What is the nitrogen cycle?
The Nitrogen Cycle. The nitrogen cycle explains the how nitrogen flows between animals, bacteria, plants, the atmosphere, and the soil on earth. The uniqueness of the nitrogen cycle is that nitrogen is the most abundant gas in the earth’s atmosphere, about 78% of all air, but it can’t be directly utilized by the animals ...
What is the process of nitrogen?
Processes of the Nitrogen Cycle. Nitrogen Fixation. Nitrogen fixation is the process of converting the atmospheric nitrogen (N 2) into biological state nitrogen. It is the first process of making nitrogen available for plants. It is defined as an anaerobic (without oxygen) process that catalyzes the reduction of atmospheric nitrogen (N 2) ...
Why is nitrogen important to plants?
Its importance is because of its key role in the formation of nucleic and amino acids. It is also an essential part of adenosine triphosphate (ATP), which is the chief energy molecule for living things. For nitrogen to be used by plants and animals, it has to change into various states through the nitrogen cycle.
What is nitrogen fixation?
Processes of the Nitrogen Cycle. Nitrogen fixation is the process of converting the atmospheric nitrogen (N 2) into biological state nitrogen. It is the first process of making nitrogen available for plants. It is defined as an anaerobic (without oxygen) process that catalyzes the reduction of atmospheric nitrogen (N 2) into ammonia (NH 3 ).
What enzyme is responsible for nitrogen fixation?
A special enzyme known as dinitrogenase is responsible for the fixation process.
What is the first step in nitrogen fixation?
Still, this process is done by the nitrogen-fixing bacteria. The first step is the oxidation of ammonia to nitrate, done by microbes termed as ammonia-oxidizers. The second step is the oxidation of nitrite (NO 2–) to nitrate (NO 3– ).
What is the process of converting nitrogen into ammonium?
Ammonification. Ammonification is also termed as the decaying process. It occurs when the plant or animal dies then decomposers such as fungi and bacteria decompose the tissues and transforms the nitrogen back into ammonium. The ammonium then reenters the nitrogen cycle where it is taken up by plants and other microorganism for development.
How does nitrogen get into the environment?
In general, human activity releases nitrogen into the environment by two main means: combustion of fossil fuels and use of nitrogen-containing fertilizers in agriculture.
What is the role of bacteria in the nitrogen cycle?
Bacteria play a key role in the nitrogen cycle. Nitrogen enters the living world by way of bacteria and other single-celled prokaryotes, which convert atmospheric nitrogen— —into biologically usable forms in a process called nitrogen fixation.
Where is nitrogen found in the body?
Key points. Nitrogen is a key component of the bodies of living organisms. Nitrogen atoms are found in all proteins and . Nitrogen exists in the atmosphere as gas. In nitrogen fixation, bacteria convert into ammonia, a form of nitrogen usable by plants. When animals eat the plants, they acquire usable nitrogen compounds.
Is nitrogen a gas?
Nitrogen exists in the atmosphere as gas. In nitrogen fixation, bacteria convert into ammonia, a form of nitrogen usable by plants. When animals eat the plants, they acquire usable nitrogen compounds. Nitrogen is a common limiting nutrient in nature, and agriculture.
What is nitrogen fixation?
When animals eat the plants, they acquire usable nitrogen compounds. Nitrogen is a common limiting nutrient in nature, and agriculture. A limiting nutrient is the nutrient that's in shortest supply and limits growth.
How does nitrogen enter the living world?
Nitrogen enters the living world by way of bacteria and other single-celled prokaryotes, which convert atmospheric nitrogen— —into biologically usable forms in a process called nitrogen fixation. Some species of nitrogen-fixing bacteria are free-living in soil or water, while others are beneficial symbionts that live inside of plants.
What are the elements that make up nitrogen?
Ammonia, nitrites, and nitrates are all fixed nitrogen and can be absorbed by plants. Denitrifying bacteria converts nitrates back to nitrogen gas. Image credit: modified from Nitrogen cycle by Johann Dréo ( CC BY-SA 3.0 ); the modified image is licensed under a CC BY-SA 3.0 license.
What is the nitrogen cycle?
The nitrogen cycle is a biogeochemical process in which nitrogen, in various forms, is circulated from the atmosphere to the living organisms and later back to the atmosphere. Living organisms require nitrogen for the synthesis of nucleic acid and proteins. The atmosphere contains almost 78% of nitrogen present in an inert form (N2).
Where does the nitrogen cycle occur?
Nitrogen cycle also exists in the marine ecosystem where the phytoplankton plants and other bacteria convert the nitrogen into nitrogen compounds. This cycle is a critical biogeochemical cycle in nature that is necessary for life processes. Share this with your friends. Share.
What are the two types of nitrogen fixers?
