What is a centrifuge used for in research?
Feb 26, 2022 · A centrifuge is a laboratory device that is used for the separation of fluids, gas or liquid, based on density. Separation is achieved by spinning a vessel containing material at high speed; the centrifugal force pushes heavier materials to the outside of the vessel. The centrifuge works using the sedimentation principle, where the centrifugal acceleration causes denser …
How do you do a centrifugation test on a sample?
Mar 05, 2020 · What is the purpose of centrifuging a sample? A centrifuge is a laboratory device that is used for the separation of fluids, gas or liquid, based on density. Separation is achieved by spinning a vessel containing material at high speed; the centrifugal force pushes heavier materials to the outside of the vessel.
Why is centrifugation used to separate mixtures?
Mar 07, 2020 · A laboratory centrifuge is a motor-driven device used in laboratories for the purposes of separating the components of a liquids. Laboratory centrifuges are widely used in hospitals or other industries where they are used for extracting suspended material from a variety of medium. Just so, why does blood separate in a centrifuge?
What is the function of sedimentation in centrifuges?
Sep 16, 2020 · One of the most common uses is to separate red blood cells and other blood components from whole blood. A centrifuge works based on the sedimentation principle. Sedimentation refers to the tendency for particles in suspension to settle out of the medium where they are entrapped and come to rest against a barrier.
How does a centrifuge work?
How a Centrifuge Works. A centrifuge gets its name from centrifugal force —the virtual force that pulls spinning objects outward. Centripetal force is the real physical force at work, pulling spinning objects inward. Spinning a bucket of water is a good example of these forces at work. If the bucket spins fast enough, ...
What is a centrifuge?
The term centrifuge can refer to a machine that houses a rapidly rotating container to separate its contents by density (noun) or to the act of using the machine (verb). Centrifuges are most often used to separate different liquids and solid particulates from liquids, but they may be used for gases.
Who invented the centrifuge?
The modern centrifuge traces its origins to a spinning arm apparatus designed in the 18th century by English military engineer Benjamin Robins to determine drag. In 1864, Antonin Prandtl applied the technique to separate the components of milk and cream. In 1875, Prandtl's brother, Alexender, refined ...
What are the differences between centrifuges?
The main differences between them are the speed of rotation and the rotor design. The rotor is the rotating unit in the device. Fixed-angle rotors hold samples at a constant angle, swinging head rotors have a hinge that allows sample vessels to swing outward as the rate of spin increases, and continuous tubular centrifuges have a single chamber rather than individual sample chambers.
What is industrial centrifuge?
Industrial Centrifuges are used to separate components of colloids (like cream and butter from milk), in chemical preparation, cleaning solids from drilling fluid, drying materials, and water treatment to remove sludge.
What is the best method to separate materials?
While centrifugation is the best option for simulating high gravity, there are other techniques that may be used to separate materials. These include filtration, sieving, distillation, decantation, and chromatography. The best technique for an application depends on the properties of the sample being used and its volume.
What is an example of centrifuge?
An example of a centrifuge is a machine that separates cream and milk. An example of a centrifuge is a washing machine that has a spin cycle to draw the moisture out of the washed clothes.
How does a centrifuge work?
A centrifuge works by spinning mixtures around a central axis (centrifugal force). The body of the centrifuge, or the body of the container within the centrifuge, provides a normal force that pushes the object toward the center of the circular path of travel.
What do you mean by centrifuge?
Centrifugation Definition. Centrifugation is the process where a mixture is separated through spinning. It is used to separate skim milk from whole milk, water from your clothes, and blood cells from your blood plasma.
What is a centrifuge cover?
Looks like it is a oil separator. Used in emission system at top of valve cover. The Teflon valve can wear and need to be replaced. Called a centrifuge because it causes the oil air gas mixture from the crankcase to spin and throws the il drops against the side which then run back down into the engine.
How does a centrifuge separate materials?
A centrifuge is able to separate different substances from each other because materials with heavier masses move faster and farther away from the central point than materials with lighter masses. A centrifuge consists of a fixed base and center stem to which arms or holders containing hollow tubes are attached.
What is centrifuge test?
A Centrifuge Test is a fully programmable process which allows automatic configuration of specified oil test parameters.
What is the process of separating blood?
