What is DNA short answer?
Deoxyribonucleic acid (abbreviated DNA) is the molecule that carries genetic information for the development and functioning of an organism. DNA is made of two linked strands that wind around each other to resemble a twisted ladder — a shape known as a double helix.
What is DNA and how it is important for life?
Definition. DNA is a complex, long-chained molecule that contains the genetic blueprint for building and maintaining all living organisms. Found in nearly all cells, DNA carries the instructions needed to create proteins, specific molecules essential to the development and functioning of the body.
What are the two main functions of DNA?
Solution : Replication and expression of genetic information in the form of polypeptides.
What are the three functions of DNA?
DNA now has three distinct functions—genetics, immunological, and structural—that are widely disparate and variously dependent on the sugar phosphate backbone and the bases.
How does DNA work simple?
0:015:23What is DNA and How Does it Work? - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipStated clearly presents what is DNA and how does it work DNA also known as deoxyribonucleic acid isMoreStated clearly presents what is DNA and how does it work DNA also known as deoxyribonucleic acid is a molecule. It's a bunch of atoms stuck. Together in the case of DNA these atoms combine to form the
What is DNA very good at?
DNA has run the show for more than four billion years for one main reason: it's very good at making copies of itself. The copies can get passed to a new generation in a couple of ways. If you're a bacterium, you might be into cloning—making exact replicas of yourself.
What is DNA made of?
The information in DNA is stored as a code made up of four chemical bases: adenine (A), guanine (G), cytosine (C), and thymine (T). Human DNA consists of about 3 billion bases, and more than 99 percent of those bases are the same in all people.
How does DNA store information?
DNA stores biological information in sequences of four bases of nucleic acid — adenine (A), thymine (T), cytosine (C) and guanine (G) — which are strung along ribbons of sugar- phosphate molecules in the shape of a double helix.
What is the purpose of RNA?
The primary function of RNA is to create proteins via translation. RNA carries genetic information that is translated by ribosomes into various proteins necessary for cellular processes. mRNA, rRNA, and tRNA are the three main types of RNA involved in protein synthesis.
What is the function of DNA from day to day?
DNA carries the instructions for the development, growth, reproduction, and functioning of all life.
What are the 4 Roles of DNA?
The sequence of the nucleotides along the backbone encodes genetic information. The four roles DNA plays are replication, encoding information, mutation/recombination and gene expression.
How do we use DNA in everyday life?
Learn more about the various ways that industries use the DNA they extract.Forensics. You likely know that DNA is a key component in many criminal investigations. ... Paternity Tests. DNA extraction is also helpful for determining the paternity of a child. ... Ancestry Tracking. ... Medical Tests. ... Genetic Engineering. ... Vaccines. ... Hormones.
Why is DNA important to living things quizlet?
DNA is important because it contains all the genes that the cell will ever need for making all the structures and chemicals necessary for life. It is what makes all of us different and gives us different traits.
The components of DNA
DNA can be described as a long, thin molecule consisting of things called (nucleotides). These nucleotides are linked together by a backbone consisting of both phosphates and the pentavalent sugar, and sometimes the nucleotides are called bases, and there are four types of nucleotides, which are:
DNA function
The cells obtain the instructions required to do their functions from DNA , so DNA can be likened to being a computer program, while the cell is the computer to be run, the program is the one that gives instructions to the computer how to do its functions, and in simple words, DNA is the one that stores the genetic material, transmitting the genetic characteristics From parents to grandparents..
DNA facts
The DNA of every person on the planet is approximately 99.9% similar to that of other people, and only 0.1% differs from one person to another, and that is what makes people different from each other.
Why is DNA a chromosome?
Because the cell is very small, and because organisms have many DNA molecules per cell, each DNA molecule must be tightly packaged. This packaged form of the DNA is called a chromosome. During DNA replication, DNA unwinds so it can be copied.
How does DNA make proteins?
First, enzymes read the information in a DNA molecule and transcribe it into an intermediary molecule called messenger ribonucleic acid, or mRNA.
What are the building blocks of DNA?
