
The 3 stage processing model of memory consists of encoding, storage and retrieval. The 3 types of encoding that you need to know are acoustic, semantic and visual. Long-term memory is divided into semantic, episodic and procedural memory.
What is levels-of-processing model of memory?
The levels of processing model of memory was proposed by Craik and Lockhart. It suggests that it is depth of processing that leads to stronger memories, rather than there being separate memory stores. According to this model, stronger memories occur as a result of a deep memory trace which happens through elaborative rehearsal.
What are the models of memory?
- State-dependent memory . State-dependent memory refers to the idea that being in the same state in which you first learned information enables you to better remember said information. ...
- Schemas. Schemas refer to the mental frameworks an individual creates to help them understand and organize new information. ...
- Chunking. ...
- Deliberate practice. ...
What is the level of processing model?
Viable System Model: Process Levels
- S1: This level is comprised of the basic activities that the organization needs to do. ...
- S2: This level is composed of all the supporting functions like HR, Finance, and Marketing etc. ...
- S3: This level is concerned with oversight and control over S1 and S2 activities. ...
- S4: This is the beginning of higher order systems. ...
What are the three steps in memory information processing?
- Memory Encoding. When information comes into our memory system (from sensory input), it needs to be changed into a form that the system can cope with, so that it can ...
- Memory Storage.
- Memory Retrieval.
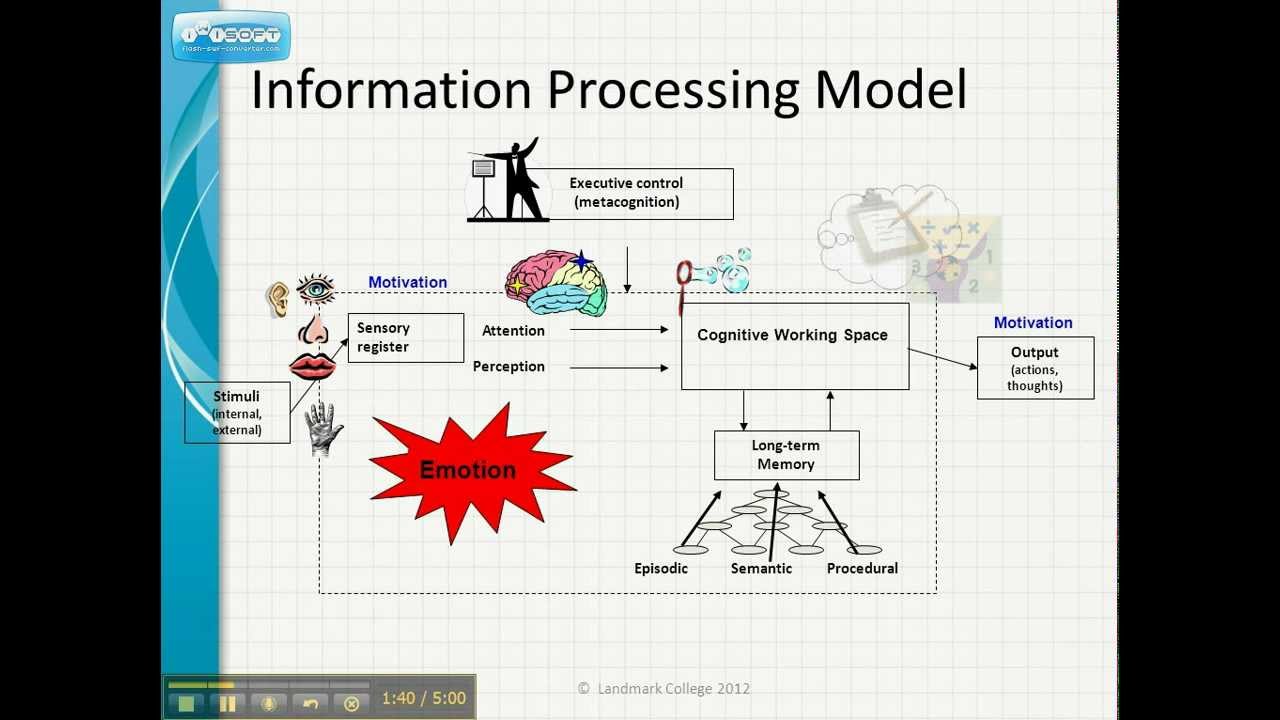
What is information processing model of memory?