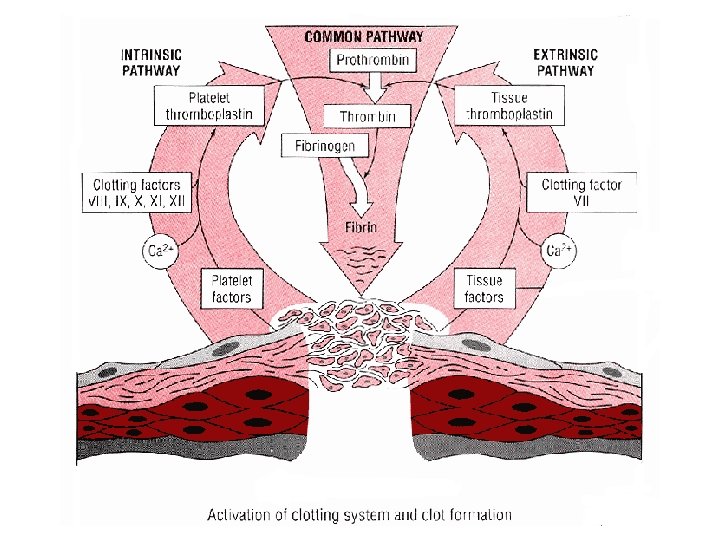
Blood fractionation is the process of fractionating whole blood, or separating it into its component parts. This is typically done by centrifuging the blood. the buffy coat, which is a thin layer of leukocytes (white blood cells) mixed with platelets in the middle, and.
What is a laboratory centrifuge?
Laboratory centrifuges are widely used in different applications, including clinical, research, and academia. They handle a wide variety of tasks such as separation, purification, and isolation of organelles, cells, and cell components for further observation.
How does a centrifuge work?
How A Centrifuge Works. A centrifuge uses a motor to spin liquid samples at high speed. There are different types of centrifuges, which vary in size and sample capacity. Centrifugal force moves the dense components to the outside of the container allowing the solids to settle completely and rapidly.
How much does a centrifuge cost?
Centrifuge costs vary widely depending on the size, type, and features of the unit. Average prices by type are: 1 Benchtop – $1,000 to $5,000 2 Large Capacity / High Speed – $10,000 to $25,000 3 Ultracentrifuge – $10,000 to $50,000
What is a centrifuge?
Centrifuges are common pieces of lab equipment, used to separate particles from a solution. These particles are separated according to the size, shape, density, and viscosity of the medium. The separation process depends on the rotor speed. Laboratory centrifuges are widely used in different applications, including clinical, research, and academia.
How fast can an ultra centrifuge spin?
Ultra centrifuges are optimized to spin at very high speeds, capable of reaching as high as 1,000,000 g (9,800 kilometers per second or 6,089 miles per second). These kinds of centrifuges are classified as either preparative or analytical.
How many g is a preparation ultracentrifuge?
Preparative ultracentrifuges reach about 600,000 g. They are used to determine the shape and mass of macromolecules, separate lipoprotein molecules from plasma, and a variety of other tasks. Preparative ultracentrifuges feature chambers that are refrigerated, sealed, and evacuated.
What is the maximum force of gravity in a benchtop centrifuge?
Small bench centrifuges have a maximum relative centrifugal field of 3,000 to 7,000x the force of gravity, known as gravitational force or g-force (g). Compared to other options, these are relatively low speed.
What is centrifugation in science?
At its core, centrifugation is separation through sedimentation. The denser particles sink to the bottom of the container, while the more lightweight particles remain suspended. Centrifugation will displace particles that are even slightly different in density, and is influenced by these four factors:
What happens when a centrifuge spins?
When the centrifuge spins, it creates a strong centrifugal force. Though separation would eventually happen naturally with Earth’s gravity, the centrifuge machine delivers rapid results for laboratory and other applications. There are many types of centrifuges, varying by intended use and rotor design.
What is the best way to clean a centrifuge?
Cleaning and disinfection are key to ensuring good centrifuge functionality in the long term. Using a neutral cleaning solution (like an alcohol-based disinfectant) and a soft cloth, wipe the: Rotors. Rotor chamber.
What is centrifugation used for?
Centrifugation is used to collect cells, to precipitate DNA, to purify virus particles, and to distinguish subtle differences in the conformation of molecules. Most laboratories undertaking active research will have more than one type of centrifuge, each capable of using a variety of rotors.
When was the centrifuge invented?
The first electrically driven centrifuges were introduced in 1910, further accelerating centrifuge development. Svedberg's invention of the analytical ultracentrifuge in 1923, operating at 10 000 rpm and equipped with transparent observation windows, marked another milestone in centrifuge technology.
How to separate molecules in a centrifuge?
Centrifugation is a method of separating molecules having different densities by spinning them in solution around an axis (in a centrifuge rotor) at high speed. It is one of the most useful and frequently employed techniques in the molecular biology laboratory. Centrifugation is used to collect cells, to precipitate DNA, to purify virus particles, and to distinguish subtle differences in the conformation of molecules. Most laboratories undertaking active research will have more than one type of centrifuge, each capable of using a variety of rotors. Small tabletop centrifuges can be used to pellet cells or to collect strands of DNA during ethanol precipitation. Ultracentrifuges can be used to band plasmid DNA in a cesium chloride gradient or to differentiate various structures of replicating DNA in a sucrose gradient.
How does counterflow centrifugation work?
In counterflow centrifugation, the cells are maintained in a fluidized bed as a result of the flow of cell suspension being parallel but opposite to the direction of centrifugal force.
What is DCS used for?
