
Methylation is a controlled transfer of a methyl group (one carbon and three hydrogen atoms) onto proteins, amino acids, enzymes and DNA in every cell and tissue of the body to regulate healing, cell energy, genetic expression of DNA, liver detoxification, immunity and neurology.
What is methylation and why is it important?
Methylation is a simple yet vitally important biochemical process in the body that is widespread and helps regulate the activity of our neurological, cardiovascular, reproductive, and detox systems. To name a few.
How do you know if you have a methylation problem?
Some common symptoms seen in people with under methylation are:
- Fatigue
- Insomnia
- Depression
- Addictions
- Obsessive-compulsive disorders
- Seasonal allergies
- Delusions
- Low threshold for pain
- Digestive issues
- Frequent headaches
What effect does the methylation cycle have on health?
- heart disease and diabetes
- anxiety and depression
- miscarriages
- fatigue
- fibromyalgia
- cervical dysplasia
- cancer
- and more
How to increase methylation?
Tips To Improve Your Methylation Pathways
- Repair Your Gut. ...
- Start With Your Stomach Acids. ...
- Ditch All Folic Acid. ...
- Prioritse Quality Sleep. ...
- Avoid Cow’s Milk. ...
- Eat Healing Greens. ...
- Get Your B’s From Real Food. ...
- Support Methylation With Supplements. ...
- Get Your Broader Micro-nutrition. ...
- Boost Your Glutathione. ...
What is methylation and why is it important?
Methylation is a critical biochemical process that happens billions of times in every single cell of the human body. It's responsible for a vast range of biological functions such as: Detoxification. DNA expression.
What is the point of DNA methylation?
DNA methylation is a biological process by which methyl groups are added to the DNA molecule. Methylation can change the activity of a DNA segment without changing the sequence. When located in a gene promoter, DNA methylation typically acts to repress gene transcription.
What does methylation do to a drug?
Methylation is a relatively minor conjugation pathway in drug metabolism, but it is very important in the biosynthesis of endogenous compounds such as epinephrine and melatonin; in the catabolism of biogenic amines such as norepinephrine, dopamine, serotonin, and histamine; and in modulating the activities of ...
What is DNA methylation in simple terms?
A chemical reaction in the body in which a small molecule called a methyl group gets added to DNA, proteins, or other molecules. The addition of methyl groups can affect how some molecules act in the body. For example, methylation of the DNA sequence of a gene may turn the gene off so it does not make a protein.
Is high DNA methylation good or bad?
A healthy body has a certain level of methylation. Irregular and over-methylated DNA can change a gene, preventing it from producing what it's meant to. Changes in the placement of methyl groups can cause diseases [6].
What happens if you have poor methylation?
Impaired methylation results in decreased production of dopamine. The altered dopamine levels ultimately lead to altered levels of the other neurotransmitters. As a result, these individuals lack focus, concentration, short-term memory, organization, emotional stability, good sleep hygiene, and hormone regulation.
What happens when there is too much methylation?
With over-methylation, the systems identified earlier (cardiovascular, neurological, reproductive, and detoxification) may start to show signs of dysfunction. A few examples are: Changes in mood. Low mood.
What happens when methylation is increased?
Hypermethylation in an abnormal state leads to transcriptional silencing and gene inactivation, whereas hypomethylation is linked to chromosomal instability and loss of imprinting (transfer of methylated patterns to daughter cells).
What is the role of DNA methylation in eukaryotes?
DNA methylation has been shown to have an important role in several eukaryotic processes, such as embryonic development, genome imprinting, inactivation of X-chromosome, and generally preserving the stability of chromosomes.
Is DNA methylation important for survival?
DNA methylation is an epigenetic mechanism known to play an important role in regulating gene expression and may serve as a biomarker for treatment response and survival.
What is the role of DNA methylation in epigenetics?
These epigenetic “markers” on DNA can be copied after DNA synthesis, resulting in heritable changes in chromatin structure. Methylation of CpG-rich promoters is used by mammals to prevent transcriptional initiation and to ensure the silencing of genes on the inactive X chromosome, imprinted genes, and parasitic DNAs.
What is the significance of DNA methylation in aging?
These studies reveal an epigenetic drift with aging and suggest that DNA methylation is associated with longevity. While more speculative, these studies also hint that DNA methylation may play a role in regulating life span. A large amount of in vitro work strongly supports these suppositions.
What is methylation in DNA?
DNA methylation is an example of one of the many mechanisms of epigenetics. Epigenetics refers to inheritable changes in your DNA that don’t change the actual DNA sequence. That means these changes are potentially reversible. Your DNA consists of four bases, called cytosine, guanine, adenine, and thymine. A chemical unit called a methyl group, ...
