
What are some examples of a positive adverb?
The Positive Adverbs : Adverbs have three degrees of comparison - the positive, the comparative, and the superlative. Most adverbs are compared by means of more and most. 1. John came promptly. [Positive.] 2. Richard came more promptly than John. [Comparative.] 3. Henry came most promptly of all. [Superlative.]
What are examples of positive adjectives?
What are some positive adjectives?
- Affectionate.
- Agreeable.
- Amiable.
- Bright.
- Charming.
- Creative.
- Determined.
- Energetic.
What are positive verbs?
Positive Verbs That Start with H. Positive connotation makes words seem pleasant, satisfying and affirmative in the context in which they are used. Following is a list of positive verbs that start with H that carry a positive connotation. 1. Help. Definition: to provide aid or assistance;
What are all of the adverbs?
List of Adverbs (Q-Z)
- Quaintly
- Queasily
- Queerly
- Questionably
- Quicker
- Quickly
- Quietly
- Quirkily
- Quizzically
- Randomly
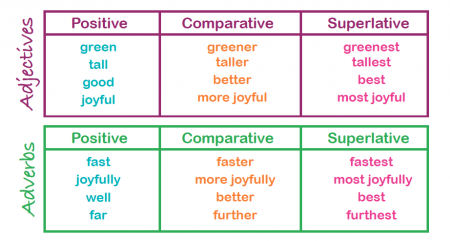
What are positive adverbs?
The positive form of adverbs is used to describe nouns (people, places or things) or to describe verbs. Some adjectives and adverbs form the positive with entirely different words - these are the irregular positive forms.
What is the positive form of an adjective or adverb?
The positive form is the basic form of an adjective or an adverb. The positive form is unmodified and uninflected.
What is the form of an adverb?
Adverbs often have the form of an adjective + -ly.
Is positivity an adverb?
positively adverb (WELL) Most children respond positively to praise and encouragement. We need to approach the issue more positively. Could we phrase this more positively? We need to present the idea very positively.
What is a positive verb example?
A positive verb denotes an action that affirmatively occurs. For example "bloom": The flowers bloom in the spring.
What is the meaning of positive form?
Definition of positive form : either of a pair of congruent crystal forms that together correspond to a single form in a class of higher symmetry.
What are the three forms of adverbs?
Now, there are three kinds of Adverbs, and they are as follows.Simple Adverbs.Interrogative Adverbs.Relative Adverbs.
How many forms of adverb are there?
There are six main types of adverbs namely adverbs of manner, adverbs of time, adverbs of place, adverbs of frequency, adverbs of degree and conjunctive adverbs.
What are the 7 types of adverb?
Adverbs of Place: Near, there, here, somewhere, inside, outside, ahead, top, high, bottom, etc. Adverbs of time: Now, then, Today, yesterday, tomorrow, late, early, tonight, again, soon etc. Adverbs of frequency: Sometimes, often, usually, frequently, seldom, daily, again and again, generally, occasionally, never, etc.
Which word has a negative adverb?
Some adverbs (e.g. hardly, little, never, only, scarcely and seldom) have a negative meaning. When we use these at the beginning of the clause, we invert the subject and verb: Hardly had we left the hotel when it started to pour with rain.
What is a positive in a sentence?
What are Positive Sentences? Positive sentences (Examples of positive sentences) are those which do not have any negative words like – not, never, etc. Positivity usually means something that is good. However, in English grammar, positive sentences are simply the type of sentences that state something that is factual.
What are some examples of adverbs?
Quickly, slowly, yesterday, last week, here, there, today, daily, never, rarely, extremely, annually, etc., are some examples of adverbs.
Is a superlative an adjective?
A superlative adjective is an adjective used in comparisons to describe something as being of the highest degree or extreme. We use superlative adjectives when making comparisons of three or more people or things. The words biggest and fastest are examples of superlative adjectives.
What are the examples of adjectives?
Adjectives are words that describe the qualities or states of being of nouns: enormous, doglike, silly, yellow, fun, fast. They can also describe the quantity of nouns: many, few, millions, eleven.
What are some examples of adverbs?
Quickly, slowly, yesterday, last week, here, there, today, daily, never, rarely, extremely, annually, etc., are some examples of adverbs.
Which word has a negative adverb?
Some adverbs (e.g. hardly, little, never, only, scarcely and seldom) have a negative meaning. When we use these at the beginning of the clause, we invert the subject and verb: Hardly had we left the hotel when it started to pour with rain.
When to use a superlative?
The superlative is used in comparing one person or thing with two or more.
