What is the purpose of the Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium model? Hardy-Weinberg Equilibrium (HWE) is used to estimate the number of homozygous and heterozygous variant carriers based on its allele frequency in populations that are not evolving.
What was the purpose of Hardy and Weinberg's work?
Hardy and Weinberg independently worked on finding a mathematical equation to explain the link between genetic equilibrium and evolution in a population of species. In fact, Weinberg was the first of the two men to publish and lecture on his ideas of genetic equilibrium in 1908.
What was the purpose of the Hardy and Weinberg 's work?
The focus of Hardy's and Weinberg's works was on very small changes at a gene level either due to chance or other circumstances that changed the gene pool of the population. The frequency at which certain alleles appeared changed over generations.
What are the 5 assumptions of the Hardy Weinberg principle?
What are the assumptions of the Hardy Weinberg model?
- Assumption 1: No Genetic Drift.
- Assumption 2: A Closed Population.
- Assumption 3: Mutations Don't Happen.
- Assumption 4: Random Mating Patterns.
- Assumption 5: No Natural Selection.
What conditions of Hardy Weinberg law is never met?
The population must be large so that no genetic drift (random chance) can cause the allele frequencies to change. No selection can occur so that certain alleles are not selected for, or against. Obviously, the Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium cannot exist in real life.

What is the purpose of the Hardy-Weinberg equation?
The Hardy-Weinberg equation is a mathematical equation that can be used to calculate the genetic variation of a population at equilibrium. In 1908, G. H. Hardy and Wilhelm Weinberg independently described a basic principle of population genetics, which is now named the Hardy-Weinberg equation.
Why is the Hardy-Weinberg principle important in population genetics?
This relationship, known as the Hardy-Weinberg principle, is important because we can use it to determine if a population is in equilibrium for a particular gene. The Hardy-Weinberg principle applies to individual genes with two alleles, a dominant allele and a recessive allele.
What does Hardy-Weinberg tell us about evolution?
Evolutionary Implications of the Hardy-Weinberg Theorem The Hardy-Weinberg Theorem demonstrates that Mendelian loci segregating for multiple alleles in diploid populations will retain predictable levels of genetic variation in the absence of forces that change allele frequencies.
Why do scientists use Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium quizlet?
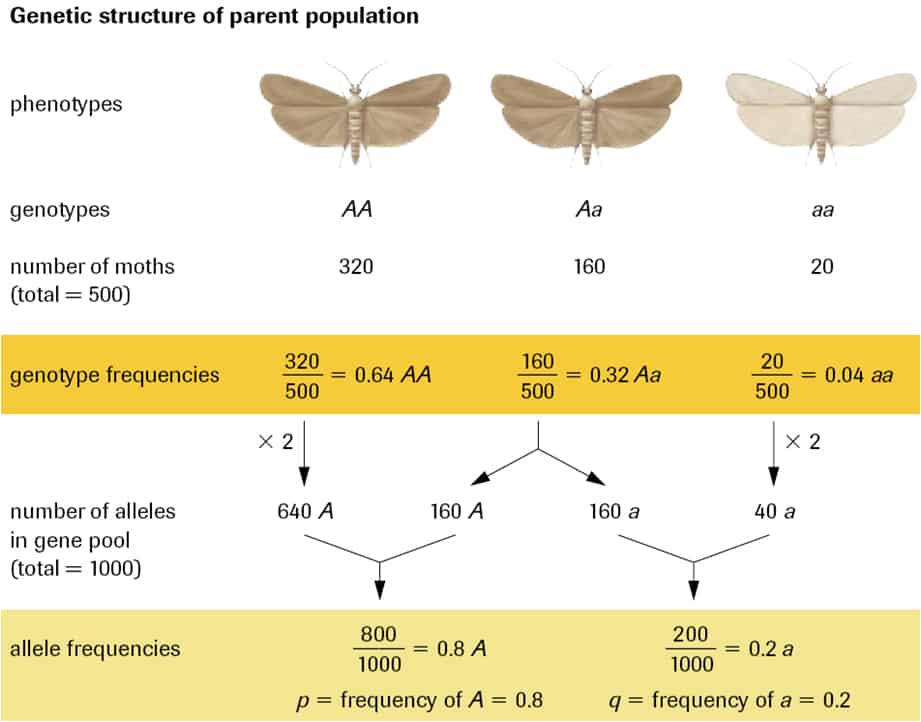
The Hardy-Weinberg equation can be used to: -Determine probable frequencies of genotypes in a population. -Track changes of genotypes from generation to generation. Genotype frequency: the percentage of a specific genotype within a population.
