What is the process in which organisms break down sugars releasing energy and carbon dioxide?
Cellular respiration is the process that occurs in the mitochondria of organisms (animals and plants) to break down sugar in the presence of oxygen to release energy in the form of ATP. This process releases carbon dioxide and water as waste products.
In which process do organisms turn sugar into energy?
During glycolysis, a glucose molecule with six carbon atoms is converted into two molecules of pyruvate, each of which contains three carbon atoms. For each molecule of glucose, two molecules of ATP are hydrolyzed to provide energy to drive the early steps, but four molecules of ATP are produced in the later steps.
What process converts glucose to carbon dioxide and water?
cellular respirationDuring cellular respiration, a glucose molecule is gradually broken down into carbon dioxide and water. Along the way, some ATP is produced directly in the reactions that transform glucose.
Does glycolysis produce CO2?
Carbon dioxide is not produced during glycolysis. Remember in glycolysis one glucose molecule yields 2 pyruvate, 2 ATP, and 2 NADH.
What is chemosynthesis process?
Chemosynthesis is the process by which food (glucose) is made by bacteria using chemicals as the energy source, rather than sunlight. Chemosynthesis occurs around hydrothermal vents and methane seeps in the deep sea where sunlight is absent.
How is CO2 produced in cellular respiration?
During aerobic cellular respiration, glucose reacts with oxygen, forming ATP that can be used by the cell. Carbon dioxide and water are created as byproducts.
During which stages of cellular respiration is CO2 released?
Answer and Explanation: The stage of cellular respiration in which carbon dioxide release takes place is the citric acid cycle. Aerobic cellular respiration has three steps, glycolysis, the citric acid cycle and the electron transport chain.
What is anaerobic respiration reaction?
Respiration is a chemical reaction which takes place in all livings cells and releases energy from glucose. Anaerobic respiration occurs without oxygen and releases less energy but more quickly than aerobic respiration. Anaerobic respiration in microorganisms is called fermentation.
What do you call a process when foods are converted into a useful form of energy?
Metabolism (pronounced: meh-TAB-uh-liz-um) is the chemical reactions in the body's cells that change food into energy.
What are the cellular respiration?
Cellular respiration is a series of chemical reactions that break down glucose to produce ATP, which may be used as energy to power many reactions throughout the body. There are three main steps of cellular respiration: glycolysis, the citric acid cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation.
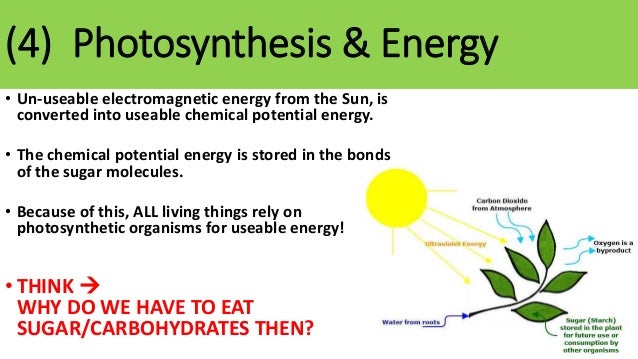
Which organelle uses energy from sunlight to sugar?
ChloroplastsChloroplasts are the food producers of the cell. The organelles are only found in plant cells and some protists such as algae. Animal cells do not have chloroplasts. Chloroplasts work to convert light energy of the Sun into sugars that can be used by cells.
What happens when ATP is formed?
When energy is needed by the cell, it is converted from storage molecules into ATP. ATP then serves as a shuttle, delivering energy to places within the cell where energy-consuming activities are taking place. All ATP biological electron-transfer reactions lead to the net production of ATP molecules.
What Molecules Enter The Krebs Cycle & What Molecules Leave The Krebs Cycle?
