What reactions are involved in the urea cycle?
What reactions are involved in the urea cycle?
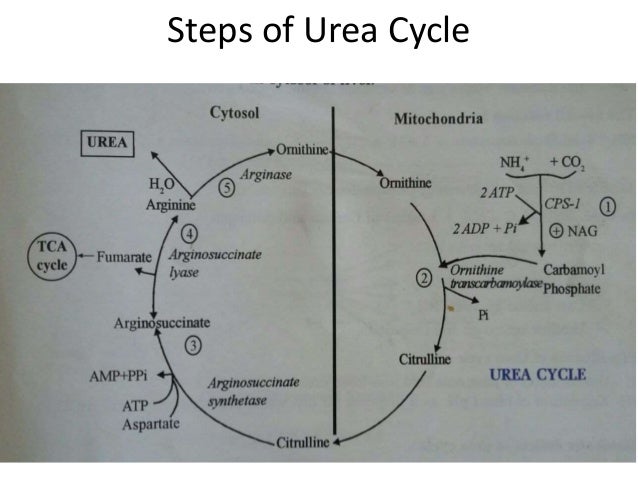
- Step I: Formation of Carbamoyl phosphate. ...
- Step II: Synthesis of Citrulline This step also occurs in the mitochondrial matrix. ...
- Step III: Condensation of Citrulline and Aspartate molecules The citrulline is transported from the mitochondrial matrix to the cytoplasm. ...
How many urea cycle occuring in the body?
Where does urea cycle happen? In humans and mammals, almost 80% of the nitrogen excreted is in the form of urea, which is produced through a series of reactions occurring in the cytosol and mitochondrial matrix of liver cells. These reactions are collectively called the urea cycle or the Krebs-Henseleit cycle. How many ATPS are used in urea cycle?
What compound is regenerated in the urea cycle?
- X-linked gene
- in mitochondria; ornithine transported into mitochondria
- carbamoyl phosphate is the carbamoyl donor which has a high transfer potential because of its phosphoanhydride bond
- inorganic phosphate released
- citrulline produced, which is transported from the mitochondria to the cytosol where the remaining reactions of the urea cycle occur
What are the symptoms of urea cycle disorder?
Symptoms and Signs of Urea Cycle Disorders. Clinical manifestations range from mild (eg, failure to thrive, intellectual disability, episodic hyperammonemia) to severe (eg, altered mental status, coma, death). Manifestations in female carriers of OTC deficiency range from growth failure, developmental delay, psychiatric abnormalities, and ...
Why is the formation of urea important?
Urea produced by the liver is then released into the bloodstream, where it travels to the kidneys and is ultimately excreted in urine. The urea cycle is essential to these organisms, because if the nitrogen or ammonia are not eliminated from the organism it can be very detrimental.
What is the function of the urea cycle quizlet?
What is the function of the urea cycle? It is to remove the toxic compound ammonia by transforming it to harmless form called urea, which is then, excreted form the body.
What is the purpose of the urea cycle and how is the urea cycle linked to the citric acid cycle?
In the adult, urea cycle enzymes change as a unit, and are largely influenced by dietary protein content. The urea cycle is closely linked to the citric acid cycle deriving one of its nitrogens through transamination of oxalacetate to form asparate and returns fumarate to that cycle.
Where does urea cycle occur 1 point?
Urea is exclusively produced in liver and then transported through the blood to the kidneys for the excretion through urine. Urea is formed from the NH4, CO2 and alpha-amino nitrogen of aspartate which requires ATP. Enzymes which catalyzes the urea cycle are present in the mitochondria and cytosol of liver cell.
What are the products of urea cycle?
Products of urea cycle are: 1 molecule of urea, 2 molecules of ADP, 1 molecule each of AMP and fumaric acid.
How is the urea cycle regulated quizlet?
Urea Cycle is primarily regulated by the availability of substrate. The higher the production rate of ammonia, the faster the cycle moves to excrete it.
Does the urea cycle produce ATP?
The urea cycle is irreversible and consumes 4 ATP. Two ATP are utilized for the synthesis of carbamoyl phosphate. One ATP is converted to AMP and PPi to produce arginosuccinate which equals to 2 ATP.
How the urea cycle facilitates disposal of nitrogen from amino acids?
The urea cycle operates only to eliminate excess nitrogen. On high-protein diets the carbon skeletons of the amino acids are oxidized for energy or stored as fat and glycogen, but the amino nitrogen must be excreted. To facilitate this process, enzymes of the urea cycle are controlled at the gene level.
How is the urea cycle linked to the citric acid cycle quizlet?
