
What is EMB agar used for?
Eosin Methylene Blue (EMB) Agar : Composition, uses and colony characteristics. It is selective culture medium for gram-negative bacteria (selects against gram positive bacteria) and is commonly used for the isolation and differentiation of coliforms and fecal coliforms. EMB media assists in visual distinction Escherichia coli,...
How to differentiate enteric bacteria on EMB agar?
Differentiation of enteric bacteria is possible due to the presence of the sugars lactose and sucrose in the EMB agar and the ability of certain bacteria to ferment the lactose in the medium.
What is the purpose of coliform isolation from EMB agar?
It is used to isolate fecal coliforms(G- bacteria rod)*** . It's used to distinguish between lactose fermenting coliforms and lactose non fermenting coliforms. Which ingredient(s) in EMB agar supply(ies)
What is the role of lactose in EMB agar?
In your own words, what is the role of lactose in EMB agar? Lactose is fermented to acid end products such as e coli. Would removing eosin Y and/or methylene blue from EMB agar alter the medium's sensitivity or specificity?
What is the purpose of EMB agar?
EMB agar is used in water quality tests to distinguish coliforms and fecal coliforms that signal possible pathogenic microorganism contamination in water samples.
What is the purpose of EMB agar quizlet?
EMB agar is used to stain gram negative bacteria. It is used to isolate fecal coliforms(G- bacteria rod)*** . It's used to distinguish between lactose fermenting coliforms and lactose non fermenting coliforms.
How does EMB work to identify bacteria in the laboratory?
The selective/ inhibitory agents of EMB are the dyes eosin Y and methylene blue. Methylene blue inhibits the gram + bacteria (eosin to a lesser extent), while eosin changes color, to a dark purple, when the medium around the colony becomes acidic.
Why do we need to use EMB agar to confirm presence of coliforms?
It is primarily used for isolation and differentiation of lactose fermenting (forms coloured colonies) and non-lactose fermenting (form colourless colonies) enteric bacilli. EMB agar aids in distinguishing coliforms and faecal coliforms that indicate possible pathogenic microorganism contamination in water samples.
What is the principle of the EMB plate?
Principle. EMB Agar contains two dyes, eosin and methylene blue which inhibit the growth of many microorganisms Gram-positives that accompany it. These dyes serve as differential indicators in response to carbohydrate fermentation.
How EMB media differentiate bacteria?
Differentiation of enteric bacteria is possible due to the presence of the sugars lactose and sucrose in the EMB agar and the ability of certain bacteria to ferment the lactose in the medium.
What bacteria can grow on EMB agar?
Limitations of EMB Agar Some gram-positive bacteria, such as enterococci, staphylococci, and yeast will grow on this medium and usually form pinpoint colonies. Non-pathogenic, non-lactose-fermenting organisms will also grow on this medium.
How does EMB agar select for E. coli?
On EMB if E. coli is grown it will give a distinctive metallic green sheen (due to the metachromatic properties of the dyes, E. coli movement using flagella, and strong acid end-products of fermentation). Some species of Citrobacter and Enterobacter will also react this way to EMB.
What is the difference between EMB agar and MacConkey Agar?
Use MacConkey agar to differentiate between Gram negative bacteria while inhibiting the growth of most Gram positive bacteria. EMB agar inhibits growth of Gram positive bacteria while cultivating growth of Gram negative enteric microorganisms (bacilli).
What does eosin do in EMB?
Eosin methylene blue agar (EMB) is a selective and differential medium used to isolate fecal coliforms. Eosin Y and methylene blue are pH indicator dyes which combine to form a dark purple precipitate at low pH; they also serve to inhibit the growth of most Gram positive organisms.
What is a coliform How would you recognize a coliform on EMB agar?
The confirmed test involves taking a sample from a positive lactose broth tube and streaking it onto Eosin Methylene Blue (EMB) agar. The appearance of dark colonies, often with a metallic sheen, indicate a coliform.
What is EMB agar?
Eosin Methylene Blue (EMB) agar is both a selective and differential culture medium. It selectively promotes the growth of Gram-negative bacteria (inhibits Gram-positive bacteria) and aids in the differentiation of lactose fermenter and non-lactose fermenting colonies.
How to make EMB agar?