What is the role of nutrition in DNA methylation?
Most of the existing research suggests that DNA methylation relies at least in part on folate, vitamin B-12, vitamin B-6, and choline, in addition to other vitamins and minerals.
What is the gene that codes for methylation of folate?
In some, the gene that codes for methylation of folate, known as the MTHFR gene , may be compromised or have a mutation that prevents the vitamin from being properly used by the body. This is referred to as a “polymorphism” and can result in a variety of symptoms and diseases.
How to improve DNA methylation?
To improve DNA methylation, you can start by adding a few key nutrients, such as folate, B vitamins, and choline, to your diet. Across several studies, these vitamins and nutrients appear to play a role in DNA methylation. As well, they’ll also improve your overall health. Last medically reviewed on May 21, 2018.
When does DNA methylation change?
The patterns of DNA methylation change throughout your life. The process occurs the most during the stages of early development and later life. found that DNA methylation patterns are constantly changing during fetal development. This allows all of the body’s organs and tissue to form properly.
What is the chemical unit of DNA?
Your DNA consists of four bases, called cytosine, guanine, adenine, and thymine. A chemical unit called a methyl group, which contains one carbon and three hydrogen atoms, can be added to cytosine. When this happens, that area of the DNA is methylated. When you lose that methyl group, the area becomes demethylated.
What is an example of a polymorphism?
An example is elevated levels of homocysteine (a type of amino acid), which can cause damage to arteries. Those who have this polymorphism may find it beneficial to take a supplement of L-methyfolate, the pre-methylated form of folate.
How does methylation of CH3 happen?
HOW DOES METHYLATION HAPPEN? CH3 is provided to the body through a universal methyl donor known as SAMe (S-adenosylmethionine). SAMe readily gives away its methyl group to other substances in the body, which enables the cardiovascular, neurological, reproductive, and detoxification systems to perform their functions.
What is the role of methylation in detoxification?
When optimal methylation occurs, it has a significant positive impact on many biochemical reactions in the body that regulate the activity of the cardiovascular, neurological, reproductive, and detoxification systems , including those relating to: DNA production. Neurotransmitter production. Detoxification.
What is methylation in biology?
WHAT IS METHYLATION? The topic of methylation is getting its fair share of attention lately, and rightly so. Methylation is a simple biochemical process – it is the transfer of four atoms - one carbon atom and three hydrogen atoms (CH3) – from one substance to another.
How to find out if you have a problem with your methylation cycle?
First, you can have a simple and easy genetic test to find out if you have a problem with your methylation cycle. This test looks at specific enzymes that are affected by your genetic makeup, including the enzyme MTHFR (methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase), which is the most important enzyme involved in creating 5-MTHF.
What is the active form of folic acid?
Folic acid from the diet or supplements must be converted to this active form, 5-MTHF, before it can be used in the body in the methylation cycle.
What happens when the methylation switch is turned off?
When the methylation switch is turned off and isn’t creating enough SAMe, then a number of important molecules cannot be efficiently produced, including: Glutathione. Coenzyme Q10. Melatonin. Serotonin.
What is the mechanism that allows the gears to turn and turns biological switches on and off?
Think of methylation, and the opposite action, demethylation, as the mechanism that allows the gears to turn, and turns biological switches on and off for a host of systems in the body.
What health issues can arise from impaired methylation?
As you continue to read, you will learn that disruptions in methylation processes can cause a variety of issues, including:
What is the MTHFR Gene?
The MTHFR gene encodes for the MTHFR enzyme. There are variations in the gene that affect the function of the enzyme. This is explained in further detail below. A simple blood test can tell you if you have a variant copy of this gene.
What is the difference between MTHFR and 1298?
The 677 refers to the nucleotide at the 677 position and 1298 is the nucleotide position of the other abnormality. This difference is often referred to as a Single Nucleotide Polymorphism (SNP). Abnormal variants are considered ‘thermolabile’ meaning that they measure the amount of enzyme activity after the enzyme is inactivated by heat.
Why is MTHFR linked to depression?
Some of these methylation reactions affect neurotransmitters, which is why impaired MTHFR activity is linked with depression. Inefficiency of the MTHFR enzyme is also linked to migraines, autism, fertility, cancer, and birth defects, all of which depend on proper methylation.
What is the nucleotide at 1298?
There are 2 possibilities for the nucleotide at the 1298 position, A & C. ‘A’ encodes for the normal glutamine amino acid and ‘C’ substitutes an Alanine amino acid. The C variant does not appear to affect the MTHFR activity nor homocysteine levels.