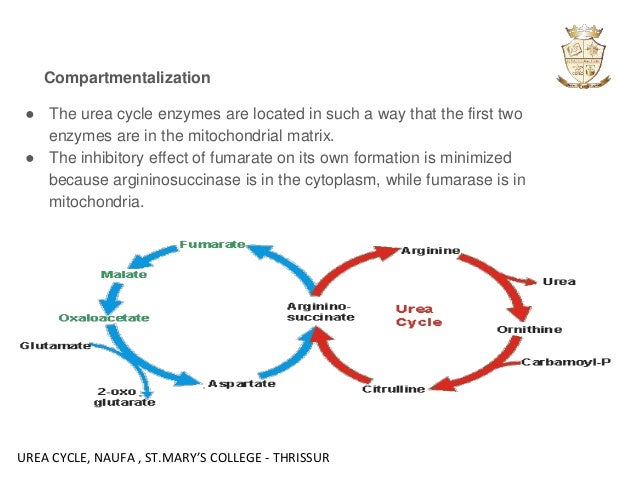
The urea cycle is linked to the citric acid cycle by fumarate and by aspartate, which can be con- verted to malate by transamination (see Figure 23.22).
Why is urea cycle called urea?
Why is the urea cycle referred to as a “bicycle”? There are actually 2 cycles going on. One takes ornithine to arginine and returns arginine to ornithine. The second takes fumarate from the argininosuccinate and returns it to aspartate.
What is urea cycle Slideshare?
1. The urea cycle is the first metabolic pathway to be elucidated. The cycle is known as Krebs–Henseleit urea cycle. Ornithine is the first member of the reaction, it is also called as Ornithine cycle. Urea is synthesized in liver & transported to kidneys for excretion in urine.
How can I remember my urea cycle?
1:194:29Mnemonics to learn urea cycle in just 5 minutes! - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipMeans anything okay the second one CA are carbamoyl phosphate then the third one C.MoreMeans anything okay the second one CA are carbamoyl phosphate then the third one C.
What is the urea cycle?
The urea cycle (also known as the ornithine cycle) is a cycle of biochemical reactions that produces urea (NH 2) 2 CO from ammonia (NH 3 ). This cycle occurs in ureotelic organisms. The urea cycle converts highly toxic ammonia to urea for excretion.
Why is the urea cycle important?
The urea cycle is essential to these organisms, because if the nitrogen or ammonia are not eliminated from the organism it can be very detrimental. In species including birds and most insects, the ammonia is converted into uric acid or its urate salt, which is excreted in solid form .
What is the first reaction in the urea cycle?
First reaction: entering the urea cycle. Before the urea cycle begins ammonia is converted to carbamoyl phosphate. The reaction is catalyzed by carbamoyl phosphate synthetase I and requires the use of two ATP molecules. The carbamoyl phosphate then enters the urea cycle.
How many enzymes are needed to enter the urea cycle?
The urea cycle consists of four enzymatic reactions: one mitochondrial and three cytosolic. This uses 6 enzymes.
How does ammonia catabolism work?
Amino acid catabolism results in waste ammonia. All animals need a way to excrete this product. Most aquatic organisms, or ammonotelic organisms, excrete ammonia without converting it. Organisms that cannot easily and safely remove nitrogen as ammonia convert it to a less toxic substance, such as urea, via the urea cycle, which occurs mainly in the liver. Urea produced by the liver is then released into the bloodstream, where it travels to the kidneys and is ultimately excreted in urine. The urea cycle is essential to these organisms, because if the nitrogen or ammonia are not eliminated from the organism it can be very detrimental. In species including birds and most insects, the ammonia is converted into uric acid or its urate salt, which is excreted in solid form .
What are some examples of urea cycle?
For example: consumption of two ATP, production of urea, generation of H+, the combining of HCO3- and NH4+ to forms where it can be regenerated, and finally the consumption of NH4+.
How rare is urea cycle disorder?
Urea cycle disorders are rare and affect about one in 35,000 people in the United States. Genetic defects in the enzymes involved in the cycle can occur, which usually manifest within a few days after birth. The recently born child will typically experience varying bouts of vomiting and periods of lethargy.
Nitrogen, As An Ammonium Ion, Is Fixed To The Bicarbonate Carbon
Carbamoyl Phosphate Synthetase I — The regulated step of urea synthesis, occurs in mitochondria, where 2 molecules of ATP are used to "fix" nitrogen to the carbon donated by the bicarbonate ion.
Deficiencies of the Urea Cycle
Deficiencies of the urea cycle are a threat to health because of the accumulation of ammonia, which is a neurotoxin. Normally free ammonia is fixed into either α-keto glutarate by glutamate dehydrogenase or glutamine by glutamine synthetase.
Glycine Synthesis
As glycine is converted to hippurate, which is excreted, the level of glycine in the body decreases. As a result, more glycine, a non-essential amino acid, is synthesized from 3 phosphoglycerate, requiring input of nitrogen as ammonia. [FH 4 = tetrahydrofolate]
What is the significance of the urea cycle?
here is the significance of Urea Cycle—. Due to catabolic metabolism of Amino acids in various tissues including extra-hepatic tissues such as muscle tissue and in brain degradation of nucleic acids ammonia is produced .
Why is the urea cycle important?
So the importance of urea cycle is conversion of ammonia into urea and help in excretion of it. Due to catabolic metabolism of Amino acids in various tissues including extra-hepatic tissues such as muscle tissue and in brain degradation of nucleic acids ammonia is produced .
