What is karyotyping?
- Definition: “A procedure to study, observe and examine chromosomes aiming to find related alteration is referred to as karyotyping.”
- Steps: The elongated forms of colchicine treated chromosomes.
- Procedure: The whole process of cell culture and harvesting was discussed in our previous article- Peripheral blood leukocyte culture.
What is a karyotype used for?
= A karyotype is an individual's collection of chromosomes. The term also refers to a laboratory technique that produces an image of an individual's chromosomes. The karyotype is used to look for abnormal numbers or structures of chromosomes.
How is karyotype analysis performed?
Analysis of karyotypes requires a comparison between a normal set of chromosomes and the subject’s chromosomes. If there are missing chromosomes (monosomy), or extra chromosomes (trisomy or polydactyl); or if individual chromosomes have extensions or deletions; the subject will then have a chromosomal disorder. a.
What is the difference between karyotyping and karyotype?
Karyotyping is a technique to grow chromosomes, while karyotype is a method or procedure to arrange it using either manual method or computational software. “A process to pair and arrange chromosomes in order to encounter any defect is known as karyotype or karyogram.” Once you get your GTG banding results, snap a photo through a good camera.
How many chromosomes are in a human karyotype?
How many chromosomes does a normal diploid human contain? 46 chromosomes. What cells can be used to make a karyotype? Those with a nucleus of any type - Lymphocytes, skin cells, cells from biopsies, tumour cells.

What is the purpose of karyotype?
Karyotyping is a test to examine chromosomes in a sample of cells. This test can help identify genetic problems as the cause of a disorder or disease.
What is the purpose of a karyotype quizlet?
A karyotype is a test to identify and evaluate the size, shape, and number of chromosomes in a sample of body cells.
What is karyotype in biology?
A karyotype is an individual's complete set of chromosomes. The term also refers to a laboratory-produced image of a person's chromosomes isolated from an individual cell and arranged in numerical order. A karyotype may be used to look for abnormalities in chromosome number or structure.
What types of information can be obtained from a karyotype?
Karyotypes can reveal changes in chromosome number associated with aneuploid conditions, such as trisomy 21 (Down syndrome). Careful analysis of karyotypes can also reveal more subtle structural changes, such as chromosomal deletions, duplications, translocations, or inversions.
How is a karyotype made quizlet?
Terms in this set (12) Describe how a karyotype is prepared and analyzed. Biologists photograph cells in mitosis, cut out the chromosomes from the photographs, and group them together in pairs. They then check whether any chromosomes are missing or have extra copies.
What can you tell from reading a karyotype quizlet?
What can you tell from a karyotype? The sex of the individual and whether they have a chromosomal abnormality (an extra or missing chromosome). You just studied 10 terms!
What information Cannot be determined by a karyotype quizlet?
Karyotyping can give information on a person's sex and chromosomal disorders. It cannot give information on a person's traits and how severe a disorder is.
How can you tell if a karyotype is a human?
0:042:184.2.7 Analyze a human karyotype to determine gender and ... - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipShow an X and a y the Y being the shorter chromosome therefore this karyotype belongs to a male. InMoreShow an X and a y the Y being the shorter chromosome therefore this karyotype belongs to a male. In this second karyotype we can see that chromosome number 21 has three copies known as trisomy 21.
What Is a Karyotype Test?
A karyotype is a photograph of the chromosomes in a cell. Karyotypes can be taken from blood cells, fetal skin cells (from amniotic fluid or the placenta), or bone marrow cells. 1
Where do karyotypes come from?
A karyotype is a photograph of the chromosomes in a cell. Karyotypes can be taken from blood cells, fetal skin cells (from amniotic fluid or the placenta), or bone marrow cells. 1
What are the situations in which a karyotype may be recommended by your physician?
These might include: 6 . Infants or children who have medical conditions which suggest a chromosomal abnormality that has not yet been diagnosed.
How to analyze chromosomes?
In order to analyze chromosomes, the sample must contain cells that are actively dividing. In blood, the white blood cells actively divide. Most fetal cells actively divide as well. Once the sample reaches the cytogenetics lab, the non-dividing cells are separated from the dividing cells using special chemicals. 8 .
What is a chromosome translocation?
Chromosome translocations in which a part of one chromosome is attached to another chromosome (and vice versa in balanced translocations.) Klinefelter's syndrome (XXY and other variations) - Klinefelter's syndrome occurs in 1 in 500 newborn males.
Can a karyotype be used for infertility?
Infertility: A genetic karyotype may be done for infertility. As noted above, some chromosomal abnormalities may go undiagnosed until adulthood. A woman with Turner syndrome or a man with one of the variants of Klinefelter's may not be aware of the condition until they are coping with infertility.
Is a karyotype test a simple blood test?
A karyotype test may sound like a simple blood test, which makes many people wonder why it takes so long to get the results. This test is actually quite complex after collection. Let's take a look at these steps so you can understand what is happening during the time you are waiting for the test.
Which chromosome is placed closer to one end than the other?