DNA is made of chemical building blocks called nucleotides. These building blocks are made of three parts: a phos phate group, a sugar group and one of four types of nitrogen bases. To form a strand of DNA, nucleotides are linked into chains, with the phosphate and sugar groups alternating.
What are the four nitrogen bases found in nucleotides?
The four types of nitrogen bases found in nucleotides are: adenine (A), thymine (T), guanine (G) and cytosine (C). The order, or sequence, of these bases determines what biological instructions are contained in a strand of DNA. For example, the sequence ATCGTT might instruct for blue eyes, while ATCGCT might instruct for brown.
Why is DNA in its compact chromosome form?
But during cell division, DNA is in its compact chromosome form to enable transfer to new cells. Researchers refer to DNA found in the cell's nucleus as nuclear DNA.
How much of the DNA is made up of genes?
The size of a gene may vary greatly, ranging from about 1,000 bases to 1 million bases in humans. Genes only make up about 1 percent of the DNA sequence. DNA sequences outside this 1 percent are involved in regulating when, how and how much of a protein is made.
How many genes are in the DNA instruction book?
The complete DNA instruction book, or genome, for a human contains about 3 billion bases and about 20,000 genes on 23 pairs of chromosomes.
Why is DNA important in biology?
On another level, DNA’s role as genetic material and an understanding of its chemistry allows us to manipulate it and use it to enhance quality of life. For example, genetically modified crops that are pest or drought resistant have been generated from wild type varieties through genetic engineering. A lot of molecular biology is dependent on the isolation and manipulation of DNA, for the study of living processes.
What is DNA in biology?
DNA Definition. Deoxyribonucleic acid, or DNA, is a biological macromolecule that carries hereditary information in many organisms. DNA is necessary for the production of proteins, the regulation, metabolism, and reproduction of the cell. Large compressed DNA molecules with associated proteins, called chromatin, ...
What are the four types of nucleotides in DNA?
The nitrogenous bases in DNA are of four types – adenine, guanine, thymine and cytosine. The phosphate and the deoxyribose sugars form a backbone-like structure, with the nitrogenous bases extending out like rungs of a ladder.
How was DNA discovered?
DNA was isolated and discovered chemically before its functions became clear. DNA and its related molecule, ribonucleic acid (RNA), were initially identified simply as acidic molecules that were present in the nucleus. When Mendel’s experiments on genetics were rediscovered, it became clear that heredity was probably transmitted through discrete particles, and that there was a biochemical basis for inheritance. A series of experiments demonstrated that among the four types of macromolecules within the cell (carbohydrates, lipids, proteins and nucleic acids ), the only chemicals that were consistently transmitted from one generation to the next were nucleic acids.
How does life begin?
Life begins from a single cell. For humans, this is the zygote formed by the fertilization of an egg by a sperm. After this, the entire dazzling array of cells and tissue types are produced by cell division. Even the maintenance of normal functions in an adult requires constant mitosis.
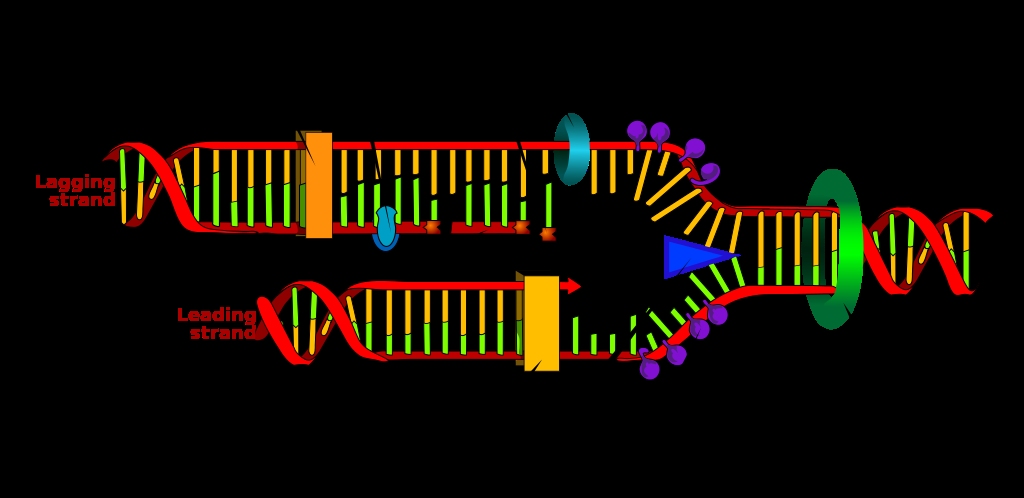
Which strand of DNA is involved in transcription?