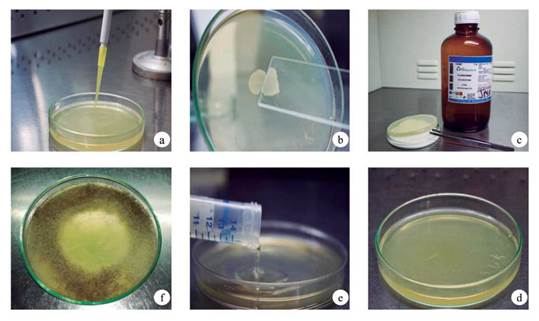
Preparation of EMB agar 1 Weigh and suspend 35.96 grams of dehydrated media in 1000 ml distilled water. 2 Mix until the suspension is uniform and heat to boiling to dissolve the medium completely. 3 Sterilize by autoclaving at 15 lbs pressure (121°C) for 15 minutes. 4 Cool to 45-50°C, and with frequent gentle swirling, pour the media into sterile Petri plates.#N#Note: frequent swirling is recommended to restore the blue color o methylene blue and to suspend the flocculent precipitate if any. 5 Label with initials of the name of the medium, date of preparation, and store the plates upside down (lids below) in the refrigerator until use.
Why is the dye purple in EMB?
Differentiation of enteric bacteria is possible due to the presence of the sugars lactose and sucrose in the EMB agar and the ability of certain bacteria to ferment the lactose in the medium. Lactose-fermenting gram-negative bacteria acidify the medium, which reduces the pH, and the dye produces a dark purple complex usually associated ...
What is performance testing of prepared EMB agar plates?
Performance testing of prepared EMB agar plates can be done by inoculating known strains of bacteria into the medium and observing growth and colonial characteristics. Organism. Growth and colony characteristics.
What is EMB media?
EMB media assists in the visual distinction of Escherichia coli, other nonpathogenic lactose-fermenting enteric gram-negative rods, and the Salmonella and Shigella genera. Escherichia coli colonies grow with a metallic sheen with a dark center. Aerobacter aerogenes colonies have a brown center, and non-lactose-fermenting gram-negative bacteria appear pink.
What is the best media for selective isolation of Gram-negative rods?
Another commonly used media for selective isolation of Gram-negative rods and differentiation of the member of Enterobacteriaceae as lactose fermenter and non-lactose fermenter is MacConkey Agar.
How big are the colonies of Enterobacter aerogenes?
Enterobacter aerogenes. Colonies are 4-6mm in diameter, raised and mucoid, tending to become confluent. No metallic sheen, grey-brown centers by transmitted light.
What is EMB agar?
Eosin Methylene Blue (EMB) agar is a differential microbiological medium, which slightly inhibits the growth of Gram-positive bacteria and provides a color indicator distinguishing between organisms that ferment lactose (e.g., E. coli) and those that do not (e.g., Salmonella, Shigella).
Why is medium important in medical laboratories?
The medium is important in medical laboratories to distinguish gram-negative pathogenic microbes in a short period of time.
What is the green sheen of E. coli?
In EMB agar, most of the strains of E. coli colonies have a characteristic green sheen. Rapid fermentation of lactose & production of strong acids, thus a rapid reduction in the pH of the EMB agar the critical factor in the formation of the green metallic sheen observed with E. coli, rapid fermentation of lactose and formation of strong acids.
Why are lactose fermenters purple?
This encourages dye absorption by the colonies and turns the colonies dark purple as the acid acts upon the dyes. In addition, certain lactose-fermenting bacteria produce flat, dark colonies with a green metallic sheen. Other lactose fermenters produce larger, mucoid colonies, often purple only in their center.
How long to sterilize methylene blue?
Sterilize by autoclaving at 15 lbs pressure (121°C) for 15 minutes. AVOID OVERHEATING. Cool to 45-50°C and shake the medium in order to oxidize the methylene blue (i.e. to restore its blue color) and to suspend the flocculent precipitate. Pour into sterile Petri plates.
How long to incubate plates after collection?
Incubate plates aerobically at 35-37°C for 18-24 hours and protect from light.
How long to incubate plates?
Incubate plates aerobically at 35-37°C for 18-24 hours and protect from light.
