PCR is very precise and can be used to amplify, or copy, a specific DNA target from a mixture of DNA molecules. What is the purpose of the polymerase chain reaction PCR quizlet? Polymerase chain reaction is a technique used to target specific fragments of DNA and artificially amplify (increase their quantity) them.
Why is PCR called a chain reaction?
This technique was named POLYMERASE CHAIN REACTION (PCR) as the name indicates the use of polymerase that is used in the repeating process. This technique was later modified by other scientists and developed new types.
What happens during a polymerase chain reaction?
Polymerase chain reaction
- PCR is a regular technique used in genetics to amplify the target DNA sequence.
- It has many applications from forensics to diagnosing infectious diseases.
- The reaction occurs in three-step cycles. ...
- In the second step, the temperature of the reaction mixture cools down so that primers bind
How to perform a polymerase chain reaction?
- When setting up a PCR experiment, it is important to be prepared. Wear gloves to avoid contaminating the reaction mixture or reagents. ...
- Arrange all reagents needed for the PCR experiment in a freshly filled ice bucket, and let them thaw completely before setting up a reaction (Figure 2). ...
- Organize laboratory equipment on the workbench. ...
What is the first step of a polymerase chain reaction?
They are:
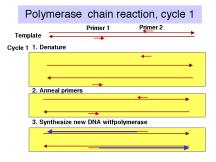
- Denaturation: The first step in PCR is denaturation. Denaturation is required to separate the double-stranded DNA sample. ...
- Annealing: The second step is the annealing of the primer. ...
- Extension: A thermostable DNA polymerase is used for this purpose. ...
What is a PCR test quizlet?
Polymerase chain reaction is a technique used to target specific fragments of DNA and artificially amplify (increase their quantity) them. Explain the use of primers in PCR. The primer is an artificial strand of DNA that is made with a complimentary base sequence to the beginning of the DNA fragment to be amplified.
What is the polymerase chain reaction in simple terms?
Listen to pronunciation. (puh-LIH-meh-rays chayn ree-AK-shun) A laboratory method used to make many copies of a specific piece of DNA from a sample that contains very tiny amounts of that DNA. Polymerase chain reaction allows these pieces of DNA to be amplified so they can be detected.
What is the main purpose of PCR?
PCR is used in molecular biology to make many copies of (amplify) small sections of DNA? or a gene?. Using PCR it is possible to generate thousands to millions of copies of a particular section of DNA from a very small amount of DNA. PCR is a common tool used in medical and biological research labs.
What is the importance of the polymerase chain reaction PCR )?
Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is often considered as one of the most important scientific advances in the field of molecular biology. With this revolutionary yet inexpensive biochemical technology, it's possible to generate millions of DNA copies from a single strand of DNA.
How does PCR work step by step?
PCR is based on three simple steps required for any DNA synthesis reaction: (1) denaturation of the template into single strands; (2) annealing of primers to each original strand for new strand synthesis; and (3) extension of the new DNA strands from the primers.
What is polymerase chain reaction and how does it work?
PCR involves using short synthetic DNA fragments called primers to select a segment of the genome to be amplified, and then multiple rounds of DNA synthesis to amplify that segment.
What is the primary purpose of PCR quizlet?
What is the main purpose of PCR? This is an enzyme whose function is to synthesize new DNA by attaching nucleotides that are complementary to a single strand of DNA.
What is the general purpose of the PCR process quizlet?
What is the general purpose of the PCR process? To make many copies of a small target piece of DNA.
What are the main principles of PCR?
2. Principle of the PCR2.1 The denaturation. It is the separation of the two strands of DNA, obtained by raising the temperature. ... 2.2 Hybridization. The second step is hybridization. ... 2.3 Elongation. The third period is carried out at a temperature of 72°C, called elongation temperature. ... 2.4 Primers. ... 2.5 Taq polymerase.
What 3 things is PCR used to do?
The polymerase chain reaction has been elaborated in many ways since its introduction and is now commonly used for a wide variety of applications including genotyping, cloning, mutation detection, sequencing, microarrays, forensics, and paternity testing.
What are four important PCR applications?
We present a survey of the following applications of PCR: 1) The amplification of gene fragments as fast alternative of cloning. 2) The modification of DNA fragments. 3) The sensitive detection of pathogenic microorganisms, if desired followed by an accurate genotyping. 4) DNA analysis of arachaeological specimens.
Where is PCR performed?
PCR reactions are performed in small tubes or plates placed into the heating block of the machine.
Why is PCR less than 100% efficient?
PCR eventually rus out of steam, and becomes less than 100% efficient. This is because repeated PCR cycles damages Taq and uses up all of the available dNTPs and primers and the amount of Mg2+ in the buffer reduces. As this happens, the reaction no longer copies every template strand in each cycle (hence amount of product no longer doubles).
How to convert RNA into cDNA?
Isolate RNA from patient's plasma, convert into cDNA by reverse transcription, use cDNA in PCR using primers specific to viral DNA sequences, primers linked to an enzyme which triggers colour reaction in tube if PCR product is present. It is highly sensitive.
What is the source of amplication and replication?
This is a piece of DNA or RNA which is the source/product of amplication and replication events (both natural and artificial).
What does it mean when the fluorescence in a sample is lower?
When this is lower, it means there were more copies of the DNA sample at the start.
What is the error rate of PCR?
Needs to be used for accurate PCR. Comes from Pyrococcus furiosus. This is a slower process (1-2 mins per 1000bp) but has an error rate of 1 in 1.3 million.
How many nucleotides are in a hydrogen bond?
18 - 22 nucleotides, any shorter and the hydrogen bonds are too weak and the likelihood of bonding to the wrong place increases.
