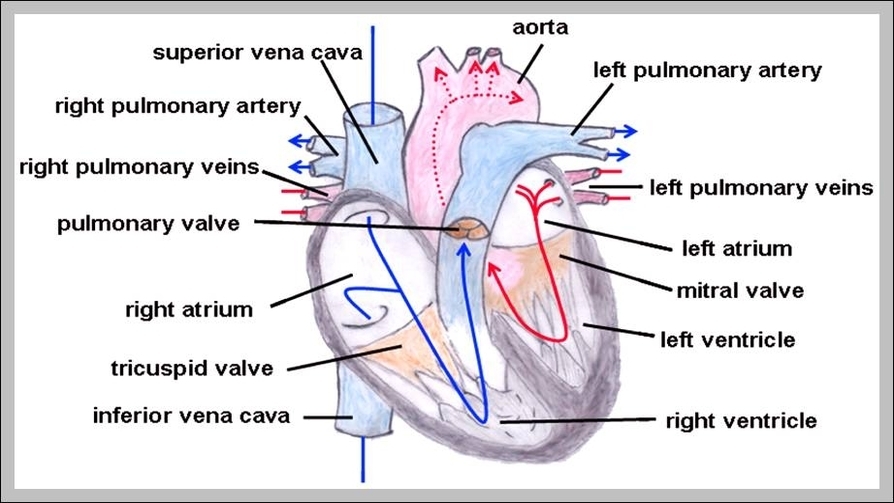
Pulmonary trunk. The pulmonary trunk is a major vessel of the human heart that originates from the right ventricle. It branches into the right and left pulmonary arteries, which lead to the lungs.
What is located between the pulmonary trunk and the aorta?
semilunar valves: Located at the base of both the trunk of the pulmonary artery and the aorta, and prevent backflow of blood from the arteries into the ventricles. What means Pulmonic? Definition of ‘pulmonic’ 1. of or relating to the lungs; pulmonary.
Which Chamber of the heart exits into the pulmonary trunk?
The right ventricle must first pump the blood to force it through the pulmonary valve and into the pulmonary trunk, which is the only outlet from the right ventricle. From here, the blood travels through each of the pulmonary arteries to reach the corresponding lungs.
What does the pulmonary trunk carry?
The main pulmonary artery, also called the pulmonary trunk, is a vessel that emerges from the heart. It divides into the left and right pulmonary arteries, which carry blood with relatively low oxygen content and high carbon dioxide content into the lungs . There, it is replenished with inhaled oxygen and excess carbon dioxide is "dropped off" to be released from the body via exhalation.
What is the normal pulmonary function?
What is normal pulmonary function? If the FVC and the FEV1 are within 80% of the reference value, the results are considered normal. The normal value for the FEV1/FVC ratio is 70% (and 65% in persons older than age 65).

What is the pulmonary trunk called?
The pulmonary trunk is a short artery transporting deoxygenated blood from the heart towards the lungs. Some authors refer to this vessel as the main pulmonary artery, or simply the pulmonary artery. The pulmonary trunk arises from the base of the right ventricle of the heart.
What does pulmonary trunk consist of?
The pulmonary trunk is a major vessel of the human heart that originates from the right ventricle. It branches into the right and left pulmonary arteries, which lead to the lungs.
Where is pulmonary trunk?
Pulmonary trunk The outflow track runs superiorly and to the left, posterior to the pulmonary valve. The pulmonary trunk bifurcates into right and left pulmonary arteries below the arch of aorta and in front of the left main bronchus.
What is the function of the pulmonary trunk quizlet?
What is the function of the pulmonary trunk? Takes deoxygenated blood from the right ventricles to the pulmonary arteries.
What drains into pulmonary trunk?
Once deoxygenated blood is pumped from the right atrium through the tricuspid valve into the right ventricle, contraction of the right ventricle will push blood through the pulmonic valve into the pulmonary artery that will carry deoxygenated blood to the lungs.
What is the pulmonary trunk quizlet?