Biological Nitrogen Fixation: There exist nitrogen-fixing bacteria and blue-green algae that convert nitrogen present in the atmosphere into nitrates. There are two types of nitrogen-fixing bacteria: 1 Free-living bacteria: E.g., Azotobacter, and Clostridium. 2 Symbiotic bacteria: E.g., Rhizobium that is present in root nodules of individual leguminous plants like nostoc and Anabaena.
What is the first step in nitrogen fixation?
Nitrogen Fixation. The first step involves the fixation (conversion) of atmospheric inert nitrogen into a usable form of nitrogen. Here, the N2 form of nitrogen is converted into NH3 (Ammonia). This process is carried out by symbiotic bacteria present in the soil called Diazotrophs.
How is nitrogen converted to nitrous oxide?
Atmospheric Nitrogen Fixation: The inert nitrogen present in the atmosphere is converted to nitrous oxide by the help of lightning due to the high-temperature present during lightning. The nitrogen is broken down into nitrogen atoms which react with oxygen to form nitrous oxide, nitrogen peroxide, and nitric oxide.
What is the reaction between nitrogen and oxygen?
The nitrogen is broken down into nitrogen atoms which react with oxygen to form nitrous oxide, nitrogen peroxide, and nitric oxide. These compounds later dissolve in the rain to form dilute nitric acid.
Is nitrogen in the atmosphere?
Nitrogen is present in the atmosphere in abunda nce, but cannot be used by the plants and other organisms directly from the atmosphere. Nitrogen is fixed in three ways which are atmospheric, industrial, and biological means. The atmospheric nitrogen is converted into ammonia.
What is the nitrogen cycle?
Definition. The nitrogen cycle refers to the cycle of nitrogen atoms through the living and non-living systems of Earth. The nitrogen cycle is vital for life on Earth. Through the cycle, atmospheric nitrogen is converted to a form which plants can incorporate into new proteins.
How is nitrogen formed?
Nitrogen was originally formed in the hearts of stars through the process of nuclear fusion. When ancient stars exploded, they flung nitrogen-containing gases across the Universe. When the Earth was formed, nitrogen gas was the main ingredient in its atmosphere.
Is nitrogen a gas?
Nitrogen, on the other hand, is inert and harmless in its gaseous form. However, nitrogen gas is not accessible to plants and animals for use in their cells. Here we will discuss how nitrogen plays a vital role in the chemistry of life – and how it gets from the atmosphere, into living things, and back again.
What is the process of nitrogen fixation?
Nitrogen Fixation. In the process of nitrogen fixation, bacteria turn nitrogen gas from the atmosphere into ammonia. These nitrogen-fixing bacteria, often called “diazotrophs,” have an enzyme called “nitrogenase” which combines nitrogen atoms with hydrogen atoms.
Why is there so much nitrogen in the atmosphere?
Because there is so much nitrogen in the atmosphere, it may seem that the process could stop there – but the atmosphere’s supply is not infinite , and keeping nitrogen inside plant and animal cells would eventually result in big changes to our soil, our atmosphere, and our ecosystems! Fortunately, that’s not what happens.
Is oxygen toxic to cells?
Today, the Earth’s atmosphere is about 78% nitrogen, about 21% oxygen, and about 1% other gases. This is an ideal balance because too much oxygen can actually be toxic to cells. In addition, oxygen is flammable. Nitrogen, on the other hand, is inert and harmless in its gaseous form.
Why is denitrification important?
In some ecosystems, this denitrification is a valuable process to prevent nitrogen compounds in the soil from building up to dangerous levels.
What is the nitrogen cycle?
The nitrogen cycle is the system by which nitrogen is converted into different chemical forms, some usable to humans and animals and some not, as it circulates among the atmosphere, the land and the oceans. Encyclopaedia Britannica/Getty Images/HowStuffWorks.
What is nitrogen taken up by?
Fixed nitrogen is taken up by plants, which are eaten by animals, which eat other animals, which die and decompose and release nitrogen back into the ecosystem to be worked on by bacteria or plants. This is the cycle of a nitrogen atom on Earth, and its journey starts either very quietly or with a humongous bang.
Is nitrogen everywhere?
However, there's a catch: It's a " water, water everywhere, but not a drop to drink" situation. Although nitrogen's lurking basically everywhere, it's not terribly abundant in the Earth's crust, and it's incredibly difficult for living things to capture atmospheric nitrogen and use it for their purposes.
Is nitrogen a part of DNA?
It's like having a pocketful of Icelandic krónur in Minneapolis, where you can't spend it. "Nitrogen is a major part of amino acids, which are the building blocks of proteins and nucleic acids such as DNA," says Jessie Motes, a Ph.D. candidate in the Odum School of Ecology at the University of Georgia, in an email.
Is nitrogen a nutrient?