When to use the comparative degree?
Use of The Comparative Adverbs and The Superlative Adverbs. The comparative degree, not the superlative, is used in comparing two persons or things. The superlative is used in comparing one person or thing with two or more. Right : Mary is the more agreeable of the two.
Is "rather" an adjective or adverb?
Note : The adverb RATHER is often used with the first adjective or adverb (such as….rather kind than wise or kind rather than wise)….but in a slightly different sense.
Can perfect be compared?
For each of these words may vary in sense. When perfect (for example) denotes absolute perfection, it cannot be compared. But perfect has also another sense: namely, “partaking in a higher or lower degree of the qualities that make up absolute perfection," so that we may describe one statue as more perfect than another, or one of three statues as the most perfect of them all. In this use, which is unobjectionable, we simply admit that nothing in the world is absolutely flawless, and assert that the three statues approach ideal perfection in various degrees.
Who said "most potent, grave, and reverend signiors"?
Most potent, grave, and reverend signiors. - Shakespeare
Can adverbs be compared?
Some adverbs are compared in both ways. Thus…..
What is a positive adverb?
A positive adverb denotes the primary degree of an adverb, i.e., the basic or uncompared form of the adverb.
What does an adverb tell us?
An adverb tells more about an adjective.
How to make an adjective into an adverb?
Almost any adjective can be made into an adverb by adding -ly.
When is "very" used as an adjective?
Very as an adjective: When it is used as an adjective, it is succeeded by a noun and it emohasizes the exactness of the discription.
Is "very" an adjective?
The word 'very' can be used both as an Adjective and as an Adberb. However, it is commonly used in its adveb form. Let us understand through some examples.
Is "loudly" a positive or negative adverb?
In the sentences, loudly, more loudly and most loudly are positive, comparative and superlative adverbs, respectively.
Does a sentence have a verb?
A sentence contains one or more verbs. A phrase doesn’t have a verb . A clause has a verb. Most of the time an Adverb can end in ‘ly’ so that is sometimes an indicator. Don’t want to complicate matters here so I won’t go into too much detail here. There are other examples. Hope this is some help.
POSITIVE ADVERBS STARTING WITH A
Abidingly Ably Absolutely Abundantly Accommodatingly Accordingly Accurately Actively Actually Acutely Adeptly Admirably Admiringly Adorably Adoringly Adroitly Aesthetically Affably Affectingly Affectionately Affirmatively Affluently Agelessly Agilely Agreeably Alertly Altruistically Always Amazingly Ambitiously Amenably Amiably Amply Amusingly Anew Angelically Appetizingly Appreciably Appreciatively Appropriately Approvingly Aptly Ardently Arrestingly Articulately Artistically Assertively Assiduously Assuredly Astonishingly Astoundingly Astutely Attentively Attractively Atypically Augustly Auspiciously Authentically Authoritatively Autonomously Avidly Awesomely.
POSITIVE ADVERBS STARTING WITH B
Beauteously Beautifully Believably Beneficently Beneficially Benevolently Benignly Best Blazingly Blessedly Blissfully Blithely Boisterously Boldly Bounteously Bountifully Bravely Brightly Brilliantly Briskly Brotherly Buoyantly Busily
POSITIVE ADVERBS STARTING WITH C
Calmly Candidly Cannily Capably Captivatingly Carefully Caringly Casually Causatively Celestially Cerebrally Certainly Charitably Charmingly Cheerfully Chicly Chivalrously Civilly Clairvoyantly Cleanly Clearly Clemently Cleverly Cogently Coherently Colourfully Comfortably Comfortingly Comically Commandingly Commendably Commiseratively Communicatively Companionably Compassionately Compatibly Compellingly Competently Completely Concisely Conclusively Confidently Confirmingly Congenially Congruously Conscientiously Consciously Considerately Consistently Consonantly Constructively Contemplatively Contently Conveniently Conversantly Convincingly Convivially Coolly Cooperatively Cordially Correctly Cosily Cosmically Courageously Courteously Creatively Credibly Creditably Cunningly Cutely.
POSITIVE ADVERBS STARTING WITH D
Dapperly Daringly Dashingly Dazzlingly Dearly Debonairly Decently Decisively Decorously Deeply Defiantly Definitely Deftly Delectably Deliberately Delicately Delightedly Delightfully Dependably Deservingly Desirably Determinedly Devotedly Devoutly Dexterously Differently Diligently Diplomatically Directly Disarmingly Discerningly Discretely Discriminatingly Distinctively Diversely Divinely Dreamily Durably Dynamically.
