What is the radioimmunoassay technique?
The radioimmunoassay technique is based on the isotope dilution principle, alongwith the use of a specific antibody to bind to a portion of the substance to be measured. If an antigen (for example, a
What is radioimmunoassay’s sensitivity?
Radioimmunoassay’s high sensitivity is based on these principles – strong binding reaction consists of antigen vs antibody reaction. Its specificity is based on competitive binding reaction and radio emission. (2, 4, and 7)
What are the components of radioimmunoassay?
Radioimmunoassay involves three components: pure antigen, radiolabeled antigen, and antiserum (antibody). In addition a separation technique is essential to estimate the distribution of radioactivity in the free and bound fractions. The sensitivity of an assay depends to a large extent on the quality of
What are radioimmunoassays (Rias)?
Radioimmunoassays (RIAs) use antibodies to detect and quantitate the amount of antigen (analyte) in a sample. These assays are typically very sensitive and specific.

What are the three basic principles of radioimmunoassay?
There are three basic based principles for radioimmunoassay that give it a high sensitivity such as the strong immune binding reaction of antigen and antibody, competitive binding reaction, and radio emission. (7, 8, and 9)
What is radioimmunoassay?
It is a type of immunological assay that analyses the presence of antigen in a highly sensitive sample. It can determine any biological sample for a particular antibody exist.
What is radiolabeled antigen?
The radiolabeled antigen is mixed with a specified amount of antibody for a particular antigen causing the two to bind to each other.
What is the difference between radioimmunoassay and elisa?
Radioimmunoassay and ELISA are two different procedures. ELISA is a procedure in which the color is produced secondary to an immune reaction . The qualitative and quantitative analysis is done based on color. In the radioimmunoassay procedure, the immune reaction is measured through the presence of radiation.
What is an antibody assay?
It is a type of immunological assay that analyses the presence of antigen in a highly sensitive sample. It can determine any biological sample for a particular antibody exist.
How to measure antigen levels?
If you want to measure the level of a specific antigen in the blood of the patient, then there are plenty of ways to do so and one of which is radioimmunoassay. A radioactive version of a specific antigen is used to find out how many antigens a person has in the bloodstream. (1, 2, 3, and 4)
What is the body's defense against diseases?
The immune system is the body’s defense against diseases. It can detect foreign body and other harmful substances and once detected would do the necessary response to remove them from the bloodstream.
What does RIA stand for in immunology?
4 Comments. RIA stands for Radioimmunoassay. It is an immunological assay. It is basically used to determine the concentration of antigen in the blood serum of the patient with high sensitivity. It has been utilized for quantitative assay of hormones, drugs, hepatitis B surface antigens, IgE and viral antigens, etc.
What is RIA in medicine?
Application of Radioimmunoassay (RIA) It is used in the assay of some drugs like morphine, digitoxin etc. It used to check the plasma level of hormones. Also used in the analysis of anti- DNA antibody in systemic lupus erythematosus. It is also used in the early detection of cancer.
What is the advantage of RIA?
Advantages of RIA (Radioimmunoassay) It is an extremely sensitive assay as it can measure antigen up to picogram quantities. It is a highly specific test as the antibody-antigen reaction is highly specific. A large number can be processed. It is an indirect method of analysis.
How sensitive is the cytokine assay?
It is an extremely sensitive assay as it can measure antigen up to picogram quantities.
What happens when you remove all unbound antigens?
Remove all the unbound antigens then only bounded form of antigen is available.
What is RIA test?
It has an application in the assay of substance which is present in trace amount in the blood. The most common example of RIA is a RAST test (Radioallergosorbent test ). It is used to detect the causative antigen for allergy.
Why is the reaction time so long?
The reaction time is long due to the use of highly diluted reagent.
How do antibodies work in radioimmunoassays?
