What is the purpose of the primary stain in Gram staining?
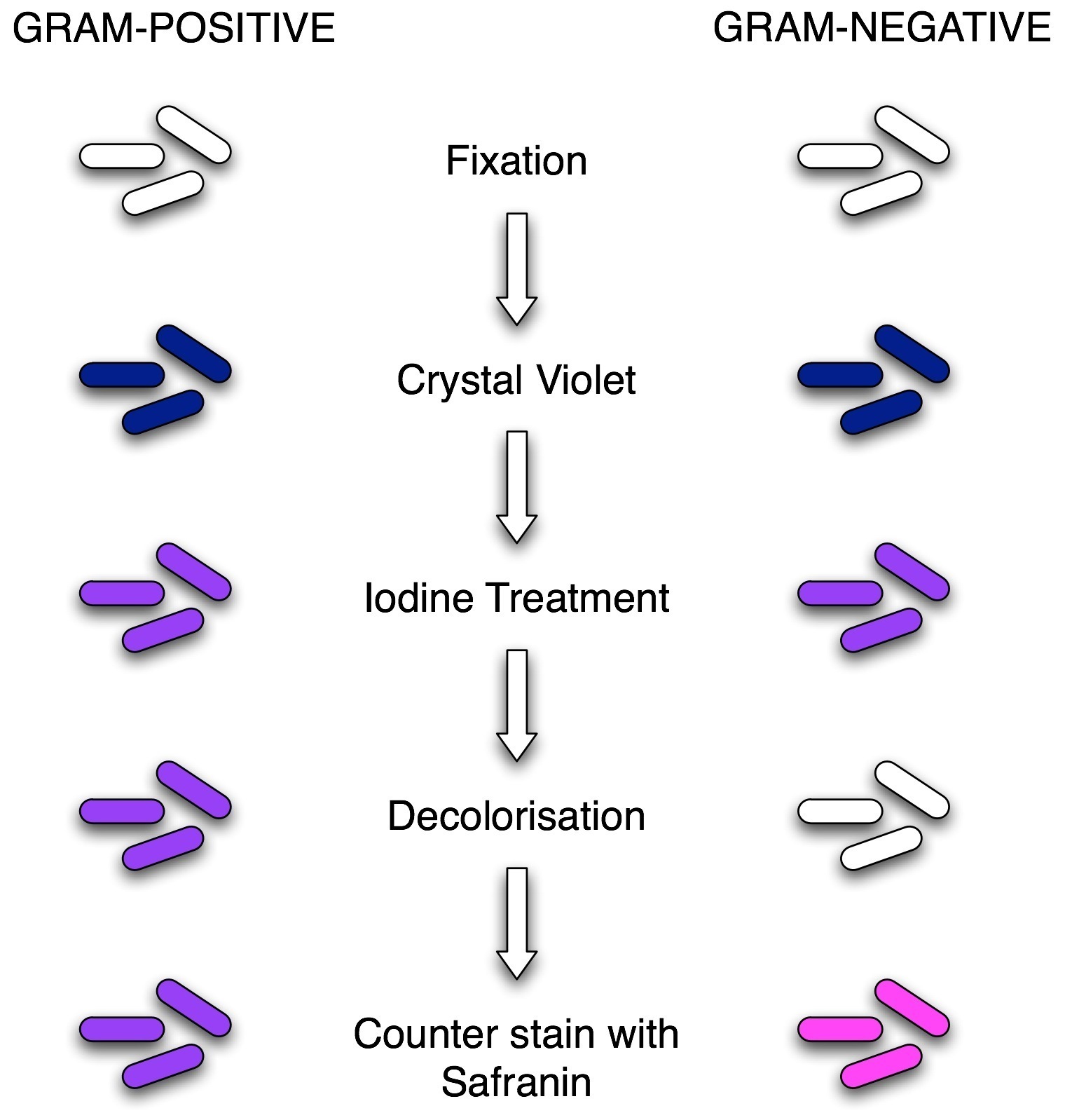
The Gram stain involves staining bacteria, fixing the color with a mordant, decolorizing the cells, and applying a counterstain. The primary stain ( crystal violet) binds to peptidoglycan, coloring cells purple. Both gram-positive and gram-negative cells have peptidoglycan in their cell walls, so initially, all bacteria stain violet.