The pulmonary trunk is a major vessel of the human heart that originates from the right ventricle. It branches into the right and left pulmonary arteries, which lead to the lungs.
What does the pulmonary trunk lead to?
Once the left pulmonary artery enters the left lung, it splits into smaller branches. The right pulmonary artery goes across the upper chest and enters the right lung.
What happens if the pulmonary trunk is blocked?
If the main pulmonary artery is completely blocked, the right ventricle (the chamber of the heart that pumps blood into the lungs) cannot get the blood into the lungs; this “right ventricular failure” then leads to death from PE. The age and health of the affected individual are also critical factors.
What are the 3 parts of trunk?
The main part of the body that contains the chest, abdomen, pelvis, and back. Most of the body's organs and the backbone are found in the trunk.
What are the three parts of the trunk?
The trunk includes the chest (in front), the back, the shoulders and the abdomen.
What is the pulmonary trunk quizlet?
The pulmonary trunk is a major vessel of the human heart that originates from the right ventricle. It branches into the right and left pulmonary arteries, which lead to the lungs.
How long is the pulmonary trunk?
The pulmonary trunk has a length of only about 5 cm. It is the direct continuation of the right ventricular outflow tract and starts at the conus arteriosus of the right ventricle. Initially located anterior to the ascending aorta, the vessel runs posteriorly and crosses the ascending aorta to the left. After its short course, the pulmonary trunk ...
What is the trunk of the pulmonary artery?
The pulmonary trunk is a short artery transporting deoxygenated blood from the heart towards the lungs. Some authors refer to this vessel as the main pulmonary artery, or simply the pulmonary artery.
What is the lumen of the pulmonary valve?
Its lumen contains the pulmonary valve which permits the blood to flow from the right ventricle to the pulmonary trunk. The cusps of the pulmonary valve form mild dilations in the pulmonary trunk wall called pulmonary sinuses. The pulmonary trunk is connected to the ascending aorta via the ligamentum arteriosum, ...
Which part of the lungs is connected to the ascending aorta?
The pulmonary trunk is connected to the ascending aorta via the ligamentum arteriosum, a remnant of the obliterated ductus arteriosus (ductus Botalli). In the developing fetus, the ductus arteriosus transports blood directly from the pulmonary trunk into the aorta and bypasses the fetal lungs.
Which pulmonary artery is at a right angle?
The left pulmonary artery is commonly a direct continuation of the pulmonary trunk's course, while the right pulmonary artery arises almost at a right angle.
Where does the pulmonary trunk terminate?
The pulmonary trunk terminates in the two pulmonary arteries.
What is PDA in medical terms?
Patent ductus arteriosus (PDA) Failure of ductus arteriosus closure after birth causes oxygenated blood to flow from the aorta back towards the pulmonary trunk and therefore into the pulmonary circulation. PDA is one of the most common congenital heart defects and shows higher prevalence in premature infants. ...
How wide is the pulmonary trunk?
The pulmonary trunk is approximately 50 mm long and 30 mm wide (most authors use 29 mm in males and 27 mm in females (axial width) as the cut-offs of normal 1,5 ). It arises as a direct superior continuation of the right ventricular outflow tract, separated by the pulmonary valve.
Which artery divides into the left and right pulmonary arteries?
At the level of the transthoracic plane, the trunk emerges from the fibrous pericardium and divides into the longer right and shorter left pulmonary arteries in the concavity of the aortic arch, anterior to left main bronchus and to the left of the carina. The left coronary artery passes between the pulmonary trunk (on the left) ...
What is the pulmonary trunk?
pulmonary trunk a vessel arising from the conus arteriosus of the right ventricle and bifurcating into the right and left pulmonary arteries. sympathetic trunk two long ganglionated nerve strands, one on each side of the vertebral column, extending from the base of the skull to the coccyx. Miller-Keane Encyclopedia and Dictionary ...
Where does the pulmonary trunk branch?