What happens if the enzyme is impaired?
If the enzyme is impaired, this detoxification reaction is impaired, leading to high homocysteine blood levels. Homocysteine is abrasive to blood vessels, essentially scratching them, leaving damage that causes heart attacks, stroke, dementia, and a host of other problems. MTHFR converts 5,10-methylenetetrahydrofolate to 5-methyltetrahydrofolate.
What is methylation in biology?
But what is methylation? Simply put, methylation is a chemical reaction that occurs in every cell and tissue in your body. Chemically speaking, methylation is the process of adding methyl groups to a molecule. A ‘methyl group’ is a chemical structure made of one carbon and three hydrogen atoms. Since methyl groups are chemically inert, adding them ...
How does DNA demethylation occur?
As Dnmt1 actively maintains DNA methylation during cell replication, its inhibition or dysfunction allows newly incorporated cytosine to remain unmethylated and consequently reduces the overall methylation level following each cell division. Active DNA demethylation can occur in both dividing and nondividing cells but the process requires enzymatic reactions to process the 5mC in order to revert it back to a naked cytosine (Mayer et al, 2000; Oswald et al, 2000; Paroush et al, 1990; Zhang et al, 2007). As of yet, there is no known mechanism in mammalian cells that can cleave the strong covalent carbon-to-carbon bond that connects cytosine to a methyl group. Instead, demethylation occurs through a series of chemical reactions that further modify 5mC, by deamination and/or oxidation reactions to a product that is recognized by the base excision repair (BER) pathway to replace the modified base with naked cytosine. Although it is generally agreed upon that the BER pathway is the final step in DNA demethylation, the specific enzymes and the chemical intermediates that are formed during DNA demethylation are still debated (Bhutani et al, 2011).
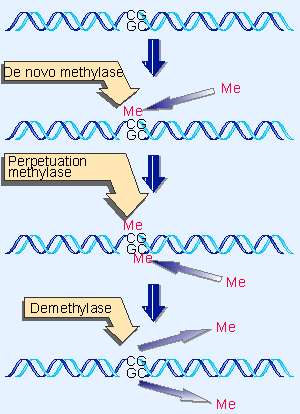
What is the methylation pathway of DNA?
DNA methylation pathways. A family of DNA methyltransferases (Dnmts) catalyzes the transfer of a methyl group from S-adenyl methionine (SAM) to the fifth carbon of cytosine residue to form 5-methylcytosine (5mC). (a) Dnmt3a and Dnmt3b are the de novoDnmts and transfer methyl groups (red) onto naked DNA. (b) Dnmt1 is the maintenance Dnmt and maintains DNA methylation pattern during replication. When DNA undergoes semiconservative replication, the parental DNA stand retains the original DNA methylation pattern (gray). Dnmt1 associates at the replication foci and precisely replicates the original DNA methylation pattern by adding methyl groups (red) onto the newly formed daughter strand (blue).
How do neuronal cells react to the environment?
Neurons react to the environment through patterns of depolarization that both relay information and encode a response. In recent years, it has become increasingly apparent that following depolarization, alterations in gene expression are accompanied by modifications of the epigenetic landscape that include alterations in the pattern of DNA methylation (Martinowich et al, 2003; Guo et al, 2011a). In order for the DNA methylation pattern to be altered, there must be both active DNA methylation and demethylation in the neuronal genome. However, no enzymes are known to cleave the methyl group directly from 5mC. As discussed below, the recent identification of 5-hydroxymethyl-cytosine (5hmC) in postmitotic neurons suggests that 5hmC serves as an intermediate in the DNA demethylation pathway. In this review, we will discuss the basic function of DNA methylation in epigenetic gene regulation, and further highlight its role in neural development and neurological disease.
How do transcription factors regulate DNA methylation?
Transcription factors can regulate DNA methylation by binding to specific DNA sequence to either recruit Dnmts for methylation or protect from DNA methylation. In some cases Dnmts bind to transcription factors or components of repressor complexes to target methylation to DNA (Brenner et al, 2005).
Why is DNA methylation important?
DNA methylation is essential for silencing retroviral elements, regulating tissue-specific gene expression, genomic imprinting, and X chromosome inactivation. Importantly, DNA methylation in different genomic regions may exert different influences on gene activities based on the underlying genetic sequence. In the following sections, we will further elaborate upon the role of DNA methylation in different genomic regions.
Where does DNA methylation occur in the human genome?