Only one of the two strands of DNA is involved in transcription. This is called the template strand and the other strand is called the coding strand . Since transcription is also dependent on complementary base pairing, the RNA sequence is nearly the same as the coding strand.
Where is DNA found?
Large compressed DNA molecules with associated proteins, called chromatin, are mostly present inside the nucleus. Some cytoplasmic organelles like the mitochondria also contain DNA molecules. DNA is usually a double-stranded polymer of nucleotides, although single-stranded DNA is also known.
Why is DNA important?
An important property of DNA is that it can replicate, or make copies of itself. Each strand of DNA in the double helix can serve as a pattern for duplicating the sequence of bases. This is critical when cells divide because each new cell needs to have an exact copy of the DNA present in the old cell.
What is DNA in biology?
Learn more. DNA, or deoxyribonucleic acid, is the hereditary material in humans and almost all other organisms. Nearly every cell in a person’s body has the same DNA.
How many bases are there in DNA?
The information in DNA is stored as a code made up of four chemical bases: adenine (A), guanine (G), cytosine (C), and thymine (T). Human DNA consists of about 3 billion bases, and more than 99 percent of those bases are the same in all people.
What are the bases of DNA called?
DNA bases pair up with each other, A with T and C with G, to form units called base pairs. Each base is also attached to a sugar molecule and a phosphate molecule. Together, a base, sugar, and phosphate are called a nucleotide. Nucleotides are arranged in two long strands that form a spiral called a double helix.
What is the order of DNA bases?
The order, or sequence, of these bases determines the information available for building and maintaining an organism, similar to the way in which letters of the alphabet appear in a certain order to form words and sentences. DNA bases pair up with each other, A with T and C with G, to form units called base pairs.
What is the structure of a nucleotide?
Nucleotides are arranged in two long strands that form a spiral called a double helix. The structure of the double helix is somewhat like a ladder, with the base pairs forming the ladder’s rungs and the sugar and phosphate molecules forming the vertical sidepieces of the ladder.
What is nuclear DNA?
Nuclear DNA is the DNA contained within the nucleus of every cell in a eukaryotic organism. It codes for the majority of the organism’s genomes while the mitochondrial DNA and plastid DNA handles the rest. The DNA present in the mitochondria of the cell is termed as mitochondrial DNA.
What is the A-DNA?
A-DNA: It is a right-handed double helix similar to the B-DNA form. Dehydrated DNA takes an A form that protects the DNA during extreme condition such as desiccation. Protein binding also removes the solvent from DNA and the DNA takes an A form.
Who Discovered DNA?
DNA was first recognized and identified by the Swiss biologist, Johannes Friedrich Miescher in 1869 during his research on white blood cells.
Why is DNA called a polynucleotide?
The DNA is called a polynucleotide because the DNA molecule is composed of nucleotides – deoxyadenylate (A) deoxyguanylate (G) deoxycytidylate (C) and deoxythymidylate (T), which are combined to create long chains called a polynucleotide. As per the DNA structure, the DNA consists of two chains of the polynucleotides.
How are proteins formed?
Polypeptide chains are further folded in secondary, tertiary and quaternary structure to form different proteins. As every organism contains many genes in their DNA, different types of proteins can be formed. Proteins are the main functional and structural molecules in most of the organisms. Apart from storing genetic information, DNA is involved in: 1 Replication process: Transferring the genetic information from one cell to its daughters and from one generation to the next and equal distribution of DNA during the cell division 2 Mutations: The changes which occur in the DNA sequences 3 Transcription 4 Cellular Metabolism 5 DNA Fingerprinting 6 Gene Therapy
How are nucleic acids formed?