However, a single pulmonary trunkarose from the common trunk prior to the arch and branched to the right and left pulmonary arteries.
What is the TA branch?
pul·mo·nar·y trunk. [TA] origin, right ventricle of heart; distribution, it divides into the right pulmonary artery and the left pulmonary artery, which enter the corresponding lungs and branch along with the segmental bronchi. Synonym (s): truncus pulmonalis [TA], arteria pulmonalis, pulmonary artery, venous artery.
What is the FATAL PULMONARY ARTERY DISSECTION?
FATAL PULMONARY ARTERY DISSECTION " COMPLICATION OF PATENT DUCTUS ARTERIOSUS. They encircle the base of the two arteries leaving the heart (aorta and pulmonary trunk) and the openings between the atria and the ventricles. Histology of cardiovascular system.
Where are lymphatics not found?
Lymphatics were not found in the semilunar valves of the aorta and the pulmonary trunk of human, pig and dog hearts [17, 28, 33, 34]. The left coronary artery arose from the right coronary sinus of Valsalva and coursed between the aorta and pulmonary trunk in the wall of the aorta.
What is the encephalic trunk?
lumbosacral trunk a trunk formed by union of the lower part of ventral branch of the fourth lumbar nerve with the ventral branch of the fifth lumbar nerve. lymphatic t's the lymphatic vessels (right or left lumbar, intestinal, right or left bronchomediastinal, right or left subclavian, ...
What is the trunk of the body?
trunk. 1. the part of the body to which the head and limbs are attached; called also torso. 2. a larger structure, such as a vessel or nerve, from which smaller divisions or branches arise, or that is created by their union. adj., adj trun´cal. brachiocephalic trunk truncus brachiocephalicus.
Where is the pulmonary trunk located?
The pulmonary trunk is located anterior to the other major vessels of the heart base (the aorta and the superior vena cava). On the right and behind it is the ascending part of the aorta, and to the left is the left ear of the heart. The pulmonary trunk located in the pericardial cavity is guided in front of the aorta to the left and back and at level IV of the thoracic vertebra (cartilage II of the left rib) is divided into the right and left pulmonary arteries. This place is called the bifurcation of the pulmonary trunk (bifurcdtio trunci pulmonalis). Between the bifurcation of the pulmonary trunk and the arch of the aorta is a short arterial ligament (ligamentum arteriosum), which is a overgrown arterial (botfull) duct (ductus arteriosus).
Which pulmonary artery is shorter?
The left pulmonary artery (a.pulmonalis sinistra) is shorter and thinner than the right, passes from the bifurcation of the pulmonary trunk along the shortest path to the gates of the left lung in the transverse direction in front of the descending part of the aorta and the left bronchus. On its way, the artery crosses the left main bronchus, and at the gates of the lung is located above it. Corresponding to two parts of the left lung, the pulmonary artery is divided into two branches. One of them breaks down into segmental branches within the upper lobe, the second - the basal part - with its branches blood supply segments of the lower lobe of the left lung.
What is the diameter of the right pulmonary artery?
The right pulmonary artery (a.pulmonalis dextra) with a diameter of 21 mm should be to the right to the gates of the right lung behind the ascending part of the aorta and the terminal section of the superior vena cava and anterior to the right bronchus. In the area of the gates of the right lung in front and under the right main bronchus, the right pulmonary artery is divided into three lobar branches. Each lobar branch in the corresponding lobe of the lung is in turn divided into segmental branches. In the upper lobe of the right lung, the apical branch (r.apicalis), the posterior descending and ascending branches (rr.posteriores descendens et ascendens), the forward descending and ascending branches (rr.anteriores descendens et ascendens) that follow in the apical, posterior and anterior segments of the right lung.
Which lobe of the lung is the apical branch?