Submetacentric - chromosome whose centromere is placed closer to one end than the other.
Why do cells leave in solution for a short time?
Cells left in solution for a short time because if left in hypotonic solution too long they will lyse.
Why is DNA heated at high temperatures?
Heated at high temperatures to achieve partial denaturation of DNA
What is the p-long arm and Q-long arm measured from?
p - short arm and q - long arm measured from the centromere.
Why is karyotyping used in genetics?
Though it is less beneficial than molecular genetic techniques, still, scientists are using karyotyping for screening and diagnosis of various genetic diseases for a long time . The present method is powerful enough to solve the subtle mysteries of chromosomes and related abnormalities. Change in chromosome number & structure, deletions, ...
What is a karyotype?
Karyotyping is a technique to grow chromosomes, while karyotype is a method or procedure to arrange it using either manual method or computational software.
What is the process of arranging, pairing, and organizing chromosomes to find chromosomal?
Karyotyping: Definition, Steps, Procedure and Applications. “The process of arranging, pairing, and organizing chromosomes to find chromosomal variations is known as karyotyping.”. The karyotyping is one of the most traditional and common cytogenetic techniques scientists have been using for long.
How to observe chromosomes?
To observe chromosomes, treat the slide with either Giemsa staining followed by GTG (Giemsa-trypsin-Giemsa) banding. Print the chromosome picture on a paper and arrange it orderly. The process of arranging chromosomes to find any changes is known as karyotype or karyogram.
Why are chromosomes different?
In humans every pair of chromosomes are different due to the centromere locations. The location of centromere makes each set unique and identifiable.
What is the purpose of preparing a karyogram?
The aim of preparing a karyogram or karyotype is to find out any chromosomal variations.
How many pairs of chromosomes are there in the human body?
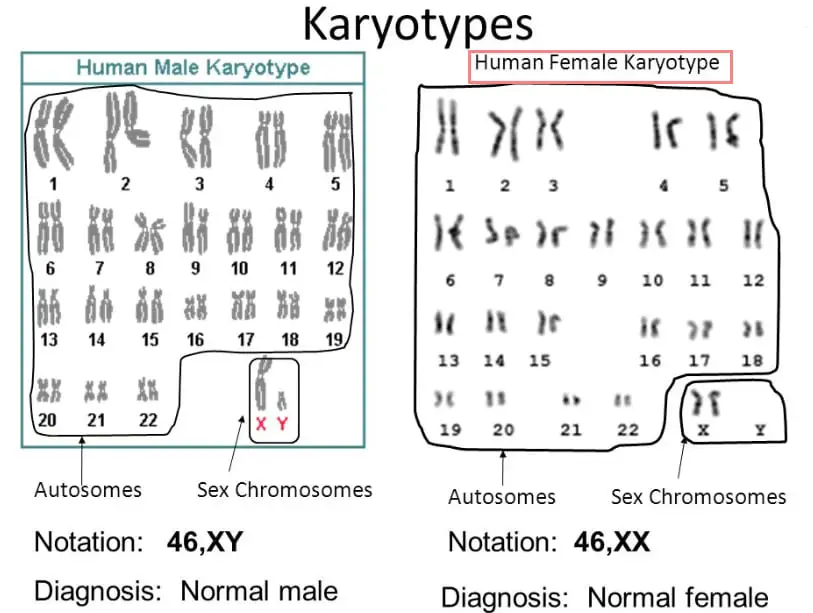
Human chromosomes are in pairs. 23 pairs with 22 autosomes and a pair of sex chromosomes are present in us. All of our DNA (except cytoplasmic DNA ), are located on chromosomes. Any alteration in numbers or structure of chromosomes causes abnormalities known as genetic disease or genetic abnormality.
Which phase of the chromosome is highly recommended?
Only the metaphase chromosomes are highly recommended because, during metaphase, chromosomes appear well-separated, condensed and larger. Abnormalities can be ruled out easily.
When can you see chromosomes under a microscope?
Chromosomes can be seen under the microscopes during the metaphase.
What is the stage of a cell division where the chromosomes are lined up in the center of the?
The metaphase is a cell division stage during which the chromosomes are lined up in the center of a cell, in a linear fashion to attach with spindle fibers.
What staining is used to visualize metaphase chromosomes?
To visualize, study and investigate various metaphase chromosomes, G staining or Giemsa sta ining, followed by GTG banding has been performed.
What is the first impression for cytogenetics?
Although the first impression for cytogenetics is to achieve well-separated chromosomes but achieving metaphase, a good metaphase chromosome plate is what the researcher needs.
How many chromosomes are in a normal metaphase cell?
In a normal metaphase cell, 46 chromosomes are present, however, in the case of aneuploidy, the number may differ. For example, in the case, of trisomy, 47 and monosomy, 45 chromosomes are seen.
What are the characteristics of metaphase chromosomes?
The metaphase chromosomes are condensed, more tightly wrapped and well-distinguishable. Also, cells become swell more, appear bigger and lack nuclear membrane.
