
What is the function of amylase?
What Are the Functions of Amylase, Protease and Lipase Digestive Enzymes
- Amylase. Amylase is a digestive enzyme that acts on starch in food, breaking it down into smaller carbohydrate molecules.
- Protease. Any enzyme that breaks down protein into its building blocks, amino acids, is called a protease, which is a general term.
- Lipase. ...
- Other Enzymes. ...
What does amylase do in the body?
Amylase is an enzyme that helps digest carbohydrates (starch and glycogen) into simple sugar [glucose (monosaccharide) and maltose (disaccharide)] for energy. Amylase is made in the pancreas and the salivary glands that make saliva. Amylase is also found in microbes, plants and animals.
What is amylase made out of?
Similarly, it is asked, what is amylase made out of? At its most basic level, salivary amylase is made from many small subunits called amino acids. In fact, all enzymes are made from amino acids. Enzymes are, believe it or not, actually protein molecules. The amino acids are individual links found in a protein (or enzyme) chain.
What does amylase mean?
Amylase is an enzyme that catalyses the breakdown of starch into sugars. Amylase is present in human saliva, where it begins the mechanical process of digestion. Foods that contain much starch but little sugar, such as rice and potato, taste slightly sweet as they are chewed because amylase turns some of their starch into sugar in the mouth.
See more
What is the function of amylase?
Amylases' main function is to hydrolyze the glycosidic bonds in starch molecules, converting complex carbohydrates to simple sugars.
What does amylase break down?
Amylases digest starch into smaller molecules, ultimately yielding maltose, which in turn is cleaved into two glucose molecules by maltase. Starch comprises a significant portion of the typical human diet for most nationalities.
Why can amylase break down starch?
amylase, any member of a class of enzymes that catalyze the hydrolysis (splitting of a compound by addition of a water molecule) of starch into smaller carbohydrate molecules such as maltose (a molecule composed of two glucose molecules).
Where does amylase take action?
CarbohydratesEnzymeProduced BySite of ActionSalivary amylaseSalivary glandsMouthPancreatic amylasePancreasSmall intestineOligosaccharidasesLining of the intestine; brush border membraneSmall intestine
Does amylase break down protein?
These digestive enzymes are categorized based on the reactions they help catalyze: Amylase breaks down starches and carbohydrates into sugars. Protease breaks down proteins into amino acids. Lipase breaks down lipids, which are fats and oils, into glycerol and fatty acids.
What does amylase break down carbohydrates into?
maltoseAmylase breaks starches into maltose and polysaccharides. Amylase is sensitive to pH and thus is inhibited in the acidic environment of the stomach.
What does amylase break down GCSE?
Different enzymes Enzymes can break down nutrients into small, soluble molecules that can be absorbed. For example, amylase causes the breakdown of starch into simple sugars.
Can amylase break down glycogen?
Amylase can't digest glycogen because of its inability to attack the branching (1→6) linkages. Perhaps, another very important reason is controlling the rate of glycogen metabolism through glycogen phosphorylase.
What is the pH of alpha amylase?
The optimum pH of alpha-amylase is 6.7–7.0.
Where are beta amylases found?
Get a Britannica Premium subscription and gain access to exclusive content. Subscribe Now. Beta-amylases are present in yeasts, molds, bacteria, and plants, particularly in the seeds.
What enzyme is used to coagulate milk protein?
In addition, the proteolytic enzyme (i.e., protease) rennin, produced in calves’ stomachs to coagulate milk protein and aid in…. distilled spirit: Mashing. Of the two enzymes— α -amylase and β -amylase—the former is the more important for conversion of other grains.
How does ptyalin work?
Ptyalin’s digestive action depends upon how much acid is in the stomach, how rapidly the stomach contents empty, and how thoroughly the food has mixed with the acid. Under optimal conditions as much as 30 to 40 percent of ingested starches can be broken down to maltose by ptyalin during digestion in the stomach.
Overview
An amylase test is a way to measure the amount of amylase in blood or urine (pee). It’s also called an “amy” test, serum amylase and urine amylase.
Test Details
Your healthcare provider will give you specific instructions. You may have to fast for eight to 12 hours. That means you shouldn’t eat or drink anything besides water. You may have to avoid alcohol for 24 hours before the test.
Results and Follow-Up
You should get amylase test results in about a day or two, depending on the lab.
Where is amylase found?
Alpha-amylase (α-Amylase) is the major form of amylase found in humans and other mammals and is mainly made the pancreas and salivary glands, but it’s also produced by the small intestine mucosa, ovaries, placenta, liver and fallopian tubes. ( 1)
How to test for amylase?
Testing can be conducted to measure the level of amylase as well as other enzymes in your blood. Amylase level testing can be done with a blood or urine test. For a urine test, it’s likely a two-hour or 24-hour sampling. For a blood test, blood is taken from a vein in your arm.
What enzymes are secreted by salivary glands?