Although the brain contains some of the highest levels of DNA methylation of any tissue in the body, 5mC only accounts for ∼1% of nucleic acids in the human genome (Ehrlich et al, 1982). The majority of DNA methylation occurs on cytosines that precede a guanine nucleotide or CpG sites. Overall, mammalian genomes are depleted of CpG sites that may result from the mutagenic potential of 5mC that can deaminate to thymine (Coulondre et al, 1978; Bird, 1980). The remaining CpG sites are spread out across the genome where they are heavily methylated with the exception of CpG islands (Bird et al, 1985). Interestingly, there is evidence of non-CpG methylation in mouse and human embryonic stem cells, however these methylation are lost in mature tissues (Ramsahoye et al, 2000; Lister et al, 2009). More thorough analysis of the murine frontal cortex has recently revealed that although the majority of methylation occurs within CpG sites, there is a significant percentage of methylated non-CpG sites (Xie et al, 2012). Because of its recent discovery, the role of non-CpG methylation is still unclear.
When was DNA methylation discovered?
Historically, DNA methylation was discovered in mammals as early as DNA was identified as the genetic material (Avery et al, 1944; McCarty and Avery, 1946). In 1948, Rollin Hotchkiss first discovered modified cytosine in a preparation of calf thymus using paper chromatography.
What is the conservation function of DNA methylation?
In mammals, around 75% of CpG dinucleotides are methylated in somatic cells, and DNA methylation appears as a default state that has to be specifically excluded from defined locations.
How does DNA methylation affect transcription?
First, the methylation of DNA itself may physically impede the binding of transcriptional proteins to the gene , and second, and likely more important, methylated DNA may be bound by proteins known as methyl-CpG-binding domain proteins (MBDs).
How much cytosine is methylated in yeast?
Many fungi have low levels (0.1 to 0.5%) of cytosine methylation, whereas other fungi have as much as 5% of the genome methylated. This value seems to vary both among species and among isolates of the same species. There is also evidence that DNA methylation may be involved in state-specific control of gene expression in fungi. However, at a detection limit of 250 attomoles by using ultra-high sensitive mass spectrometry DNA methylation was not confirmed in single cellular yeast species such as Saccharomyces cerevisiae or Schizosaccharomyces pombe, indicating that yeasts do not possess this DNA modification. : abstract
What are CPG islands?
CpG islands are usually defined as regions with: 1) a length greater than 200bp, 2) a G+C content greater than 50% , 3) a ratio of observed to expected CpG greater than 0.6, although other definitions are sometimes used. Excluding repeated sequences, there are around 25,000 CpG islands in the human genome, 75% of which being less than 850bp long. They are major regulatory units and around 50% of CpG islands are located in gene promoter regions, while another 25% lie in gene bodies, often serving as alternative promoters. Reciprocally, around 60-70% of human genes have a CpG island in their promoter region. The majority of CpG islands are constitutively unmethylated and enriched for permissive chromatin modification such as H3K4 methylation. In somatic tissues, only 10% of CpG islands are methylated, the majority of them being located in intergenic and intragenic regions.
Where is DNA methylation found?
In mammals however, DNA methylation is almost exclusively found in CpG dinucleotides, with the cytosines on both strands being usually methylated.
What is the function of DNA methylation?
In almost all species where DNA methylation is present, DNA methylation is especially enrich ed in the body of highly transcribed genes. The function of gene body methylation is not well understood. A body of evidence suggests that it could regulate splicing and suppress the activity of intragenic transcriptional units (cryptic promoters or transposable elements). Gene-body methylation appears closely tied to H3K36 methylation. In yeast and mammals, H3K36 methylation is highly enriched in the body of highly transcribed genes. In yeast at least, H3K36me3 recruits enzymes such as histone deacetylases to condense chromatin and prevent the activation of cryptic start sites. In mammals, DNMT3a and DNMT3b PWWP domain binds to H3K36me3 and the two enzymes are recruited to the body of actively transcribed genes.
How many genes are silenced in cancer?
Generally, in progression to cancer, hundreds of genes are silenced or activated. Although silencing of some genes in cancers occurs by mutation, a large proportion of carcinogenic gene silencing is a result of altered DNA methylation (see DNA methylation in cancer ).

What is DNA methylation?
- DNA methylation is an example of one of the many mechanisms of epigenetics. Epigenetics refe…
Your DNA consists of four bases, called cytosine, guanine, adenine, and thymine. A chemical unit called a methyl group, which contains one carbon and three hydrogen atoms, can be added to cytosine. When this happens, that area of the DNA is methylated. When you lose that methyl gr… - DNA methylation often inhibits the expression of certain genes. For example, the methylation pr…
Experts are currently working to better understand the factors that affect DNA methylation. Based on their early findings, there’s some evidence that diet plays a role. This opens up the potential to reduce genetic risk of developing certain conditions, such as breast cancer or heart disease, thr…
What does the research say?