The Information Processing Model is a framework used by cognitive psychologists to explain and describe mental processes. The model likens the thinking process to how a computer works. Just like a computer, the human mind takes in information, organizes and stores it to be retrieved at a later time.
What are the 3 steps of the information processing model of memory?
Psychologists distinguish between three necessary stages in the learning and memory process: encoding, storage, and retrieval (Melton, 1963).
What are the 3 models of memory?
The three main stores are the sensory memory, short-term memory (STM) and long-term memory (LTM).
What is the main idea of processing theory?
The premise of Information Processing Theory is that creating a long-term memory is something that happens in stages; first we perceive something through our sensory memory, which is everything we can see, hear, feel or taste in a given moment; our short-term memory is what we use to remember things for very short ...
What are the 3 types of information processing theory?
In order for a memory to go into storage (i.e., long-term memory), it has to pass through three distinct stages: Sensory Memory, Short-Term Memory, and finally Long-Term Memory. These stages were first proposed by Richard Atkinson and Richard Shiffrin (1968).
What is information processing model theory?
The information processing theory simplified is comparing the human brain to a computer or basic processor. It is theorized that the brain works in a set sequence, as does a computer. The sequence goes as follows, "receives input, processes the information, and delivers an output".
What are the types of memory models?
Different Models of MemoryThe Atkinson-Shiffrin Model. This Model divides memory into: ... The Level of Processing Model. ... Tulving's Model of memory. ... Parallel Distributed Processing.
What are the four models of memory?
MODELS OF MEMORYThe Atkinson-Shiffrin Model.The Levels-of Processing Approach.Tulving's Model.The Parallel Distributed Processing Approach.
What are two models of memory?
Two models that attempt to describe how memory works are the Multi-Store Model of Memory, developed by Atkinson & Shiffrin (1968), and the Working Memory Model of Memory, developed by Baddeley & Hitch (1974).
What is Piaget's information processing theory?
Piaget's stage theory suggests that the cognitive limitations are based on what developmental stage the child is in; the information-processing theory suggests that limitations are due to a child's functional short-term memory capacity which is linked to age.
What are the 4 components of the information processing model?
An abstract model of an information system features four basic elements: processor, memory, receptor, and effector (Figure 1).
What is the main idea of processing theory quizlet?
What is the main idea of levels of processing theory? If you want to remember a piece of information, you should think about it more deeply and link it to other information and memories to make it more meaningful.
What are the three stages of information processing quizlet?
The three stages of information processing are: stimulus identification, response selection, and movement programming.
What are the three stages of memory quizlet?
The three-stage memory system that involves sensory memory, short-term memory, and long-term memory.
What are the 3 main means of encoding for sensory memory?
Summary. Memory encoding is a process by which the sensory information is modified and stored in the brain. The three major types of memory encoding include visual encoding, acoustic encoding, and semantic encoding.
Encoding
The first process in the memory system is to get sensory information (sight, sound, etc.) into a form that the brain can use.
Storage
The process in memory to hold on to the information for some period of time in a process called storage.
Retrieval
Retrieval is the process of memory that retrieves the information that was stored in the memory.
How did the levels of processing model change the direction of memory research?
It showed that encoding was not a simple, straightforward process. This widened the focus from seeing long -term memory as a simple storage unit to seeing it as a complex processing system.
What is memory in science?
The basic idea is that memory is really just what happens as a result of processing information. Memory is just a by-product of the depth of processing of information, and there is no clear distinction between short term and long term memory.
What is deep processing?
Deep processing involves elaboration rehearsal which involves a more meaningful analysis (e.g. images, thinking, associations etc.) of information and leads to better recall. For example, giving words a meaning or linking them with previous knowledge.
Why is memory useful in everyday life?
This explanation of memory is useful in everyday life because it highlights the way in which elaboration, which requires deeper processing of information, can aid memory. Three examples of this are. • Reworking – putting information in your own words or talking about it with someone else.
What is structural processing?
1. Structural processing (appearance) which is when we encode only the physical qualities of something. E.g. the typeface of a word or how the letters look.
What is the idea that the way information is encoded affects how well it is remembered?