This process is slow, but it's the way that nitrogen is built as a nutrient in soil and aquatic and marine environments — terrestrial plants, for instance, can absorb ammonium and nitrate through their root hairs. The organisms that specialize in nitrification are also important in treating municipal wastewater.
Can bacteria convert nitrogen to nitrogen?
It's possible to convert bioavailable nitrogen into atmospheric nitrogen again, and that process is called denitrification. Nitrification is performed by bacteria and archaea that can tolerate oxygen — not all prokaryotes can. In the case of denitrification, certain anaerobic bacteria that don't need oxygen convert nitrate to nitrogen gas, which floats up into the atmosphere and plays hard to get until some lightning or a crafty nitrogen fixing bacterium comes along and ropes it into the nitrogen cycle yet again.
How does anthropogenic activity affect the nitrogen cycle?
"Like most natural processes, anthropogenic activities are disrupting the nitrogen cycle through nitrogen deposition ," says Motes. "Too much nitrogen can lead to increased emissions of the greenhouse gas nitrous oxide, as well as eutrophication, which is nitrogen pollution of water sources."
What is the nitrogen cycle?
The nitrogen cycle, explained. Nitrogen is one of the most essential nutrients for plant growth. Although nitrogen gas in the atmosphere represents the largest quantity of the nutrient in the environment, it’s unavailable to most plants as a direct source.
What causes nitrogen loss?
The most common nitrogen fertilizer loss is by the removal of crop portions containing nitrogen during harvest, but losses can also occur by leaching, denitrification, volatilization, or as a result of runoff and erosion.
Where is nitrogen found in soil?
More than 90 per cent of soil nitrogen is found in soil organic matter (animal manure, plant residues, fixation by legumes) in forms unavailable to plants. Organic nitrogen becomes available when soil organic matter is decomposed by soil organisms.
What are the losses of nitrogen fertilizer?
The most common nitrogen fertilizer loss is by the removal of crop portions containing nitrogen during harvest, but losses can also occur by leaching, denitrification, volatilization, or as a result of runoff and erosion.
What are the two forms of nitrogen that plants can take up?
Plants can take up two forms of nitrogen: nitrate (NO 3 -) and ammonium (NH 4 +). Although you can apply either organic or inorganic forms of nitrogen, plants will only take up these two forms. Once in the soil, all forms of nitrogen undergo chemical changes to ultimately transform into plant-available nitrogen.
What is the opposite of mineralization?
Immobilization is the opposite of mineralization. Nitrification: Nitrate nitrogen is the form taken up by plants in the largest quantity. In warm, moist soils, ammonium rapidly converts to nitrate by soil microbes to be better absorbed by plant roots.
What is the nitrogen cycle?
In nature, the nitrogen cycle describes the process where nitrogen moves from the air to plants, to animals to bacteria, and then back to air. That system works just fine and needs no human intervention. However, the cycle works differently in the enclosed environment of the aquarium.
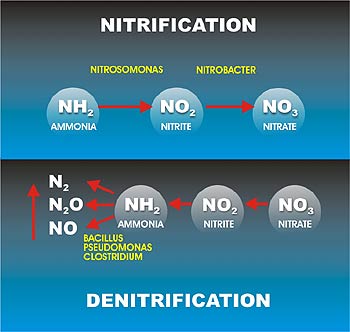
What is the first stage of the nitrogen cycle?
The first stage in the nitrogen cycle is the decay of organic matter, such as uneaten food, dead plant leaves, dead organisms, and the waste produced by fish and invertebrates. As bacteria cause these materials to break down, the metabolism of protein produces ammonia.
What is the nitrogen cycle in an aquarium?
Nitrogen Cycle In Aquariums – An Easy Guide For Beginners. Unlike the natural habitats of most tropical fish species, where dangerous levels of nitrogen-containing compounds are rare, the freshwater home aquarium is a closed environment in which overcrowding and overfeeding are common. That makes your fish tank conducive to excess ammonia ...
What happens when you add fish to an aquarium?
When you add fish to your new aquarium, they begin to produce waste and ammonia, and decaying fish food will also be added to the mix. Unfortunately, these fish often don’t survive, earning them the nickname “suicide fish.”
What to check before cycling an aquarium?
Before you begin cycling your aquarium, whichever method you decide to use, you’ll need to invest in several test kits that you will use to check the levels of ammonia, nitrite, and nitrate in the water.
How to speed up aquarium cycling?
Another way to speed up the aquarium cycling process is by adding concentrated, live nitrifying bacteria from a bottle. That sounds great in principle, but the results tend to vary, largely because not all these products contain the same species of bacteria.
Can you cycle an aquarium?
First, and most importantly, you must cycle your aquarium correctly, using one of the methods we’ve described above. A properly cycled tank will be safe for your fish and gets you off to the best start possible.