What Molecules Enter the Krebs Cycle & What Molecules Leave the Krebs Cycle? Glucose is broken down into useable energy during the process of cellular respiration. The Krebs cycle is the second of three main steps that comprise cellular respiration in the presence of oxygen. The Krebs Cycle receives molecules that are the end products of Glycolysis, the first step in cellular respiration, and contributes molecules to the Electron Transport Chain, which is the third stage of cellular respiration. The Krebs Cycle, which consists of eight separate chemical reactions, requires the participation of enzymes and transport molecules, which are recycled back to their original form at the completion of the cycle. During Glycolysis, one molecule of glucose is converted into two molecules of pyruvic acid in the cytoplasm of the cell. Pyruvic acid is then moved into the inner matrix of the mitochondria, which is the organelle within the cell responsible for the generation of energy. The pyruvic acid molecule is converted into acetyl Co-A, which is the molecule that enters the Krebs Cycle. In the Krebs Cycle, acetyl Co-A is attached to oxaloacetate acid to form citric acid; the Krebs Cycle is alternately known as the citric acid cycle. As three-carbon pyruvic acid is converted to the two-carbon acetyl Co-A, a CO2 molecule is released, although this occurs before the official beginning of the Krebs Cycle. During the breakdown of acetyl Co-A in the Krebs Cycle, two more molecules of CO2 are released, making a total of three carbon dioxide molecules created for each molecule of pyruvic acid. Since glucose is converted into two molecules of pyruvic acid, a total of six CO2 molecules are released for each molecule of glucose undergoing respiration. ATP (adenosine triphosphate) is a molec Continue reading >>
How do cells get energy?
Just like we need energy to get through the day, individual cells need energy for survival too. Cellular respiration is the process by which cells get their energy in the form of ATP. There are two types of cellular respiration, aerobic and anaerobic. Aerobic respiration is more efficient and can be utilized in the presence of oxygen, while anaerobic respiration does not require oxygen. Many organisms (or cells) will use aerobic respiration primarily, however, if there is a limited oxygen supply they can utilize anaerobic respiration for survival. Although there are some organisms (or cells) that always require anaerobic respiration and others that will always require aerobic respiration. Anaerobic respiration has fewer steps, so lets start there. The first step in both anaerobic and aerobic respiration is called glycolysis . This is the process of taking one glucose (sugar) molecule and breaking it down into pyruvate and energy (2 ATP). We will discuss this in depth during aerobic respiration. The second step in anaerobic respiration is called fermentation. Fermentation starts with pyruvate (the end product of glycolysis). Depending on the organism, pyruvate can either be fermented into ethanol (a fancy name for alcohol) or lactate (lactic acid). Fermentation releases CO2, but does not make any ATP all ATP during anaerobic respiration is produced during glycolysis. Since glycolysis produces 2 ATP, anaerobic respiration yields 2 ATP for every molecule of glucose. Both glycolysis and fermentation take place within the cytosol/cytoplasm of a cell. In fact, the entire process of anaerobic respiration takes place in the cytosol. Fermentation is the process by which we make wine and other types alcohol. Through an anaerobic process, yeast will break down the glucose in the Continue reading >>
What is the first step of aerobic and anaerobic respiration?
The first step in both anaerobic and aerobic respiration is called glycolysis . This is the process of taking one glucose (sugar) molecule and breaking it down into pyruvate and energy (2 ATP). We will discuss this in depth during aerobic respiration. The second step in anaerobic respiration is called fermentation.
What is the process of fermentation of alcohol?
Yeast, when under anaerobic conditions, convert glucose to pyruvic acid via the glycolysis pathways, then go one step farther, converting pyruvic acid into ethanol, a C-2 compound. Fermentation of ethanol. Image fr Continue reading >>.
How does cellular respiration work?