What is a basic dye as used in Gram staining?
What is the primary stain and counterstain stain used in the Gram stain procedure?
- Crystal Violet, the primary stain.
- Iodine, the mordant.
- A decolorizer made of acetone and alcohol (95%)
- Safranin, the counterstain.
What are the steps in a Gram stain?
Stain Reaction: The four basic steps of the Gram Stain are: 1) Application of the primary stain Crystal Violet (CV) to a heat-fixed smear of bacterial culture. CV dissociates in aqueous solutions into CV+ and Cl – ions. These two ions then penetrate through the cell wall and cell membrane of both Gram-positive and Gram-negative cells.
Why is Gram stain so important?
What Is the Importance of Gram Staining in Microbiology? In microbiology, gram staining is an important test used because it can determine the presence of bacteria in a sample, as well as differentiate between the two distinct bacteria species, which are gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria.
How Does Gram Staining Work?
Why do Gram positive bacteria stain violet?
How to stain a cell?
What is the process of staining cells with crystal violet?
Does alcohol decolorize a cell?
See 2 more
About this website
What is the counter or secondary stain used in the Gram stain?
0:004:14Gram Stain - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipA decolorizer is then applied which washes away the primary stain from the cell. Finally a secondaryMoreA decolorizer is then applied which washes away the primary stain from the cell. Finally a secondary or counter stain such as safranin replaces the primary stain in the cell.
What is a primary stain?
A primary stain is a chemical used in differential staining in the first step. This reagent colors all the cells of the microorganism being tested. After using the decolorizing agent, the primary stain may be washed or can be retained by the cells, which decides different categories of microorganisms.
What is a Gram stain and what is it used for?
0:177:31How to prepare the perfect Gram stain - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipToday the gram stain is used to distinguish between gram-positive. And gram-negative cells it is theMoreToday the gram stain is used to distinguish between gram-positive. And gram-negative cells it is the most commonly used method to observe bacteria.
What are the 2 types of Gram stain?
There are two main categories of bacterial infections: Gram-positive and Gram-negative. The categories are diagnosed based on the how the bacteria reacts to the Gram stain. A Gram stain is colored purple. When the stain combines with bacteria in a sample, the bacteria will either stay purple or turn pink or red.
What is primary stain secondary stain?
primary stain. Its function is to impart its color to. all cells. The second stain is a mordant used to in- tensify the color of the primary stain.
Why safranin is used in Gram staining?
The safranin is also used as a counter-stain in Gram's staining. In Gram's staining, the safranin directly stains the bacteria that has been decolorized. With safranin staining, gram-negative bacteria can be easily distinguished from gram-positive bacteria.
Which stain is used to detect Gram positive?
crystal violet dyeThe staining method uses crystal violet dye, which is retained by the thick peptidoglycan cell wall found in gram-positive organisms. This reaction gives gram-positive organisms a blue color when viewed under a microscope.
What is used to stain bacteria?
Gram staining is used to determine gram status to classifying bacteria broadly based on the composition of their cell wall. Gram staining uses crystal violet to stain cell walls, iodine (as a mordant), and a fuchsin or safranin counterstain to (mark all bacteria).
Does safranin stain gram positive?
Bacteria that retain the initial crystal violet stain (purple) are said to be "gram-positive," whereas those that are decolorized and stain red with carbol fuchsin (or safranin) are said to be "gram-negative." This staining response is based on the chemical and structural makeup of the cell walls of both varieties of ...
Why crystal violet is used in Gram staining?
The gram stain utilizes crystal violet as the primary stain. This basic dye is positively charged and, therefore, adheres to the cell membranes of both gram negative and positive cells. After applying crystal violet and waiting 60 seconds the excess stain is rinsed off with water.
Why is iodine used in Gram staining?
The first step in gram staining is the use of crystal violet dye for the slide's initial staining. The next step, also known as fixing the dye, involves using iodine to form crystal violet- iodine complex to prevent easy removal of dye.
What is Ziehl Neelsen stain used for?
Conventional smear microscopy with the Ziehl-Neelsen (ZN) stain is a rapid and practical method for detecting acid-fast bacilli (AFB), especially in low-income countries, due to its rapidity, low cost, and high positive predictive value for tuberculosis (14).