The amylase secreted by the salivary glands kicks off the the enzymatic digestion of starches in the mouth as food is chewed and mixed with saliva. It might be surprising, but it’s true that the breakdown of larger, more complex starches into simpler sugars actually starts in your mouth with simple chewing.
How long does amylase stay high in urine?
When it comes to blood, amylase levels rise for only a short time. In the urine, amylase may remain high for several days.
What is the role of digestive enzymes in the body?
The role of digestive enzymes is to act as catalysts in speeding up specific, life-preserving chemical reactions in the body. Essentially, digestive enzymes assist in breaking down larger molecules into more easily absorbed particles that the body can use to survive and thrive.
What enzymes are released by the parietal cells of the stomach?
The parietal cells of the stomach are then triggered into releasing acids, pepsin and other enzymes, including gastric amylase, and the process of degrading the partially digested food into chyme (a semifluid mass of partly digested food) begins. The acid also has the effect of neutralizing the salivary amylase, ...
Which type of amylase is found in the small intestine?
In addition, cells in your pancreas make another form of amylase called pancreatic amylase, which passes through a duct to reach your small intestine. Pancreatic amylase completes the digestion of carbohydrates. 2. More Energy.
Where is amylase found?
Amylase is also found in microbes, plants and animals. Amylases are broadly classified into α (alpha), β (beta), and γ (gamma) subtypes, of which the first two have been the most widely studied. Alpha amylase (α-Amylase) is a faster-acting enzyme than beta amylase (β-amylase).
Where does amylase enzyme release glucose?
In human, amylase enzyme is secreted through the pancreatic duct into the first part of the small intestine (duodenum), where it helps break down dietary carbohydrates.
What is the enzyme that makes sugar into glucose?
What is amylase. Amylase is an enzyme that helps digest carbohydrates (starch and glycogen) into simple sugar [glucose (monosaccharide) and maltose (disaccharide)] for energy. Amylase is made in the pancreas and the salivary glands that make saliva. Amylase is also found in microbes, plants and animals. Amylases are broadly classified ...
What causes low amylase levels?
Low levels of amylase can indicate: 1 Chronic pancreatitis, an inflammation of the pancreas that gets worse over time and can lead to permanent damage. Chronic pancreatitis is most often caused by heavy alcohol use. 2 Liver disease 3 Cystic fibrosis 4 Cancer of the pancreas 5 Damage to the pancreas 6 Kidney disease 7 Toxemia of pregnancy
Why is my amylase level low?
Increased blood amylase levels with normal to low urine amylase levels may indicate the presence of a macroamylase, a benign complex of amylase and other proteins that accumulates in the blood.
How long does it take for amylase to increase?
The increase occurs within 4 to 8 hours of injury to the pancreas and generally remains elevated until the cause is successfully treated.
Which enzyme inhibits glucose uptake?
Mammalian pancreatic alpha amylase (α-amylase) binds specifically to glycoprotein N-glycans in the brush-border membrane to activate starch digestion, whereas it significantly inhibits glucose uptake by Na + /glucose cotransporter 1 (SGLT1) at high concentrations 19). However, how the inhibition is stopped was unknown.
What is the function of amylase?
Amylase Function. Amylase is an enzyme that breaks down complex carbs into simpler ones. Digestion of carbs is extremely important since carbs are ultimately broken down into glucose – the main energy source that fuels our bodies. There are two main types of amylase – salivary and pancreatic [ 1, 2 ].
Why is amylase important?
Low levels have been linked to insulin resistance, metabolic syndrome, obesity, and diabetes. High amylase can be due to issues with the salivary glands or the pancreas, which produce this enzyme.
What is the amylase test?
Blood (serum) amylase consists of approximately equal amounts of salivary and pancreatic amylase. Therefore, abnormal levels of either will affect the total blood levels [ 6, 1 ]. Most often, your doctor will order an amylase test if they suspect issues with your pancreas, such as inflammation (pancreatitis).
Why is amylase high in the blood?
High levels of amylase in the blood (hyperamylasemia) are caused by either too much of the enzyme entering the bloodstream or not enough of it being cleared (by the kidneys) [ 2 ]. Amylase will usually build up in the blood as a result of issues with the salivary glands or the pancreas.
Why is amylase used instead of blood?
When needed, urine amylase may be used instead of the blood test because it’s less invasive [ 30 ].
Which genes produce amylase?
Your genes may hold the answer. Salivary amylase is produced by the AMY1A, while pancreatic amylase is produced by the AMY2A and AMY2B genes. Many people have multiple copies of these genes. Having multiple copies is an evolutionary adaptation to eating carbs (starch-rich diets).
What is the normal range for salivary amylase?
These tests can zero in on exactly what is going on in your body with greater precision [ 2 ]. For salivary amylase, the normal range is around 11 – 83 U/L.
What is an amylase?