Levels of processing: The idea that the way information is encoded affects how well it is remembered. The deeper the level of processing, the easier the information is to recall.
Is depth of processing a circular argument?
The ideas of 'depth' and 'elaboration' are vague and ill defined (Eysenck, 1978). As a result, they are difficult to measure. Indeed, there is no independent way of measuring the depth of processing. This can lead to a circular argument - it is predicted that deeply processed information will be remembered better, but the measure of depth of processing is how well the information is remembered.
What is memory model in psychology?
Memory Models in Psychology – understanding human memory. Memory is perhaps the most alluring topic of research in psychology, cognitive science, and neuroscience. Through decades of trivial and breakthrough research insights, we know a little bit about memory. In fact, some of the aspects of memory have become common knowledge.
Why is the memory model important?
Although dozens of models are created by different research times every now and then, this model improves the scale at which it is useful – explain memory diseases , evidence without explanations , complexities of working memory , etc.
Why is memory a dual store?
It gets the dual-store title because the researchers consider short-term and long-term memory as disparate units of storage. This assumption has evidence from memory studies done on patients with amnesia (memory loss). The most famous one is the case of Henry Molaison, popularly known as HM in psychology textbooks.
How does information go into long term storage?
As per the model, information needs to be attended to and then encoded (changing its form) to go into long-term storage. Information can be forgotten from any of the 3 registers. Once information is in the STM, it can be recalled. For it to move to long-term memory, STM contents need to be rehearsed and thereby strengthened. To recall information that has transferred to LTM, retrieval is necessary to bring it back into STM and then recalled. A key strength of this model is that it laid a structured foundation for studying memory. Their distinction between STM and LTM is still functional today.
What is implicit memory?
Implicit memory (non-declarative memory): Internalized aspects of memory that are largely unconscious. Such as swimming or singing the lyrics of a song you haven’t deliberately learned. It also includes information that affects your actions without your awareness such as obeying game rules or driving maneuvers.
What is working memory?
Working memory: A reconceptualization of Short-term memory where information is not just temporarily stored but is also manipulated (active thinking, logic, mental math, mentally updating a grocery list). Implicit memory (non-declarative memory): Internalized aspects of memory that are largely unconscious.
What is short term memory?
Short-term memory: A temporary storage of information (one time passwords, phone numbers) Long-term memory: The long-term storage of memory (life events, personal details, unique skills). This may not be genuinely unlimited/infinite but can keep growing.
What is the level of processing model of memory?
LEVELS-OF-PROCESSING MODEL OF MEMORY: "One of the many models which aims to explain the process of memory is the levels-of-processing concept which suggests that memory is in two parts- the idea and the information individuals then associated with the idea."
Who first proposed the encoding of a specific memory?
first proposed by Canadian psychology M. Craik (1935 - ), suggesting that the encoding of a specific memory is dependent on the level of elaboration and understanding of the information associated with the memory is.
What is the stage model of memory?
Initially proposed in 1968 by Richard Atkinson and Richard Shiffrin, this theory outlines three separate stages of memory: sensory memory, short-term memory, and long-term memory.
What is the earliest stage of memory?
Sensory Memory. Sensory memory is the earliest stage of memory. During this stage, sensory information from the environment is stored for a very brief period of time, generally for no longer than a half-second for visual information and 3 or 4 seconds for auditory information.
How Long Do Memories Last?
Some memories are very brief, just seconds long , and allow us to take in sensory information about the world around us.
Why is memory not encoded?
Sometimes things are not properly encoded in memory in the first place. Memory problems can range from minor annoyances like forgetting where you left your car keys to major diseases, like Alzheimer's and other kinds of dementia, that affect the quality of life and the ability to function.
How are memories formed?
In order to form new memories, information must be changed into a usable form, which occurs through the process known as encoding. Once the information has been successfully encoded, it must be stored in memory for later use.
Why is it important to have long term memory?
The ability to access and retrieve information from long-term memory allows us to actually use these memories to make decisions, interact with others, and solve problems. But how is information organized in memory?
What is the semantic network model?
One way of thinking about memory organization is known as the semantic network model. This model suggests that certain triggers activate associated memories. A memory of a specific place might activate memories about related things that have occurred in that location.