To the segments of the upper lobe of the left lung, the branches of the upper lobe (rr.lobi superioris), which give the apical branch (r.apicalis), the front ascending and descending (rr.anteriores ascendens et descendens), the posterior (r.posterior) and the ligulum (r .lingularis) branches. The upper branch of the lower lobe (r.superior lobi inferioris), as in the right lung, follows the lower lobe of the left lung, to its upper segment. The second share branch - the basal part (pars basalis) is divided into four basal segmental branches: medial, lateral, anterior and posterior (rr.basales medialis, lateralis, anterior and posterior), which branch out in the corresponding basal segments of the lower lobe of the left lung.
What are the pulmonary arteries?
The pulmonary arteries carry blood from the right side of the heart to the lungs. In medical terms, the word “pulmonary” means something that affects the lungs.
What is the purpose of the pulmonary valve?
The pulmonary valve opens to let oxygen-poor blood flow out of the heart and into the pulmonary arteries on its way to the lungs for oxygen. When closed, the pulmonary valve keeps blood from flowing backward ...
What role do the pulmonary arteries play in the circulatory system?
The pulmonary arteries work with other parts of your heart to help blood circulate through your lungs. Here’s how:
What are the most common problems with the pulmonary arteries?
The most common problems with the pulmonary arteries are congenital heart defect s , meaning the issue is present at birth. To understand these defects you have to understand a little about the development of the heart and the circulation before you are born.
What is the communication between the pulmonary and systemic circulation?
Normal development of the heart and pulmonary arteries requires that the two sides of the heart shares the work equally and the way that happens is that there are two communications between the pulmonary and the systemic circulation, one atrial (foramen) and one between the pulmonary artery and the aorta (ductus).
How to prevent pulmonary artery disease?
While you can’t prevent these problems, these actions can promote better heart health: Eat a heart-healthy diet with plenty of fresh fruits and vegetables. Get at least 150 minutes (2.5 hours) of cardiovascular physical activity every week.
Which veins carry oxygenated blood to the heart?
Pulmonary veins: The veins do the opposite job of pulmonary arteries and collects the oxygenated blood and carry it from the lungs back to the heart. The veins merge into larger veins. Each lung has two pulmonary veins that deliver blood to the heart’s top left chamber or atrium. Left atrium: This atrium sends oxygenated blood into ...
Where is the pulmonary trunk located?
The pulmonary trunk, which is relatively short and wide, is located at the exit of the right ventricle. This main arterial branch is located above the heart to the left of the ascending aorta . The right pulmonary artery wedges in the aortic arch, behind the ascending aorta and in front of the descending aorta.
What is the shape of the pulmonary trunk?
The pulmonary trunk and the right and left pulmonary arteries are shaped somewhat like a capital letter "T", with the trunk forming the lower portion and the left and right branches each forming one of the two sides at the top.
What is the valve between the right ventricle and the pulmonary trunk?
This valve, which is composed of two cusps of connective tissue, is structured to open when the heart pumps so the blood can flow from the right ventricle to the pulmonary trunk. As the heart muscle relaxes, the valves close to prevent blood from flowing backward ...
How many branches does the pulmonary artery have?
Generally, each pulmonary artery divides into three to seven branches. The most common anatomic variations of the pulmonary arteries are variations in the number of arterial branches in the lungs. 2 And sometimes, one or more divisions can branch off before the right or left pulmonary artery enters the heart.
Why do pulmonary arteries have narrow walls?
As with all arteries, the walls of the pulmonary arteries have several layers of muscle that allow them to dilate (widen) and con strict (become narrow).
What is a congenital defect that causes shortness of breath?
Pulmonary artery stenosis: This congenital defect is characterized by a narrow pulmonary artery. It can be associated with a variety of heart defects and cause fatigue and shortness of breath, as well as symptoms of any such co-existing heart defects. Surgical repair may involve widening the artery with a stent.
What is the condition where the pulmonary valve does not open properly?
Pulmonary atresia: This is a condition in which the pulmonary valve does not open properly, resulting in diminished blood flow from the heart to the lungs. Symptoms, such as rapid breathing and slow childhood growth, can vary depending on the extent of the anatomical malformation. 3 This defect is treated surgically.