Cellular respiration is the process of breaking sugar into a form that the cell can use as energy. This happens in all forms of life. Cellular respiration takes in food and uses it to create ATP , a chemical which the cell uses for energy. Usually, this process uses oxygen , and is called aerobic respiration. It has four stages known as glycolysis , Link reaction , the Krebs cycle , and the electron transport chain . This produces ATP which supplies the energy that cells need to do work. When they don't get enough oxygen, the cells use anaerobic respiration , which doesnt require oxygen. However, this process produces lactic acid , and is not as efficient as when oxygen is used. Aerobic respiration, the process that does use oxygen, produces much more energy and doesnt produce lactic acid. It also produces carbon dioxide as a waste product, which then enters the circulatory system . The carbon dioxide is taken to the lungs, where it is exchanged for oxygen. The simplified formula for aerobic cellular respiration is: C6H12O6 + 6 O2 6 CO2 + 6 H2O + Energy (as ATP ) In glycolysis, glucose in the cytoplasm is broken into two molecules of pyruvate . Ten enzymes are needed for the ten intermediate compounds in this process. Two energy-rich ATP kick-start the process. At the end are two pyruvate molecules, plus Four molecules of ATP are made and two NADH molecules. Both types are energy-rich and used in other cell reactions. In cells which use oxygen , the pyruvate is used in a second process, the Krebs cycle , which produces more ATP molecules. Productivity of the cycle [ change | change source ] Biology textbooks often state that 38 ATP molecules can be made per oxidised glucose molecule during cellular respiration (two from glycolysis, two from the Krebs cycle, and about 34 Continue reading >>
What would happen if we didn't breathe?
Of course if you didn't breathe, you couldn't survive. Why do you need air to live? You need the gas oxygen to perform cellular respiration to get energy from your food. The Process of Cellular Respiration Cellular respiration is the process of extracting energy in the form of ATP from the glucose in the food you eat. How does cellular respiration happen inside of the cell? Cellular respiration is a three step process. Briefly: In stage one, glucose is broken down in the cytoplasm of the cell in a process called glycolysis. In stage two, the pyruvate molecules are transported into the mitochondria. The mitochondria are the organelles known as the energy "powerhouses" of the cells (Figure below). In the mitochondria, the pyruvate, which have been converted into a 2-carbon molecule, enter the Krebs cycle. Notice that mitochondria have an inner membrane with many folds, called cristae. These cristae greatly increase the membrane surface area where many of the cellular respiration reactions take place. In stage three, the energy in the energy carriers enters an electron transport chain. During this step, this energy is used to produce ATP. Oxygen is needed to help the process of turning glucose into ATP. The initial step releases just two molecules of ATP for each glucose. The later steps release much more ATP. What goes into the cell? Oxygen and glucose are both reactants of cellular respiration. Oxygen enters the body when an organism breathes. Glucose enters the body when an organism eats. What does the cell produce? The products of cellular respiration are carbon dioxide and water. Carbon dioxide is transported from your mitochondria out of your cell, to your red blood cells, and back to your lungs to be exhaled. ATP is generated in the process. When one molecule of glu Continue reading >>
How do microorganisms obtain energy?
Other types of microorganisms such as nonphotosynthetic bacteria, fungi, and protozoa are unable to perform this process. Therefore, these organisms must rely upon preformed carbohydrates in the environment to obtain the energy necessary for their metabolic processes. Cellular respirationis the process by which microorganisms obtain the energy available in carbohydrates. They take the carbohydrates into their cytoplasm, and through a complex series of metabolic processes, they break down the carbohydrate and release the energy. The energy is generally not needed immediately, so it is used to combine ADP with phosphate ions to form ATP molecules. During the process of cellular respiration,carbon dioxideis given off as a waste product. This carbon dioxide can be used by photosynthesizing cells to form new carbohydrates. Also in the process of cellular respiration, oxygen gas is required to serve as an acceptor of electrons. This oxygen gas is identical to the oxygen gas given off in photosynthesis. The overall mechanism of cellular respiration involves four subdivisions:glycolysis, in which glucose molecules are broken down to form pyruvic acid molecules; theKrebs cycle, in which pyruvic acid is further broken down and the energy in its molecule is used to form high-energy compounds such as NADH; theelectron transport system, in which electrons are transported along a series of coenzymes and cytochromes and the energy in the electrons is released; andchemiosmosis, in which the energy given off by electrons is used to pump protons across a mem Continue reading >>
Why do bacteria use CO2?
Isotope labeling of the carbon dioxide molecules revealed that the bacteria were indeed using CO2 to create a significant portion of their body mass, including all the sugars needed to make the cell.
How do bacteria make sugar?
Weizmann Institute scientists have engineered bacteria to create sugar from the greenhouse gas carbon dioxide. All life on the planet relies, in one way or another, on a process called carbon fixation – the ability of plants, algae and certain bacteria to “pump” carbon dioxide (CO 2) from the environment, add solar or other energy ...
Why are humans heterotrophs?