α Amylases are starch hydrolases with several amino acid sequences that are highly conserved amongst family members. Amylases of A. hydrophila strains are about 48–49 kDa in size, although a larger amylase (70 kDa) is found in A. hydrophila JMP636. The α amylase of A. hydrophila MCC-1 shows conservation in catalytic- and substrate-binding residues. In addition, three of four calcium-binding residues (Asn100, Asp167, His201) present in other α amylases are retained in MCC-1, consistent with the fact that this enzyme requires calcium for activity.
How is amylase measured?
Amylase is most commonly measured by absorbance or fluorescence assays in which a labeled substrate is cleaved. View chapter Purchase book. Read full chapter. URL: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/B0123868602000253.
What enzymes catalyze starch?
Amylase. Amylases are a class of enzymes that catalyze the hydrolysis of starch into sugars such as glucose and maltose (Sundarram and Murthy, 2014). From: Biotechnology of Microbial Enzymes, 2017. Download as PDF. About this page.
How long does it take for amylase to increase in urine?
The amylase levels in the urine also increase in acute pancreatitis, but it is important to know that the values are increased 10 days longer than those of serum amylase, so if the value of serum amylase is in normal range after 5 days, we can observe the increase in value of amylase in the urine.
How long does it take for amylase to peak?
Amylase has a half‐life of approximately 10 hours, peaks within 12 hours, and may be normal in 24 hours if no additional amylase spillage occurs.
What are the products of amylase acting on starch?
The resulting products of amylase acting on starch, referred to as dextrins, are α-1,4-linked glucose dimers (maltose), α-1,4-linked glucose trimers (maltotriose), and branched oligosaccharides of 6 to 8 glucose units that contain both α-1,6 and α-1,4 linkages (limit dextrins). Starch digestion can begin in the mouth and in a swallowed bolus ...
How many subsites does amylase have?
The porcine and human enzymes appear to have five subsites, and subsite three is probably the catalytic site.
Why do I need amylase?
Why do I need it? Your caregiver may want to get an amylase level if you have stomach pain. An amylase level can help tell if the pain is caused by pancreatitis. The amylase level is also helpful to see how the treatment for pancreatitis is working.
What is the name of the enzyme that speeds up a chemical reaction in the body?
What is it? Amylase (am-uh-lase) is an enzyme (n-zime) released by the pancreas (pan-kree-us). An enzyme is a protein that speeds up a chemical reaction in your body. The pancreas is a small organ located near the stomach.
What enzymes help break down food?
Many of the enzymes released from the pancreas help break food down so it can be used by your body. Amylase is most specific for pancreatitis (pan-kree-uh-ti-tis). Pancreatitis is inflammation (swelling) of the pancreas.
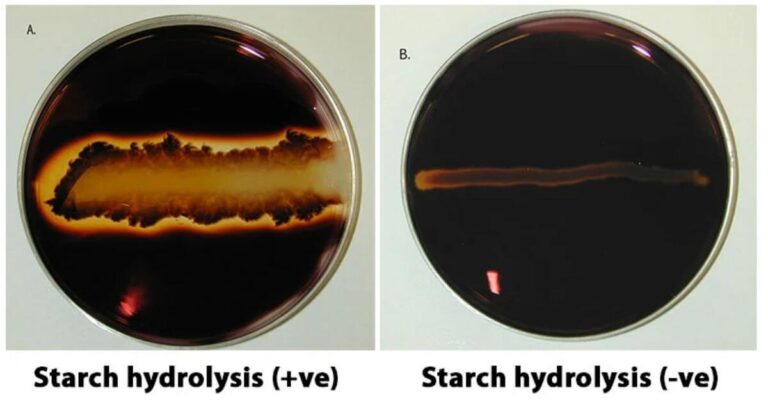
What Is Amylase?
Health Benefits
- What are some of the ways that amylase can benefit your health? Well, aside from the most key and central function to properly digest carbohydrates, it also holds a lot of other valuable health benefits that will probably surprise you.
Testing
- Testing can be conducted to measure the level of amylase as well as other enzymes in your blood. Amylase level testing can be done with a blood or urine test. For a urine test, it’s likely a two-hour or 24-hour sampling. For a blood test, blood is taken from a vein in your arm. There is more work involved with collecting your urine over a period of time, but there are also no risks, p…
How to Use
- Natural dietary sources of amylase include raw fruits and vegetables, along with sprouted seeds, nuts, legumes and whole grains. Both short- and long-term sprouting helps the body regulate amylase-enzyme activity that’s needed to properly digest glucose, which is especially helpful to diabetics. Royal jellyis also another excellent source. When it comes to supplements, you’ll find …
Risks and Side Effects
- Digestive enzymes are essentially nontoxic and typically don’t cause side effects. Occasional side effects of digestive enzymes can include mild gastrointestinal distress, diarrhea or allergic reactions. If any of these effects persist or worsen, you should discontinue use of the supplement and speak with your health care provider. If you take a supplement that includes the digestive en…