What are the three types of stains?
Based on the nature of chromogen, there are three types of stain.Acidic stain (Anionic stain)Basic stain (Cationic stain)neutral stain.
What is a basic stain in microbiology?
0:025:51Acidic vs. Basic Stains in Microbiology - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipToday we're going to be talking about acidic versus basic stains. And their uses in microbiology.MoreToday we're going to be talking about acidic versus basic stains. And their uses in microbiology. You can use the word stain. Or dye interchangeably. So acidic or basic stains acidic or basic dyes.
What is the difference between simple and differential stain?
Simple staining uses only one staining reagent and is used to determine shape, dimensions, and arrangement of microbial cells. Differential staining uses more than one staining reagent (dye) to differentiate cellular structures.
What are the different types of staining techniques?
Types of staining techniques. Simple staining.Differential staining. (Use of of single stain)(Use of two contrasting stains) Direct.Indirect. Separation.Visualization. (Positive)(Negative) into groups. of structures.Gram stain. Flagella stain.Acid fast. Capsule stain.More items...
Gram stain | Definition, Procedure, & Facts | Britannica
Gram stain, a widely used microbiological staining technique that greatly aids in the identification and characterization of bacteria. It was devised by a Danish physician, Hans Christian Gram, in 1884. The Gram reaction reflects fundamental differences in the biochemical and structural properties of bacteria. A slide containing a heat-fixed smear of bacterial cells is treated with crystal ...
How Does Gram Staining Work?
Gram staining involves three processes: staining with a water-soluble dye called crystal violet, decolorization, and counterstaining, usually with safanin. Due to differences in the thickness of a peptidoglycan layer in the cell membrane between Gram positive and Gram negative bacteria, Gram positive bacteria (with a thicker peptidoglycan layer) retain crystal violet stain during the decolorization process, while Gram negative bacteria lose the crystal violet stain and are instead stained by the safranin in the final staining process. The process involves three steps:
Why do Gram positive bacteria stain violet?
Gram positive bacteria stain violet due to the presence of a thick layer of peptidoglycan in their cell walls, which retains the crystal violet these cells are stained with. Alternatively, Gram negative bacteria stain red, which is attributed to a thinner peptidoglycan wall, which does not retain the crystal violet during the decoloring process.
How to stain a cell?
How To- Staining Protocol and Concerns: 1 Make a slide of cell sample to be stained. Heat fix the sample to the slide by carefully passing the slide with a drop or small piece of sample on it through a Bunsen burner three times. 2 Add the primary stain (crystal violet) to the sample/slide and incubate for 1 minute. Rinse slide with a gentle stream of water for a maximum of 5 seconds to remove unbound crystal violet. 3 Add Gram's iodine for 1 minute- this is a mordant, or an agent that fixes the crystal violet to the bacterial cell wall. 4 Rinse sample/slide with acetone or alcohol for ~3 seconds and rinse with a gentle stream of water. The alcohol will decolorize the sample if it is Gram negative, removing the crystal violet. However, if the alcohol remains on the sample for too long, it may also decolorize Gram positive cells. 5 Add the secondary stain, safranin, to the slide and incubate for 1 minute. Wash with a gentle stream of water for a maximum of 5 seconds. If the bacteria is Gram positive, it will retain the primary stain (crystal violet) and not take the secondary stain (safranin), causing it to look violet/purple under a microscope. If the bacteria is Gram negative, it will lose the primary stain and take the secondary stain, causing it to appear red when viewed under a microscope.
What is the process of staining cells with crystal violet?
The process involves three steps: Cells are stained with crystal violet dye. Next, a Gram's iodine solution (iodine and potassium iodide) is added to form a complex between the crystal violet and iodine. This complex is a larger molecule than the original crystal violet stain and iodine and is insoluble in water.
Does alcohol decolorize a cell?
However, if the alcohol remains on the sample for too long, it may also decolorize Gram positive cells. Add the secondary stain, safranin, to the slide and incubate for 1 minute.
How to decolorize a gram?