These nucleic acids are formed by the combination of nitrogenous bases, sugar molecules and the phosphate groups that are linked by different bonds in a series of sequences. The DNA structure defines the basic genetic makeup of our body. In fact, it defines the genetic makeup of nearly all life on earth.
What are the different parts of DNA?
DNA comprises a sugar-phosphate backbone and the nucleotide bases (guanine, cytosine, adenine and thymine).
Why is DNA testing important?
By tracing the DNA of a person, testing can be used to provide a risk assessment of that person's chances of being affected by certain medical conditions. The National Cancer Institute reports that by studying the DNA of people affected by certain types of cancers, certain genes have been identified as being present in their bodies. By identifying these genes, DNA testing can be used as a preventative measure, allowing people at high risk to maintain high levels of preventative medical care in an attempt to lower their risk of becoming affected by cancers such as colon and breast cancer.#N#Read More: Importance of DNA Fingerprinting
What is DNA testing?
One of the most common uses of DNA testing is to provide information on the parentage of a child. The DNA Junction website reports that DNA testing is used for the purpose of testing the parentage of children in adoption, child support and custody, as well as for immigration purposes. As DNA is made up of a mixture of the DNA of a person's parents, ...
Why is DNA testing controversial?
One of the purposes of DNA testing that has become controversial in the first decade of the 21st century is the storage of DNA samples in law enforcement databases . When crimes are committed the Genetics website reports evidence samples are often compared to those held on government databases to look for matches with convicted felons. There are many ethical concerns associated with the storage of DNA samples, including those surrounding the privacy of individuals.
When was DNA testing first used?
Colorado State University explains that the development of DNA testing for the purposes of identification was as important a breakthrough in the 1980s as the development of fingerprinting technology in the 1880s. DNA identifications testing is often used for the purpose of identifying the victims of crimes and terrorist attacks such as those on Sept. 11, 2001. The Genetics website reports DNA testing is often used for the purpose of eliminating a suspect from a police inquiry and, in other cases, for placing a suspect at the scene of a crime.
What is the name of the four bands of DNA?
When DNA is tested, it is split into four bands known as A,T,G and C . A person's DNA provides the basis of every aspect of that person's genetic makeup, giving information on areas of the human body such as hair and eye color.
Why is victimology important?
Importance of Victimology. The Scientific Testimony website reports DNA to be a material grown inside the bodies of living organisms. In an Australian court case where DNA-tested samples were used as evidence, a jury was told the chances of matching DNA evidence to anyone other than the suspect were 1 in 43 trillion, ...

Overview
- Deoxyribonucleic acid is a molecule composed of two chains that coil around each other to form a double helix carrying genetic instructions for the development, functioning, growth and reproduction of all known organisms and many viruses. DNA and ribonucleic acid are nucleic acids; alongside proteins, lipids and complex carbohydrates, nucleic acids are one of the four m…
- Proteins are chains of chemical building blocks called amino acids. A protein could contain just a few amino acids in its chain or it could have several thousand. Proteins form the basis for most of what your body does such as digestion, making energy, and growing.