DCS is used to measure the NP size distribution, where the NP size ranges from 2 nm to 80 μm. Major advantages of DCS are as follows: (i) ultrahigh resolution capability, (ii) measure peaks of different sizes, and (iii) also measure of small additional peaks, which can be compared with SEM. The study of Zeljkakrptic et al. on gold NP functionalized with organic ligands (peptides and PEG thiol) shows that DCS can be used to measure even the small thickness variation of as small as 0.1 nm on particle. The study of another group, Angela Jedlovszky et al., reveals that DCS is not capable to provide the quantitative structural data of protein-SPION complexes, but it can provide the valuable qualitative information ( Jedlovszky-Hajdu et al., 2012 ). The study of Waczyk et al. interprets that DCS can measure the size distribution in semiqualitative way in a protein complex mixture ( Walczyk et al., 2010; Kharazian et al., 2016 ).
What is the speed of a fixed angle rotor?
Bacteria cells can usually be pelleted with a centrifugation speed of 8000 × g , which is equivalent to a centrifugal force of 8000 times greater than the Earth’s gravitational force.
What is centrifugation used for?
It is used to separate skim milk from whole milk, water from your clothes, and blood cells from your blood plasma. Although centrifugation is primarily used to separate mixtures, it is also used to test the effects of gravity on people and objects. We'll delve into all of this later in the lesson, but let's start by discussing how centrifugation ...
Why do centrifuges work?
No matter what size, centrifuges work because of some fairly simple physics. Objects, like particles, want to continue down their original path, so when the centrifuge spins, the larger particles continue outward, thus causing them to end up further away from the center of the centrifuge.
What is a centrifuge?
Centrifuge: device that can rapidly spin. Centrifugation is used to separate: skim and whole milk. water from washed clothes. components of blood at the hospital. parts of cells/DNA in laboratory tests. components of uranium ore for nuclear weapons. simulates increased gravity for astronauts.
What is a centrifuge used for?
Centrifuges are used in various laboratories to separate fluids, gases, or liquids based on density. In research and clinical laboratories, centrifuges are often used for cell, organelle, virus, protein, and nucleic acid purification. An example of centrifuge use in a clinical setting is for the separation of whole blood components.
Why do you need to balance a centrifuge?
Prior to starting the centrifuge, it is necessary to load it correctly. Balancing the centrifuge prevents potential damage to the instrument, and is crucial for safe operation.
How to maintain a centrifuge?
Centrifuge care and maintenance 1 Keep the centrifuge properly lubricated. O-rings are the main source of protection against sample leakage, and must be lubricated prior to installation of a new rotor or following cleaning. Any threaded components should also be cleaned regularly and lubricated with an approved grease to ensure proper operation and to prevent cross-threading and corrosion. 2 Ensure all users are aware of how to properly operate the centrifuge, including ensuring buckets are properly seated in their pins, balancing tubes in the rotor, operating rotors within stated guidelines for speed and maximum compartment mass, and avoiding scratching the rotor. 3 Inspect critical components, and look for signs of wear including scratches, or effects of chemical exposure on the rotor. 4 Pay close attention to noise, vibration, shaking, or grinding and stop the unit immediately if this occurs.
What is the principle of centrifugation?
A centrifuge is used to separate particles suspended in a liquid according to particle size and density, viscosity of the medium, and rotor speed. Within a solution, gravitational force will cause particles of higher density than the solvent to sink, and those less dense than the solvent to float to the top.
Is it normal to have a little vibration in a centrifuge?
A little vibration is normal, but excessive amounts can mean danger. First, double check that the tubes are correctly balanced. If this does not resolve the issue, do not operate the centrifuge until it has been serviced by the manufacturer or dealer.
What is the maximum speed of a centrifuge?
Centrifuges may be classified based on maximum speeds, measured as revolutions per minute (RPM). Speeds range from 0-7,500 RPM for low-speed centrifuges, all the way to 20,000 RPM or higher.
What happens when a rotor spins?
As the rotor spins around a central axis, it generates a centrifugal force acting to move particles away from the axis of rotation. If the centrifugal force exceeds the buoyant forces of liquid media and the frictional force created by the particle, the particles will sediment.

Invention and Early History of The Centrifuge
How A Centrifuge Works
- A centrifuge gets its name from centrifugal force—the virtual force that pulls spinning objects outward.Centripetal force is the real physical force at work, pulling spinning objects inward. Spinning a bucket of water is a good example of these forces at work. If the bucket spins fast enough, the water is pulled inward and doesn't spill. If the bucket is filled with a mixture of sand …
Types and Uses of Centrifuges
- The types of centrifuges are all based on the same technique but differ in their applications. The main differences between them are the speed of rotation and the rotordesign. The rotor is the rotating unit in the device. Fixed-angle rotors hold samples at a constant angle, swinging head rotors have a hinge that allows sample vessels to swing outward as the rate of spin increases, a…
Related Techniques
- While centrifugation is the best option for simulating high gravity, there are other techniques that may be used to separate materials. These include filtration, sieving, distillation, decantation, and chromatography. The best technique for an application depends on the properties of the sample being used and its volume.