POSITIVE ADVERBS STARTING WITH E
Eagerly Earnestly Easily Ebulliently Economically Ecstatically Edifyingly Educationally Effectively Effectually Effervescently Efficiently Effortlessly Elaborately Elatedly Electrically Elegantly Eloquently Eminently Empathetically Emphatically Enchantingly Encouragingly Endearingly Enduringly Energetically Engagingly Engrossingly Enjoyably Enlighteningly Enliveningly Enrichingly Enterprisingly Enthrallingly Enthusiastically Enticingly Entirely Entrancingly Equally Equitably Eruditely Especially Essentially Ethically Euphorically Even-handedly Evenly Evocatively Exactly Exceedingly Excellently Exceptionally Excitingly Executively Exhaustive Exhilaratingly Exotically Expansively Expectantly Expeditiously Expensively Expertly Explicitly Expressively Exquisitely Extensively Extraordinarily Extravagantly Exuberantly Exultantly Exultingly.
POSITIVE ADVERBS STARTING WITH F
Fabulously Facilely Fain Fair Fairly Faithfully Famously Fantastically Fascinatingly Fashionably Favorably Fearlessly Felicitously Fertilely Fervently Festively Fetchingly Finely Firm First First-rate Fitly Fittingly Flamboyantly Flat out Flavorfully Fleetly Flexibly Flourishingly Fluently Fondly Forcefully Foremost Forever Forgivingly Formally Forthrightly Fortuitously Fortunately Forward Frankly Fraternally Free Freshly Frolicsomely Fruitfully Full Fully Funnily Futuristically.
POSITIVE ADVERBS STARTING WITH G
Gaily Gainfully Gallantly Gamesomely Generously Genially Gently Genuinely Gladly Gleefully Gloriously Glowingly Good-humoredly Good-naturedly Good-heartedly Goodly Gorgeously Gracefully Graciously Gradely Graithly Grandly Gratefully Gratifyingly Greatly Guidingly Gymnastically
What are adjectives and adverbs?
Adjectives in the positive form describe people, places or things. Adverbs in the positive form describe actions. Some adjectives and adverbs form the positive with entirely different words and are called the irregular positive forms. To unlock this lesson you must be a Study.com Member. Create your account.
What is the positive form of a word?
The positive form is used to describe nouns (people, places or things) or to describe verbs (actions). Some adjectives and adverbs form the positive with entirely different words. These are the irregular positive forms.
What is the adverb form of "efficiently"?
So for example: In the sentence, 'Karen works efficiently,' the positive adverb form of 'efficiently' is used to describe the particular action in the sentence, or how Karen 'works.'.
What are irregular positive forms?
These are called the irregular positive forms and consist of: good/well, bad/badly, much, many, some, little, late and far. For example:
How many sentences can you write in a positive form?
Write your own sentences using the positive form. Write three sentences with an adjective in the positive form and three sentences with an adverb in the positive form for a total of six sentences.
How do you describe people?
We describe people, places or things every day. We describe actions every day. We describe people by saying things like, 'Eva is smart' or 'Brian is tall.' We describe places, by saying things like, 'Chicago is a cold and windy city,' and things by saying, 'I like ice cream because it is so rich and creamy.' We describe actions by saying things like, 'Sally runs fast' or 'Nancy speaks slowly.' We use the positive form every day.
What is the adjective for the Amazon rainforest?
In the sentence, The Amazon rainforest is lush and green, the positive adjective forms of lush and green are used to describe a particular rainforest, the 'Amazon rainforest.'
What is the normal form of an adjective or adverb?
An adjective or adverb that does not make a comparison is said to be in the positive degree. (In other words, the "positive degree" is the normal form of an adjective or adverb.) In English, there are three degrees of comparison: The Positive Degree.
Why Should I Care about the Positive Degree?
The positive degree is the normal form of an adjective or adverb, and, as such, it is not responsible for causing many writing errors. Most of the writing errors related to the degrees of comparison are associated with the comparative degree and the superlative degree. Here are two common ones:
Who wrote the smashing grammar book?
Buy a grammar book written by Craig Shrives. less... "Smashing Grammar". Written by the founder of Grammar Monster, "Smashing Grammar" includes a comprehensive A-Z glossary of essential grammar terms, a detailed punctuation section, and a chapter on easily confused words.
What is comparative degree?
The comparative degree of an adjective or adverb shows the greater or lesser degree. For example: The Superlative Degree. The superlative degree of an adjective or adverb shows the greatest or least degree. For example: Read more about forming the comparative and superlative degrees of adjectives.