- Messenger RNA (mRNA) is one of the three types of RNA present in organisms. It is a single-stranded nucleic acid composed of ribonucleotides. Similar to deoxyribonucleotide, ribonucleotide also contains a pentose sugar (ribose sugar), a phosphate group and a nitrogenous base (adenine, guanine, cytosine, and uracil). The formation of mRNA occurs inside the nucleus …
Purpose
- A person's DNA contains information about their heritage, and can sometimes reveal whether they are at risk for certain diseases. DNA tests, or genetic tests, are used for a variety of reasons, including to diagnose genetic disorders, to determine whether a person is a carrier of a genetic mutation that they could pass on to their children, and to examine whether a person is at risk fo…
Structure
- Nucleotides are attached together to form two long strands that spiral to create a structure called a double helix. If you think of the double helix structure as a ladder, the phosphate and sugar molecules would be the sides, while the bases would be the rungs. The bases on one strand pair with the bases on another strand: adenine pairs with thymine, and guanine pairs with cytosine. D…
- The Nucleotides are the basic structural unit of DNA. Each Nucleotide is a pair of polymers with backbones made up of sugar and phosphate groups connected by ester bonds. The two anti-parallel strands run freely in the nucleus. Four types of bases are attached to each sugar. The arrangement of these bases along the backbone encrypts information which is accessed throug…
- The nucleus is the command center of the cell, containing the genetic instructions for all of the materials a cell will make (and thus all of its functions it can perform). The nucleus is encased within a membrane of two interconnected lipid bilayers, side-by-side. This nuclear envelope is studded with protein-lined pores that allow materials to be trafficked into and out of the nucleus…
Genetic Recombination
- A DNA helix usually does not interact with other segments of DNA, and in human cells, the different chromosomes even occupy separate areas in the nucleus called "chromosome territories". This physical separation of different chromosomes is important for the ability of DNA to function as a stable repository for information, as one of the few times chromosomes interac…
- Genes are packaged in bundles called chromosomes. Humans have 23 pairs of chromosomes, resulting in 46 individual chromosomes. Of those pairs, one pair, the x and y chromosome, determines whether you are male or female, plus some other body characteristics. Females have an XX pair of chromosomes while men have a pair of XY chromosomes. The other 22 pairs are a…
- The gene is the basic physical and functional unit of heredity. It consists of a specific sequence of nucleotides at a given position on a given chromosome that codes for a specific protein (or, in some cases, an RNA molecule).Genes consist of three types of nucleotide sequence: 1. coding regions, called exons, which specify a sequence of amino acids 2. non-coding regions, called intr…
- The different nucleotides of our DNA sequences among all human beings form genes. Genes are the basis of heredity. These sequences are called genotypes.At times, the results of our genetic makeup are obvious and visible to the naked eye and, at other times, these genetic traits are not at all obvious and visible to the naked eye. For example, the color of our eyes is obvious and visibl…
Discovery
- DNA was first observed by a German biochemist named Frederich Miescher in 1869. But for many years, researchers did not realize the importance of this molecule. It was not until 1953 that James Watson, Francis Crick, Maurice Wilkins and Rosalind Franklin figured out the structure of DNA — a double helix — which they realized could carry biological information. Watson, Crick an…
- Working in the 19th century, biochemists initially isolated DNA and RNA (mixed together) from cell nuclei. They were relatively quick to appreciate the polymeric nature of their \"nucleic acid\" isolates, but realized only later that nucleotides were of two types--one containing ribose and the other deoxyribose. It was this subsequent discovery that led to the identification and naming of …
- First observed in the 1800s by Swiss Biochemist Frederich Miescher, it took scientists nearly a century to discover the importance of DNA in life. Visual representations of DNA take the form of a double helix model, which resembles a ladder. Each rung of the ladder is made up a base pair. The bases pair in a very specific pattern, with adenine always pairing with thymine and cytosine …
- DNA is one of a class of molecules called nucleic acids. Nucleic acids were originally discovered in 1868 by Friedrich Meischer, a Swiss biologist, who isolated DNA from pus cells on bandages. Although Meischer suspected that nucleic acids might contain genetic information, he could not confirm it. In 1943, Oswald Avery and colleagues at Rockefeller University showed that DNA take…
Function
- DNA provides living organisms with guidelines—genetic information in chromosomal DNA—that help determine the nature of an organism's biology, how it will look and function, based on information passed down from former generations through reproduction. The slow, steady changes found in DNA over time, known as mutations, which can be destructive, neutral, or bene…
- Nucleotides are the basic cells that serve as the building blocks of both RNA and DNA. Nucleotides in DNA are referred to as A, C, G and T that are connected to each other in an array with hydrogen bonds; it is A, C, G and T are the nucleotides that contain our information.
