ca. 6.8, at equilibrium carbonic acid will be almost 50% dissociated in the extracellular fluid (cytosol) which has a pH of ca. 7.2.
Pure carbonic acid
Carbonic acid, H2CO3, is stable at ambient temperatures in strictly anhydrous conditions. It decomposes to form carbon dioxide in the presence of any water molecules.
Carbonic acid forms as a by-product of CO2/H2O irradiation, in addition to carbon monoxide and radical species (HCO and CO3). Another route to form carbonic acid is protonation of bicarbonates (HCO3 ) with aqueous HCl or HBr. This has to be done at cryogenic conditions to a…
Further reading
• "Climate and Carbonic Acid" in Popular Science Monthly Volume 59, July 1901
• Welch, M. J.; Lifton, J. F.; Seck, J. A. (1969). "Tracer studies with radioactive oxygen-15. Exchange between carbon dioxide and water". J. Phys. Chem. 73 (335): 3351. doi:10.1021/j100844a033.
• Jolly, W. L. (1991). Modern Inorganic Chemistry (2nd Edn.). New York: McGraw-Hill. ISBN 978-0-07-112651-9.
External links
• Carbonic acid/bicarbonate/carbonate equilibrium in water: pH of solutions, buffer capacity, titration and species distribution vs. pH computed with a free spreadsheet
• How to calculate concentration of Carbonic Acid in Water