
What are NSAIDs and why are they used?
NSAIDs are usually used for the treatment of acute or chronic conditions where pain and inflammation are present. NSAIDs are generally used for the symptomatic relief of the following conditions: In addition, when used in combination with paracetamol the analgesic effect on post-operative pain has been proven to be improved.
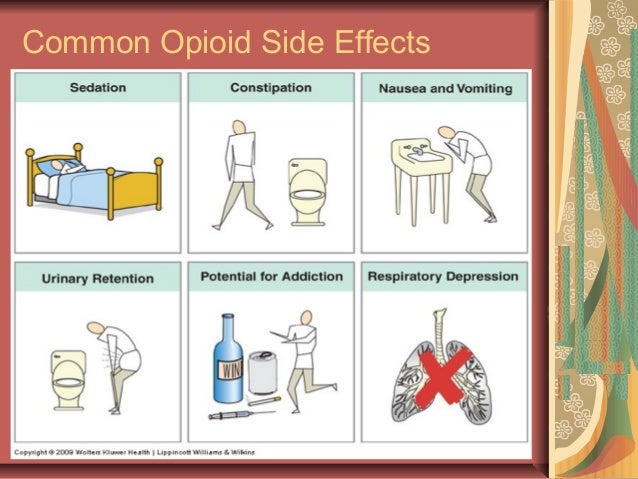
What is the prototype drug for opioid analgesics?
Morphineis the prototype of opioid analgesics[1][3] Propranololis the prototype of the beta blockers[4][5] Chlorpromazineis the prototypical phenothiazineantipsychotic[6][7] Imipramineis the prototypical tricyclic antidepressant, and itself a derivative of chlorpromazine[6][8]
What are NSAIDs and how are they administered parenterally?
Specific NSAIDs can also be administered parenterally; for example, intravenous ibuprofen is available, given as a 30-minute infusion; this can be used as a non-opioid analgesic to manage pain and can also reduce fever.
Do NSAIDs cause rare kidney problems in unborn babies?
^ a b c d "NSAIDs may cause rare kidney problems in unborn babies". U.S. Food and Drug Administration. 21 July 2017. Retrieved 15 October 2020. This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
What is the prototype of aspirin?
Mechanisms of Action of Aspirin Aspirin is a prototype of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), and member of the family of salicylates that have in common salicylic acid as the active agent. Salicylic acid is composed of a benzene ring and two radicals, one hydroxyl and one carboxyl.
What is the prototype of a drug?
In pharmacology and pharmaceutics, a prototype drug is an individual drug that represents a drug class – group of medications having similar chemical structures, mechanism of action and mode of action.
What is the prototype for analgesics?
Morphine is considered the prototype opiate, against which other agents are measured for their analgesic effects as well as adverse side effects.
What is the prototype for acetaminophen?
The prototype is aspirin; hence these compounds are often referred to as aspirin-like drugs. All aspirin-like drugs are antipyretic, analgesic, and anti-inflammatory, but there are important differences in their activities. For example, acetaminophen is antipyretic and analgesic but is only weakly anti-inflammatory.
What is a prototype example?
The definition of a prototype is the original model. An example of a prototype is the first model of a new robot.
What do you understand by prototype?
Prototyping is an experimental process where design teams implement ideas into tangible forms from paper to digital. Teams build prototypes of varying degrees of fidelity to capture design concepts and test on users. With prototypes, you can refine and validate your designs so your brand can release the right products.
What is the prototype of sedative?
The barbitu- rates are the prototype drug and constitute the principal member of the sedative/hypnotic class if the benzodiazepines are not included. The benzo- diazepines belong in the class of sedative/hypnotic drugs if actual pharma- cological properties are used for classification.
What is the prototype drug for benzodiazepines?
In 1955, Hoffmann-La Roche chemist Leo Sternbach serendipitously identified the first benzodiazepine, chlordiazepoxide (Librium). By 1960, Hoffmann-La Roche marketed it as Librium, and it pursued molecular modifications for enhanced activity.
What is a prototype in nursing?
Abstract. A prototype is being developed for a computerized nursing information system that will not only record, transmit, and retrieve information but also aid clinical decision-making and facilitate research and evaluation.
What is the prototype for ibuprofen?
Aspirin (acetylsalicylic acid) is the prototype of the salicylates and other NSAIDs (Table 36–1). The other older nonselective NSAIDs (ibuprofen, indomethacin, many others) vary primarily in their potency, analgesic and anti-inflammatory effectiveness, and duration of action.
What is the prototype of penicillin?
Methicillin is the prototype for these drugs, albeit rarely used due to a higher incidence of interstitial nephritis. Nafcillin and oxacillin are available for intravenous use only, whereas cloxacillin and dicloxacillin can be used orally.
What is the prototype for ondansetron?
AntiemeticsPrototype DrugRelated DrugsDrug Classificationondansetron (Zofran)dolasetron (Anzemet) granisetron (Kytril) palonosetron (Aloxi)5-HT3 receptor antagonistsThere is no prototype drug for this classificationdronabinol (Marinol) trimethobenzamide (Tigan)Miscellaneous agents3 more rows•Oct 21, 2016
What is a prototype drug?