- In many species of organism, only a small fraction of the total sequence of the genome appears to encode protein. The function of the rest is a matter of speculation. It is known that certain nucleotide sequences specify affinity for DNA binding proteins, which play a wide variety of vital roles, in particular through control of replication and transcription. These sequences are frequen…
- The information contained in DNA, which is coded into the sequence of nucleotides, carries instructions for making proteins. The nucleotides in a DNA strand form long chains that are called genes. Each gene contains information that can be translated by a cells protein-making machinery into a sequence of amino acids that form a protein. Each gene codes for one specific protein, an…
Introduction
- DNA sequencing is technology that allows researchers to determine the order of bases in a DNA sequence. The technology can be used to determine the order of bases in genes, chromosomes, or an entire genome. In 2000, researchers completed the first full sequence of the human genome, according to a report by the National Human Genome Research Institute.
- Nucleic acids are large macromolecules present in all known forms of life. There are two major types of nucleic acids as Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and Ribonucleic acid (RNA). Furthermore, RNA exists in three forms. They are messenger RNA (mRNA), transfer RNA (tRNA), and ribosomal RNA (rRNA). DNA, in the form of genes, contains the genetic information to code for proteins. A…
- Recognition of a specific nucleotide sequence by a DNA-binding protein is determined by the atomic interactions between the amino acids of the latter and the nucleotides of the former. While numerous studies introducing protein–DNA structures have gone a long way to explaining the basis of specificity in individual or highly-related complexes, no simple rules have been found fo…
Definition
- Simply defined, a chromosome is a cell that, has shown in the picture above, contains protein and one DNA molecule that is found in the nucleus of the cell.
- Within a gene, the sequence of nucleotides along a DNA strand defines a protein, which an organism is liable to manufacture or \"express\" at one or several points in its life using the information of the sequence. The relationship between the nucleotide sequence and the amino-acid sequence of the protein is determined by simple cellular rules of translation, known collecti…
- DNA typing is a laboratory procedure that detects normal variations in a sample of DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid). DNA typing is most often used to establish identity, parentage, family relationship and appropriate matches for transplantation of organs and tissues.
Rna
- Image 3: RNA is a single strand molecule available in different types and shapes. Picture Source: wikimedia.org...
- Following receipt of a construct ready for microinjection along with the necessary paperwork, the minimum time required to produce transgenic founders that can be transferred to the client is about 8 weeks. This includes about 2 weeks to order and prepare the egg donors, 3 weeks gestation time, and 3 weeks from birth to weaning.Please note - the turnaround time can be long…
- RNA is unstable. As soon as the protein is assembled, the notes are erased, i.e., the RNA molecule falls apart. This instability of RNA is an important feature because as long as the RNA stays in tact, more and more proteins will be assembled (DNA expression). By falling apart relatively quickly, RNA is able to regulate how much protein is translated. If a lot of protein is needed, mor…
Chromosomes
- The label eukaryote is taken from the Greek for 'true nucleus', and eukaryotes (all organisms except viruses, Eubacteria and Archaea) are defined by the possession of a nucleus and other membrane-bound cell organelles.The nucleus of each cell in our bodies contains approximately 1.8 metres of DNA in total, although each strand is less than one millionth of a centimetre thick. …
- Simply defined, a chromosome is a cell that, has shown in the picture above, contains protein and one DNA molecule that is found in the nucleus of the cell.Nucleotides are the basic cells that serve as the building blocks of both RNA and DNA. Nucleotides in DNA are referred to as A, C, G and T that are connected to each other in an array with hydrogen bonds; it is A, C, G and T are th…
- Within the nucleus the DNA strands are tightly packed to form chromosomes. During the cell division the chromosomes are visible.Each chromosome has a constriction point called the centromere from where two arms are formed. The short arm of the chromosome is labelled the “p arm.” The long arm of the chromosome is labeled the “q arm.”Each pair of chromosome is shap…
- The Human beings have 23 pairs of chromosomes (22 pairs of autosomes and one pair of sex chromosomes) in every cell, giving a total of 46 per cell. A photograph of a person’s chromosomes, arranged according to size, is called a karyotype. The preparation and study of karyotypes are part of cytogenetics.The sex chromosomes (allosome) determine whether you ar…