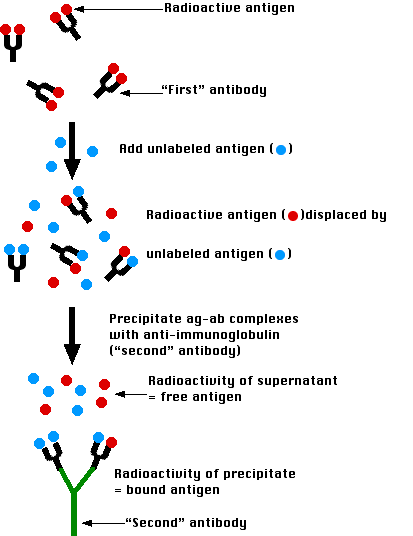
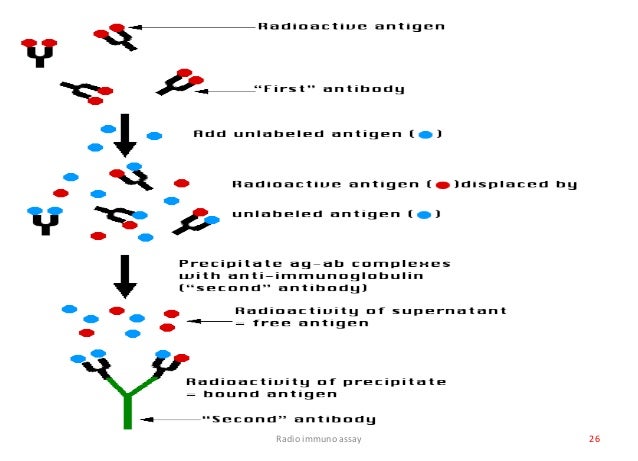
Radioimmunoassays (RIAs) use antibodies to detect and quantitate the amount of antigen (analyte) in a sample. These assays are typically very sensitive and specific. It is possible to detect as low as a few picograms of analyte in the experimental tube when using antibodies of high affinity (Kd = 10 -8 - 10 -11 M). The basic principle of radioimmunoassay is competitive binding, where a radioactive antigen ("tracer") competes with a non-radioactive antigen for a fixed number of antibody or receptor binding sites. When unlabeled antigen from standards or samples and a fixed amount of tracer (labeled antigen) are allowed to react with a constant and limiting amount of antibody, decreasing amounts of tracer are bound to the antibody as the amount of unlabeled antigen is increased.
What is the principle of a competitive binding radioimmunoassay?
Radiolabeled antigen ("tracer") added to an antibody specific to the antigen leads to formation of an antigen-antibody complex. Unlabeled antigen from a sample or standard solution can also bind antibody, leading to unlabeled antigen-antibody complex. In the radioimmunoassay, the amount of radiolabeled antigen (tracer) is held constant. Increasing amounts of unlabeled antigen in the sample will compete with tracer for binding to the antibody, leading to more unlabeled antigen-antibody complex.
What do I need to run this assay?
A typical buffer might be 50 mM phosphate pH 7 with 0.9% NaCl and 0.05% sodium azide. To minimize nonspecific antigen “sticking” to the reaction tubes, 0.3% bovine serum albumin may be added. Other additives may include 10 mM EDTA and/or 0.5% Tween-20.
How to separate antibody-antigen complexes from free antigen?
In our 125 I and 3 H radioimmunoassay kits, separation of the antibody-antigen complexes from free antigen is achieved by precipitation of the antibody-bound tracer with either a secondary antibody solution directed against the genus or species specific immunoglobulins of the primary antibody, or by use of polyethylene glycol. Both precipitators generally require the presence of carrier immunoglobulin. After centrifugation, the supernatant containing the unbound antigen is decanted, and the pellet containing the antibody-antigen complex is counted in a scintillation counter. Results obtained for the standards are used to construct a standard (dose-response) curve from which the unknowns are calculated by interpolation.
When unlabeled antigen from standards or samples and a fixed amount of tracer (labeled answer?
When unlabeled antigen from standards or samples and a fixed amount of tracer (labeled antigen) are allowed to react with a constant and limiting amount of antibody, decreasing amounts of tracer are bound to the antibody as the amount of unlabeled antigen is increased.
What buffer is used for a phosphate reaction?
A typical buffer might be 50 mM phosphate pH 7 with 0.9% NaCl and 0.05% sodium azide. To minimize nonspecific antigen “sticking” to the reaction tubes, 0.3% bovine serum albumin may be added. Other additives may include 10 mM EDTA and/or 0.5% Tween-20.