A prototype drug is the first form of a drug or medication that is used to create alternative forms, states Drugs.com. Prototype drugs are also called lead agents, according to Virginia Commonwealth University. According to Weber State University, aspirin is a prototype drug that acts as an anti-inflammatory and analgesic or pain killer.
What are the two drugs that are similar to aspirin?
Drugs derived from the prototype drug aspirin include acetaminophen and ibuprofen. These are both aspirin-like drugs, although the specific benefits may differ. For example, acetaminophen has fewer side effects than aspirin, but it does not produce the same anti-inflammatory effects.
Is aspirin an anti-inflammatory?
According to Weber State University, aspirin is a prototype drug that acts as an anti-inflammatory and analgesic or pain ki ller. This class of drugs provides relief from pain, but does not address the cause of the pain.
What is a prototype drug?
Jump to navigation Jump to search. In pharmacology and pharmaceutics, a prototype drug is an individual drug that represents a drug class – group of medications having similar chemical structures, mechanism of action and mode of action. Prototypes are the most important, and typically ...
What is the prototypical antimalarial agent?
Diphenhydramine (Benadryl) is the prototype ethanolamine antihistamine. Nifedipine is the prototype dihydropyridine calcium channel blocker. Chloroquine is the prototypical antimalarial agent.
What is nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory?
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) Inhibitors of cyclooxygenase; the term nonsteroidal differentiates them from steroid drugs that mediate anti-inflammatory effects through activation of glucocorticoid receptors (eg, cortisol; Chapter 39) Reye's syndrome.
What is gout inflammatory?
Gout is an inflammatory joint disease caused by precipitation of uric acid crystals. Treatment of acute episodes targets inflammation, whereas treatment of chronic gout targets both inflammatory processes and the production and elimination of uric acid. + + + +. | Download (.pdf) | Print.
Is aspirin a salicylate?
Aspirin ( acetylsalicylic acid) is the prototype of the salicylates and other NSAIDs ( Table 36–1 ). The other older nonselective NSAIDs ( ibuprofen, indomethacin, many others) vary primarily in their potency, analgesic and anti-inflammatory effectiveness, and duration of action. Ibuprofen and naproxen have moderate effectiveness;

Overview
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAID) are members of a therapeutic drug class which reduces pain, decreases inflammation, decreases fever, and prevents blood clots. Side effects depend on the specific drug, its dose and duration of use, but largely include an increased risk of gastrointestinal ulcers and bleeds, heart attack, and kidney disease.
Medical uses
NSAIDs are often suggested for the treatment of acute or chronic conditions where pain and inflammation are present. NSAIDs are generally used for the symptomatic relief of the following conditions:
• Osteoarthritis
• Rheumatoid arthritis
Contraindications
NSAIDs may be used with caution by people with the following conditions:
• Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS)
• Persons who are over age 50, and who have a family history of gastrointestinal (GI) problems
• Persons who have had previous gastrointestinal problems from NSAID use
Adverse effects
The widespread use of NSAIDs has meant that the adverse effects of these drugs have become increasingly common. Use of NSAIDs increases risk of a range of gastrointestinal (GI) problems, kidney disease and adverse cardiovascular events. As commonly used for post-operative pain, there is evidence of increased risk of kidney complications. Their use following gastrointestinal surgery remains controversial, given mixed evidence of increased risk of leakage from any bowel
Mechanism of action
Most NSAIDs act as nonselective inhibitors of the cyclooxygenase (COX) enzymes, inhibiting both the cyclooxygenase-1 (COX-1) and cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) isoenzymes. This inhibition is competitively reversible (albeit at varying degrees of reversibility), as opposed to the mechanism of aspirin, which is irreversible inhibition. COX catalyzes the formation of prostaglandins and thromboxane from arachidonic acid (itself derived from the cellular phospholipid bilayer by phosph…
Classification
NSAIDs can be classified based on their chemical structure or mechanism of action. Older NSAIDs were known long before their mechanism of action was elucidated and were for this reason classified by chemical structure or origin. Newer substances are more often classified by mechanism of action.
• Aspirin (acetylsalicylic acid)
Pharmacokinetics
Most nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are weak acids, with a pKa of 3–5. They are absorbed well from the stomach and intestinal mucosa. They are highly protein-bound in plasma (typically >95%), usually to albumin, so that their volume of distribution typically approximates to plasma volume. Most NSAIDs are metabolized in the liver by oxidation and conjugation to inactive metabolites that typically are excreted in the urine, though some drugs are partially excreted in bile. …
History
It is widely believed that naturally occurring salicin in willow trees and other plants was used by the ancients as a form of analgesic or anti-inflammatory drug, but this story, although compelling, is untrue. Hippocrates does not mention willow at all. Dioscorides's De materia medica was arguably the most influential herbal from Roman to Mediaeval times but, if he mentions willow at …