How many nitrogen atoms are needed for urea synthesis?
For urea synthesis, two nitrogen atoms are required. One nitrogen atom is derived from the free N H 4 + molecule and the other is provided by amino acid- aspartate. Step I: Formation of Carbamoyl phosphate. The cycle begins with the synthesis of carbamoyl phosphate by the reaction of N H 4 + and H C O.
Why is urea important to mammals?
The Urea cycle is very important in so mammals in that it helps us excretes Ammonia , helps produce fumarate which would be used for other metabolic reactions, maintain homeostasis, maintain pH, etc. And it also helps us conserve water since Urea is very polar. 3.6K views. ·.
How is NH3 converted to urea?
This is highly toxic and needs to be converted to other form to reduce toxicity. Hence it is converted to urea by going through a number of intermediates. The different intermediates of urea cycle are as follows:
What is the first step of the Krebs-Henseleit cycle?
In the first step of the Krebs-Henseleit cycle, ammonia produced in the mitochondria is converted to carbamoyl phosphate by an enzyme called carbamoyl phosphate synthetase I. The reaction can be given as follows: NH3 + CO2 + 2ATP → carbamoyl phosphate + 2ADP + Pi.
How are amino acids broken down?
Each amino acid molecule is broken down into two by the process called deamination. One molecule is converted to carbohydrate or fat and used as a source of energy.
Steps in The Urea Cycle
- The urea cycle is a series of five reactions catalyzed by several key enzymes. The first two steps in the cycle take place in the mitochondrial matrix and the rest of the steps take place in the cytosol. Thus the urea cycle spans two cellular compartments of the liver cell. 1. In the first step …
Diagnosis of Urea Cycle Defects
- A blood aminogram is routinely used in the diagnosis of urea cycle disorders. The concentration of the nitrogen-carrying amino acids, glutamine and alanine, in plasma is elevated in the case of OTC deficiency. In babies, elevated levels of orotic acid in the urine may be an indicator of OTC deficiency. Increased levels of blood citrulline and argininosuccinate are also seen in cases of ci…
References
Further Reading
Overview
The urea cycle (also known as the ornithine cycle) is a cycle of biochemical reactions that produces urea (NH2)2CO from ammonia (NH3). This cycle occurs in ureotelic organisms. The urea cycle converts highly toxic ammonia to urea for excretion. This cycle was the first metabolic cycle to be discovered (Hans Krebs and Kurt Henseleit, 1932), five years before the discovery of the TCA cycle. This cycle was described in more detail later on by Ratner and Cohen. The urea cycle take…
Function
Amino acid catabolism results in waste ammonia. All animals need a way to excrete this product. Most aquatic organisms, or ammonotelic organisms, excrete ammonia without converting it. Organisms that cannot easily and safely remove nitrogen as ammonia convert it to a less toxic substance, such as urea, via the urea cycle, which occurs mainly in the liver. Urea produced by the liver is then released into the bloodstream, where it travels to the kidneys and is ultimately excrete…
Reactions
The entire process converts two amino groups, one from NH 4 and one from aspartate, and a carbon atom from HCO 3, to the relatively nontoxic excretion product urea. This occurs at the cost of four "high-energy" phosphate bonds (3 ATP hydrolyzed to 2 ADP and one AMP). The conversion from ammonia to urea happens in five main steps. The first is needed for ammonia to enter the cycle …
Products of the urea cycle
As stated above many vertebrates use the urea cycle to create urea out of ammonium so that the ammonium does not damage the body. Though this is helpful, there are other effects of the urea cycle. For example: consumption of two ATP, production of urea, generation of H+, the combining of HCO3- and NH4+ to forms where it can be regenerated, and finally the consumption of NH4+.
Regulation
The synthesis of carbamoyl phosphate and the urea cycle are dependent on the presence of N-acetylglutamic acid (NAcGlu), which allosterically activates CPS1. NAcGlu is an obligate activator of carbamoyl phosphate synthetase. Synthesis of NAcGlu by N-acetylglutamate synthase (NAGS) is stimulated by both Arg, allosteric stimulator of NAGS, and Glu, a product in the transamination reactions and one of NAGS's substrates, both of which are elevated when free amino acids are el…
Link with the citric acid cycle
The urea cycle and the citric acid cycle are independent cycles but are linked. One of the nitrogen atoms in the urea cycle is obtained from the transamination of oxaloacetate to aspartate. The fumarate that is produced in step three is also an intermediate in the citric acid cycle and is returned to that cycle.
Urea cycle disorders
Urea cycle disorders are rare and affect about one in 35,000 people in the United States. Genetic defects in the enzymes involved in the cycle can occur, which usually manifest within a few days after birth. The recently born child will typically experience varying bouts of vomiting and periods of lethargy. Ultimately, the infant may go into a coma and develop brain damage. New-borns with UCD are at a much higher risk of complications or death due to untimely screening tests and misdiagn…
Additional images
• Urea cycle.
• Urea cycle colored.