Humans are, of course, heterotrophs in the biological sense because the food they consume originates from the carbon fixation processes of nonhuman producers. The Rehovot scientists wanted to know if it was possible to “reprogram” an organism that is higher in the food chain and consumes sugar and releases carbon dioxide,so ...
Why is carbon fixation important?
This includes the need to supply food to a growing population on shrinking land resources while using less fossil fuel.
What did the Rehovot scientists want to know?
The Rehovot scientists wanted to know if it was possible to “reprogram” an organism that is higher in the food chain and consumes sugar and releases carbon dioxide.
What enzyme is used to fix carbon?
Yet the main enzyme for plants to fix carbon, RuBisCO, uses as a substrate for the CO2 fixation reaction a metabolite that is toxic for the bacterial cells. Thus, the design had to include precise regulation of the expression levels of the various genes across this multi-step pathway.
How did scientists force bacteria to learn?
Thus, by changing the conditions of their environment and stressing them, the scientists forced the bacteria to learn, by adaptation and development, to use the more abundant material in their environment. A month went by, and things remained fairly static. The bacteria did not seem to “get the hint.”.
How do organisms make food?
The majority of life on the planet is based on a food chain which revolves around sunlight, as plants make food via photosynthesis. However, in environments where there is no sunlight and thus no plants, organisms instead rely on primary production through a process called chemosynthesis, which runs on chemical energy. Together, photosynthesis and chemosynthesis fuel all life on Earth.
What is the energy used in photosynthesis?
All photosynthetic organisms use solar energy to turn carbon dioxide and water into sugar (food) and oxygen: 6CO 2 + 6H 2 O -> C 6 H 12 O 6 + 6O 2. Chemosynthesis occurs in bacteria and other organisms and involves the use of energy released by inorganic chemical reactions to produce food.
Where are chemosynthetic communities found?
Since then, chemosynthetic bacterial communities have been found in hot springs on land and on the seafloor around hydrothermal vents, cold seeps, whale carcasses, and sunken ships. No one had ever thought to look for them, but these communities were there all along.
What is the process of pyruvic acid?
Glycolysis produces pyruvic acid, which enters the mitochondrion. There, it is converted to acetyl CoA, which enters the citric acid cycle. Electron carriers bring electrons from the first three steps to the electron transport chain, and ATP is made
How does the electron transport chain convert ADP into ATP?
These molecules convert ADP into ATP by pumping hydrogen ions from the mitrochondrial matrix into the intermembrane space of the mitochondrion (the space between the inner and outer membranes of the mitochondrion). This creates a higher concentration of hydrogen ions in the intermembrane space than in the matrix. As the hydrogen ions diffuse back into the matrix through special ATP synthase channels, the ATP synthase molecules in the inner membrane convert ADP into ATP.
How does the citric acid cycle work?
NOTE: Your textbook describes Acetyl-CoA production and the citric acid cycle as two separate steps, but we are going to keep it simple, and describe them together as the citric acid cycle.] In the citric acid cycle (also known as Krebs cycle), each carbon in the 3-carbon pyruvic acid (or pyruvate) is split off and released as carbon dioxide. (That makes a total of six molecules of carbon dioxide for each molecule of glucose.) The citric acid cycle (Krebs cycle) takes place in the matrix (the inside) of the mitochondrion. In the citric acid cycle, the net energy gain from one molecule of glucose is again only 2 ATP, but we get 8 NADH and 2 FADH2.
What is the process of glycolysis?
glycolysis → acetyl CoA → citric acid cycle → electron transport chain. Glycolysis produces pyruvic acid, which enters the mitochondrion. There, it is converted to acetyl CoA, which enters the citric acid cycle. Electron carriers bring electrons from the first three steps to the electron transport chain, and ATP is made.
Which cycle transfers electrons to NADH and FADH2?
The citric acid cycle transfers electrons to NADH and FADH2.
How many NADH molecules are produced by glycolysis?
Two NADH molecules are produced by glycolysis.
Which chain of molecules passes electrons through the electron transport chain?
NADH delivers electrons to an electron transport chain, which passes the electrons through carrier molecules in a series of redox reactions to the final electron acceptor, oxygen.