Decolorize using 1-2 drops of acetone/alcohol. This shrinks the peptidoglycan in Gram-Positive cells, thus retaining the dye, this dehydrated peptidoglycan then holds the iodine, crystal violet complex. While in Gram-Negative cells, the peptidoglycan is very thin with large pores and the ethanol extracts lipids and increases the pores, thus removing the crystal violet iodine complex.
What is the difference between Gram positive and Gram negative bacteria?
Gram positive bacteria have a thick peptidoglycan layer and no outer lipid membrane while Gram negative bacteria have a thin peptidoglycan layer and have an outer lipid membrane.
What is used to decolorize cells?
Alcohol or acetone will be used to decolorize the cells and Gram-Positive cells will keep the crystal violet color.
Which chemical combines with crystal violet and makes it more difficult to remove from the cell?
Iodine, which is a chemical that combines with crystal violet and makes it more difficult to remove from the cell.
How long to counterstain with safranin?
Counterstain with safranin for 10 seconds. This dye adheres to Gram-Negative cells.
What is the advantage of Gram staining?
The advantage of this staining procedure is that those cells that decolorize can be differetiated from the cells that resist decolorization by alcohol. Describe the process of the Gram Stain? The procedure involves a primary dye which is added to the bacteria for a minute.
Why is mordant added to stain?
It is added to chemically change the shape of the dye molecule and therefore trap it in the cell wall. Describe differences in sta ining as they pertain to the differences in the stucture of the cell wall. The primary dye is attracted to the cell wall and will not wash off easily with water. The mordant is added to change the shape ...
What is the primary dye in a safranin?
The primary dye is Crystal Violet, the counterstain is Gram Safranin, and the decolorizer is Ethanol.
Does primary dye wash off easily?
The primary dye is attracted to the cell wall and will not wash off easily with water. The mordant is added to change the shape of the dy and trap it in the cell wall.
How Does Gram Staining Work?
Gram staining involves three processes: staining with a water-soluble dye called crystal violet, decolorization, and counterstaining, usually with safanin. Due to differences in the thickness of a peptidoglycan layer in the cell membrane between Gram positive and Gram negative bacteria, Gram positive bacteria (with a thicker peptidoglycan layer) retain crystal violet stain during the decolorization process, while Gram negative bacteria lose the crystal violet stain and are instead stained by the safranin in the final staining process. The process involves three steps:
Why do Gram positive bacteria stain violet?
Gram positive bacteria stain violet due to the presence of a thick layer of peptidoglycan in their cell walls, which retains the crystal violet these cells are stained with. Alternatively, Gram negative bacteria stain red, which is attributed to a thinner peptidoglycan wall, which does not retain the crystal violet during the decoloring process.
How to stain a cell?
How To- Staining Protocol and Concerns: 1 Make a slide of cell sample to be stained. Heat fix the sample to the slide by carefully passing the slide with a drop or small piece of sample on it through a Bunsen burner three times. 2 Add the primary stain (crystal violet) to the sample/slide and incubate for 1 minute. Rinse slide with a gentle stream of water for a maximum of 5 seconds to remove unbound crystal violet. 3 Add Gram's iodine for 1 minute- this is a mordant, or an agent that fixes the crystal violet to the bacterial cell wall. 4 Rinse sample/slide with acetone or alcohol for ~3 seconds and rinse with a gentle stream of water. The alcohol will decolorize the sample if it is Gram negative, removing the crystal violet. However, if the alcohol remains on the sample for too long, it may also decolorize Gram positive cells. 5 Add the secondary stain, safranin, to the slide and incubate for 1 minute. Wash with a gentle stream of water for a maximum of 5 seconds. If the bacteria is Gram positive, it will retain the primary stain (crystal violet) and not take the secondary stain (safranin), causing it to look violet/purple under a microscope. If the bacteria is Gram negative, it will lose the primary stain and take the secondary stain, causing it to appear red when viewed under a microscope.
What is the process of staining cells with crystal violet?
The process involves three steps: Cells are stained with crystal violet dye. Next, a Gram's iodine solution (iodine and potassium iodide) is added to form a complex between the crystal violet and iodine. This complex is a larger molecule than the original crystal violet stain and iodine and is insoluble in water.
Does alcohol decolorize a cell?
However, if the alcohol remains on the sample for too long, it may also decolorize Gram positive cells. Add the secondary stain, safranin, to the slide and incubate for 1 minute.