- DNA methylation status throughout life
The patterns of DNA methylation change throughout your life. The process occurs the most during the stages of early development and later life. A 2015 review found that DNA methylation patterns are constantly changing during fetal development. This allows all of the body’s organs and tissu… - DNA methylation and diet
The process DNA methylation partly relies on several nutrients. For example, a 2014 study looked at DNA methylation of tumor cells in women with breast cancer. The study’s investigators found that participants who consumed more alcohol were more likely to have decreased DNA methylat…
How can I learn about my own methylation cycle?
- Experts use several methods to analyze DNA methylation, depending on the type of information …
Some clinics do offer DNA methylation profile testing. The results of these tests are difficult to interpret, especially in a way that would be meaningful to you. In addition, several online retailers offer kits you can use to collect a sample of your own DNA to send off for analysis. However, the…
Is there anything I can do to support my methylation cycle?
- While the relationship between diet and DNA methylation needs more exploration, nutrition doe…
Increasing your intake of these nutrients may help to support DNA methylation, preventing certain genes from being expressed. While all of these are available as dietary supplements, it’s best to get as much of them from food as possible.
The bottom line
- DNA methylation is a complex process that could hold major clues to health and aging, but man…
To improve DNA methylation, you can start by adding a few key nutrients, such as folate, B vitamins, and choline, to your diet. Across several studies, these vitamins and nutrients appear to play a role in DNA methylation. As well, they’ll also improve your overall health.
Causes
Introduction
- Chemically speaking, methylation is the process of adding methyl groups to a molecule. A methyl group is a chemical structure made of one carbon and three hydrogen atoms. Since methyl groups are chemically inert, adding them to a protein (the process of methylation) changes how that protein reacts to other substances in the body, thus affecting how that protein behaves. Enz…
Function
- Another role of methylation is to help the enzymes in our bodies work efficiently. Enzymes are proteins that act like switches for chemical reactions they initiate very important processes in every cell and tissue. In a similar way, methylation affects our genes, which are also made up of proteins. In fact, methylation can turn genes on or off, which can be good or bad for our health, d…
Benefits
- Some nutrients affect the process of methylation quite dramatically methyl donors (nutrients like folate and choline) actually donate methyl groups to proteins and methylating factors (nutrients like vitamin B12 and zinc) helps this process along by monitoring specific methylation reactions. How well your body methylates is important to your overall health.
Risks
- As you continue to read, you will learn that disruptions in methylation processes can cause a variety of issues, including:
Overview
- MTHFR (methyletetrahydrofolate reductase) is an enzyme that converts folate into a usable form that our bodies need. It is a key enzyme in an important detoxification reaction in the body one that converts homocysteine (toxic) to methionine (benign). If the enzyme is impaired, this detoxification reaction is impaired, leading to high homocysteine blood levels. Homocysteine is a…
Synthesis
- MTHFR converts 5,10-methylenetetrahydrofolate to 5-methyltetrahydrofolate. It is the 5-methyltetrahydrofolate that converts homocysteine to methionine by the enzyme methionine synthase. Homocysteine can also be converted to methionine by betaine-homocysteine methyltransferase. This enzyme does not require folic acid.
Clinical significance
- Additionally, when the enzyme MTHFR is impaired, other methylation reactions are compromised. Some of these methylation reactions affect neurotransmitters, which is why impaired MTHFR activity is linked with depression. Inefficiency of the MTHFR enzyme is also linked to migraines, autism, fertility, cancer, and birth defects, all of which depend on proper methylation.
Treatment
- If the MTHFR enzyme is inefficient, you may be able to compensate for your bodys inability to methylate efficiently since this biological process is dependent on several B vitamins. You may simply need more B vitamins than someone without a variant copy of this gene, such as vitamin B6, B12 (methylcobalamin) and the active form of folate (5-methyl tetrahydrofolate). Other methy…
Genetics
- There are DNA sequence variants of MTHFR and the two most commonly evaluated are 677 & 1298. These two differ by one nucleotide at either of 2 locations. The 677 refers to the nucleotide at the 677 position and 1298 is the nucleotide position of the other abnormality. This difference is often referred to as a Single Nucleotide Polymorphism (SNP). Abnormal variants are considere…
Structure
- There are 2 possibilities for the nucleotide at the 1298 position, A & C. A encodes for the normal glutamine amino acid and C substitutes an Alanine amino acid. The C variant does not appear to affect the MTHFR activity nor homocysteine levels.