What does it mean if a population is not in Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium?
If the allele frequencies after one round of random mating change at all from the original frequencies, the population is not in Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium and evolution has occurred within the population.
How do you interpret Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium?
To know if a population is in Hardy-Weinberg Equilibrium scientists have to observe at least two generations. If the allele frequencies are the same for both generations then the population is in Hardy-Weinberg Equilibrium.
Why is HWE useful to evolutionary biologists?
The Hardy-Weinberg is used as a crucial tool in evolutionary biology even though it does not take place in nature because it essentially provides certain mathematical derivation or proof on account of evolution that it will not take place in the absence of genetic drift, natural selection, migration, or mutation.
What is the Hardy-Weinberg principle?
Hardy, an English mathematician, and Wilhelm Weinberg, a German physician—independently worked out a mathematical relationship that related genotypes to allele frequencies called the Hardy-Weinberg principle, a crucial concept in population genetics. It predicts how gene frequencies will be inherited from generation to generation given a specific set of assumptions. When a population meets all the Hardy-Weinberg conditions, it is said to be in Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium (HWE). Human populations do not meet all the conditions of HWE exactly, and their allele frequencies will change from one generation to the next, so the population evolves. How far a population deviates from HWE can be measured using the “goodness-of-fit” or chi-squared test (χ2) (See Box 12.4 ).
What is the graphic representation of the Hardy-Weinberg principle?
Graphical representation of the Hardy–Weinberg principle. The frequency of A alleles is denoted by p and the proportion of B alleles by q. AA homozygotes are represented by white, AB heterozygotes by gray, and BB homozygotes by gold. Shaded areas are proportional to the probability of observing each genotype.
What is the Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium?
Hardy–Weinberg Equilibrium (HWE) is a null model of the relationship between allele and genotype frequencies, both within and between generations, under assumptions of no mutation, no migration, no selection, random mating, and infinite population size.
Who invented the biases of ascertainment?
Corrections for these so-called biases of ascertainment were devised by Weinberg (of the Hardy–Weinberg law), Bernstein (of ABO fame), and Fritz Lenz and Lancelot Hogben (whose names are combined in the Lenz–Hogben correction), as well as by Fisher, Norman Bailey, and Newton E. Morton.
Does Hardy Weinberg principle include genes?
Although the Hardy–Weinberg principle can also be generalized to include genes located on sex chromosomes ( e.g., X chr omosomes in humans), it is important to note that it can take multiple generations for genotype frequencies at sex-linked loci to reach equilibrium values. View chapter Purchase book. Read full chapter.
Why is the Hardy Weinberg Equation used?
Here are some of the Uses & Applications of the Hardy Weinberg Equation. Let’s Know:
What happens if the Hardy Weinberg Equilibrium is violated?
If the Hardy Weinberg equilibrium is violated due to the various factors of evolution then the allele frequency will change. Simply meaning that the allele frequencies may change from one generation to the next.
What are the factors that affect the Hardy Weinberg equilibrium?
The factors that can affect the Hardy Weinberg equilibrium equation are Genetic Recombination, Mutation, Gene drift, Gene flow, and Natural selection.
What is the Hardy Weinberg equation for genotype frequency?
The Hardy Weinberg Equation for genotype frequency is (p+q)2=1 or p2+2pq+q2=1, because the total frequency of the genotypes consisting of two alleles will also be 100% when the population is not evolving.
Why is the Hardy Weinberg equilibrium equation always equal to 1?
The Hardy Weinberg equilibrium equation is always equal to 1 because it indicates that the population is not evolving, and so, is stable.
Who is Ronit Dey?
This post is written by Ronit Dey. Ronit Dey is a graduate in Zoology. Here, he has started sharing a lot of things that he has seen, learned, and researched so far related to Zoology.